比赛的时候读错了题意我去。。一直TLE+WA..
赛后看了题解才知道读错了题意。。愧疚啊我去。。这次比赛我读的两道题都读错了题意,坑死队友。。
Description
Yi Sima was one of the best counselors of Cao Cao. He likes to play a funny game himself. It looks like the modern Sudoku, but smaller.
Actually, Yi Sima was playing it different. First of all, he tried to generate a
 board with every row contains 1 to 4, every column contains 1 to 4. Also he made sure that if we cut the board into four
board with every row contains 1 to 4, every column contains 1 to 4. Also he made sure that if we cut the board into four
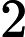
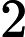 pieces, every piece contains 1 to 4.
pieces, every piece contains 1 to 4.
Then, he removed several numbers from the board and gave it to another guy to recover it. As other counselors are not as smart as Yi Sima, Yi Sima always made sure that the board only has one way to recover.
Actually, you are seeing this because you've passed through to the Three-Kingdom Age. You can recover the board to make Yi Sima happy and be promoted. Go and do it!!!
Actually, Yi Sima was playing it different. First of all, he tried to generate a

 board with every row contains 1 to 4, every column contains 1 to 4. Also he made sure that if we cut the board into four
board with every row contains 1 to 4, every column contains 1 to 4. Also he made sure that if we cut the board into four
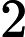
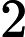 pieces, every piece contains 1 to 4.
pieces, every piece contains 1 to 4.
Then, he removed several numbers from the board and gave it to another guy to recover it. As other counselors are not as smart as Yi Sima, Yi Sima always made sure that the board only has one way to recover.
Actually, you are seeing this because you've passed through to the Three-Kingdom Age. You can recover the board to make Yi Sima happy and be promoted. Go and do it!!!
Input
The first line of the input gives the number of test cases,
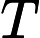



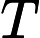




 .
.
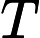 test cases follow. Each test case starts with an empty line followed by 4 lines. Each line consist of 4 characters. Each character represents the number in the corresponding cell (one of '1', '2', '3', '4'). '*' represents that number was removed by Yi Sima.
test cases follow. Each test case starts with an empty line followed by 4 lines. Each line consist of 4 characters. Each character represents the number in the corresponding cell (one of '1', '2', '3', '4'). '*' represents that number was removed by Yi Sima.
It's guaranteed that there will be exactly one way to recover the board.
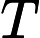



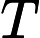




 .
.
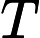 test cases follow. Each test case starts with an empty line followed by 4 lines. Each line consist of 4 characters. Each character represents the number in the corresponding cell (one of '1', '2', '3', '4'). '*' represents that number was removed by Yi Sima.
test cases follow. Each test case starts with an empty line followed by 4 lines. Each line consist of 4 characters. Each character represents the number in the corresponding cell (one of '1', '2', '3', '4'). '*' represents that number was removed by Yi Sima.
It's guaranteed that there will be exactly one way to recover the board.
Output
For each test case, output one line containing
Case #x:, where
 is the test case number (starting from 1). Then output 4 lines with 4 characters each. indicate the recovered board.
is the test case number (starting from 1). Then output 4 lines with 4 characters each. indicate the recovered board.
 is the test case number (starting from 1). Then output 4 lines with 4 characters each. indicate the recovered board.
is the test case number (starting from 1). Then output 4 lines with 4 characters each. indicate the recovered board.
Sample Input
3
****
2341
4123
3214
*243
*312
*421
*134
*41*
**3*
2*41
4*2*
Sample Output
Case #1:
1432
2341
4123
3214
Case #2:
1243
4312
3421
2134
Case #3:
3412
1234
2341
4123
这里提供两种方法:
方法一:
思路:用res数组记录一下要填数字的点 用dfs枚举当前点可以填的所有数字。暴力搜索就可以了。
代码+注释如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=7;
char mp[maxn][maxn];
bool vis[maxn][maxn],flag;
int res[maxn*maxn][2];
int resnum;
void input()//输入
{
resnum=0;
flag=false;
memset(vis,false,sizeof(vis));
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)scanf("%s",(&mp[i][0])+1);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
//记录一下要填数字的点
if(mp[i][j]=='*'){res[resnum][0]=i,res[resnum][1]=j,resnum++;}
else vis[i][j]=true;
}
void dfs(int step)
{
if(flag||step==resnum){flag=true;return;}
int tx=res[step][0],ty=res[step][1];
int book[maxn]={false};
//枚举4个2*2的小矩阵
if(tx<=2&&ty<=2)for(int i=1;i<=2;i++)for(int j=1;j<=2;j++)if(mp[i][j]!='*')book[mp[i][j]-'0']=true;
if(tx<=2&&ty>2)for(int i=1;i<=2;i++)for(int j=3;j<=4;j++)if(mp[i][j]!='*')book[mp[i][j]-'0']=true;
if(tx>2&&ty<=2)for(int i=3;i<=4;i++)for(int j=1;j<=2;j++)if(mp[i][j]!='*')book[mp[i][j]-'0']=true;
if(tx>2&&ty>2)for(int i=3;i<=4;i++)for(int j=3;j<=4;j++)if(mp[i][j]!='*')book[mp[i][j]-'0']=true;
//枚举列和行
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
if(mp[tx][i]!='*')book[mp[tx][i]-'0']=true;
if(mp[i][ty]!='*')book[mp[i][ty]-'0']=true;
}
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
if(!book[i])
{
mp[tx][ty]=i+'0';
dfs(step+1);
if(flag)return;
mp[tx][ty]='*';
}
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int tcase=1;tcase<=T;tcase++)
{
input();
dfs(0);
printf("Case #%d:\n",tcase);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)printf("%s\n",(&mp[i][0])+1);
}
}方法二:
思路:每次都填一次那个可以确定的点,不能填的点放在队列中,队列为空则OK!
用xvis[i][num]数组表示第i行num这个数出现过了没---------------yvis数组同理
再用jz[i][num]数组表示矩阵i中num这个数出现过了没。
然后每次都填那个可以确定的点 然后继续更新这三个标记数组,然后该点出列。直到队列为空。
代码如下:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<queue>
#include<cstdio>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
const int maxn=10;
struct node
{
int x,y;
};
bool xvis[maxn][5] ,yvis[maxn][5],jz[maxn][maxn];
char mp[maxn][maxn];
node temp,head;
queue<node>Q;
int findjz(int tx,int ty)//判断是在哪个矩阵
{
if(tx<=2&&ty<=2)return 1;
if(tx<=2&&ty>2)return 2;
if(tx>2&&ty<=2)return 3;
return 4;
}
void init()//初始化
{
memset(xvis,false,sizeof(xvis));
memset(yvis,false,sizeof(yvis));
memset(jz,false,sizeof(jz));
}
void input()
{
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)scanf("%s",mp[i]+1);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
for(int j=1;j<=4;j++)
if(mp[i][j]=='*'){temp.x=i,temp.y=j,Q.push(temp);}
else
{
int num=mp[i][j]-'0';
jz[findjz(i,j)][num]=xvis[i][num]=yvis[j][num]=true;//该数所处的行-列-矩阵都标记一下 }
}
}
bool solve(node& head)
{
int tx=head.x,ty=head.y;
int sum=0,last;
int pos=findjz(tx,ty);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)
{
if(xvis[tx][i]||yvis[ty][i]||jz[pos][i])sum++;
else last=i;
}
if(sum==3)//所以该要填的数字就可以确定了
{
xvis[tx][last]=yvis[ty][last]=jz[pos][last]=true;//更新标记
mp[tx][ty]=last+'0';
return true;
}
return false;
}
int main()
{
int T;
scanf("%d",&T);
for(int tcase=1;tcase<=T;tcase++)
{
init();
input();
while(!Q.empty()){head=Q.front(),Q.pop();if(!solve(head))Q.push(head);}
printf("Case #%d:\n",tcase);
for(int i=1;i<=4;i++)printf("%s\n",(&mp[i][0])+1);
}
}







 本文介绍了一种简化版的Sudoku游戏,并提供了两种解决该问题的方法。游戏由四个2x2的矩阵组成,每行、每列及每个小矩阵内包含1到4的数字。文章详细介绍了使用深度优先搜索和迭代填充策略的解决方案。
本文介绍了一种简化版的Sudoku游戏,并提供了两种解决该问题的方法。游戏由四个2x2的矩阵组成,每行、每列及每个小矩阵内包含1到4的数字。文章详细介绍了使用深度优先搜索和迭代填充策略的解决方案。
















 819
819

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








