2020.5.1 21. 合并两个有序链表
算法一:遍历
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(-1);
ListNode tail = dummy;
ListNode p1 = l1, p2 = l2;
while (p1 != null && p2 != null) {
int val = 0;
if (p1.val <= p2.val) {
val = p1.val;
p1 = p1.next;
} else {
val = p2.val;
p2 = p2.next;
}
ListNode tmp = new ListNode(val);
tail.next = tmp;
tail = tmp;
}
tail.next = p1 == null ? p2 : p1;
return dummy.next;
}
}
算法二:递归
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* public class ListNode {
* int val;
* ListNode next;
* ListNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode l1, ListNode l2) {
if (l1 == null) return l2;
if (l2 == null) return l1;
if (l1.val <= l2.val) {
l1.next = mergeTwoLists(l1.next, l2);
return l1;
} else {
l2.next = mergeTwoLists(l1, l2.next);
return l2;
}
}
}
2020.5.2 3. 无重复字符的最长子串
算法一:暴力
暴力找出所有的子串时间复杂度为 O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2),对于每个子串遍历一遍查看有无重复元素时间复杂度为 O ( n ) O(n) O(n),所以总的时间复杂度为 O ( n 3 ) O(n^3) O(n3),会超时,所以想一下如何做优化。
算法二:滑动窗口
将左右指针初始化成0,左指针每次向右移动1,右指针一直向右移动直到碰到重复的元素,这样一定能找到答案,因为这样是按照子串的开头遍历的,所以一定包含所有的情况。时间复杂度:因为i和j分别最多移动n次,所以为 O ( 2 n ) O(2n) O(2n)
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Set<Character> hash = new HashSet<>();
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = 0; i < s.length(); i++) {
if (i > 0) {
hash.remove(s.charAt(i - 1)); // 因为i向右移动1,那么i-1位置上的字符从hash中删除
}
while (j < s.length() && !hash.contains(s.charAt(j))) { // 只要j不超过长度并且无重复元素则一直向右移动
hash.add(s.charAt(j)); // 将该字符加到hash中
j++;
}
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i); // 这里要注意的是不是j-i+1因为j停止时是包含重复元素的所以要再减去1
}
return ans;
}
}
以右指针遍历,参考yxc
class Solution {
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
Map<Character, Integer> map = new HashMap<>();
int ans = 0;
for (int j = 0, i = 0; j < s.length(); j++) {
if (map.containsKey(s.charAt(j))) {
int k = i;
i = map.get(s.charAt(j)) + 1;
for (int u = k; u < i; u++) {
map.remove(s.charAt(u));
}
}
map.put(s.charAt(j), j);
ans = Math.max(ans, j - i + 1);
}
return ans;
}
}
2020.5.3 53. 最大子序和
算法一:动态规划
动态规划问题。定义f[i]为以nums[i]为结尾子序列的最大值,那么f[i]怎么求呢?将f[i]分为两类,只包含nums[i]一个数,还有其他的数,第一种情况很好求就是nums[i],第二种情况为f[i - 1] + nums[i],所以f[i] = max(0, f[i - 1]) + nums[i],然后又可以用滚动数组的思想省去空间改成s = max(0, s) + nums[i]。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
int ans = nums[0];
for (int i = 1, s = nums[0]; i < nums.length; i++) {
s = nums[i] + Math.max(0, s);
ans = Math.max(ans, s);
}
return ans;
}
}
算法二:分治
先找到中点mid,将区间一分为二[l, mid][mid + 1, r],所有的子序列只有三种情况:
1. 在左区间内部,就是这样:
[ ]
[l, mid][mid + 1, r]
2. 在右区间内部,就是这样:
[ ]
[l, mid][mid + 1, r]
3. 两个区间都有,就是这样:
[ ]
[l, mid][mid + 1, r]
然后对于这三种情况取max就可以了。
class Solution {
public int maxSubArray(int[] nums) {
return getMax(nums, 0, nums.length - 1);
}
public int getMax(int[] nums, int l, int r) {
if (l >= r) return nums[l];
int mid = l + r >> 1;
int res = Math.max(getMax(nums, l, mid), getMax(nums, mid + 1, r));
int leftMax = nums[mid];
for (int i = mid - 1, s = nums[mid]; i >= l; i--) {
s += nums[i];
leftMax = Math.max(leftMax, s);
}
int rightMax = nums[mid + 1];
for (int i = mid + 2, s = nums[mid + 1]; i <= r; i++) {
s += nums[i];
rightMax = Math.max(rightMax, s);
}
res = Math.max(res, leftMax + rightMax);
return res;
}
}
2020.5.4 45. 跳跃游戏 II
算法一:动态规划
这道题一看就是有限集合的最优化问题,所以想到用动态规划,定义f[i]为调到点i需要的最小步数。
时间复杂度: O ( n 2 ) O(n^2) O(n2)
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> f(n, 0x3f3f3f3f);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!i) f[i] = 0;
else {
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++) {
if (j + nums[j] >= i) {
f[i] = min(f[i], f[j] + 1);
}
}
}
}
return f[n - 1];
}
};
算法二:动态规划+贪心
很遗憾超时了,所以想办法优化。
我们会发现f[i]是具有单调性的,也就是f[i + 1] >= f[i]。用反证法:假设f[i + 1] < f[i],不妨设是从k,(k <= i)点跳到i + 1,即:k + nums[k] >= i + 1,那么k + nums[k]也必然大于i,此时:f[i + 1] = f[i]了。如果nums数组每一项都为1,则:f[i + 1] > f[i],综上:f[i + 1] >= f[i],与假设矛盾。
因此f[i]就变成了0 1...1 2...2 3...3 ......,在动态规划时瓶颈就在于更新每个点的最小值时需要遍历所有能跳到i的点,而有了单调性以后就可以用第一个能调到i的点更新了。
时间复杂度: O ( n ) O(n) O(n)
class Solution {
public:
int jump(vector<int>& nums) {
int n = nums.size();
vector<int> f(n);
for (int i = 0, last = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (!i) f[i] = 0;
else {
while (last < n && last + nums[last] < i) last++;
f[i] = f[last] + 1;
}
}
return f[n - 1];
}
};
class Solution {
public int jump(int[] nums) {
int n = nums.length;
int[] f = new int[n];
for (int i = 0, last = 0; i < n; i++) {
if (i == 0) f[i] = 0;
else {
while (last < n && last + nums[last] < i) last++;
f[i] = f[last] + 1;
}
}
return f[n - 1];
}
}
2020.5.5 98. 验证二叉搜索树
递归
一开始做的时候,写了这样的代码:
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *root) {
if (root == NULL || root->left == NULL && root->right == NULL) return true;
if (root->left) if (root->left->val >= root->val) return false;
if (root->right) if (root->right->val <= root->val) return false;
return dfs(root->left) && dfs(root->right);
}
};
这样写的问题就是:可能会出现父节点的右儿子的左儿子的值小于父节点的值,但是BST要满足的是右子树所有的值都要大于父节点的值,所以要修改代码。
我们自顶向下递归,左儿子的值要小于父节点的值,右儿子要大于父节点的值,这样递归下去,能取到的区间范围会越来越小。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* struct TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode *left;
* TreeNode *right;
* TreeNode(int x) : val(x), left(NULL), right(NULL) {}
* };
*/
typedef long long LL;
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidBST(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root, INT_MIN, INT_MAX);
}
bool dfs(TreeNode *root, LL minv, LL maxv) {
if (!root) return true;
if (root->val < minv || root->val > maxv) return false;
return dfs(root->left, minv, root->val - 1LL) &&
dfs(root->right, root->val + 1LL, maxv);
}
};
2020.5.6 983. 最低票价
唉,太菜了(╥╯^╰╥),知道是DP但是咋做也做不出来,题解写的也是模棱两可,好在官方的题解写的还是很好理解,学习一波吧。😭😭
class Solution {
public int[] costs;
public Set<Integer> set = new HashSet<>();
public Integer[] f;
public int ed;
public int mincostTickets(int[] days, int[] costs) {
this.ed = days[days.length - 1];
this.costs = costs;
f = new Integer[ed + 1];
for (int v : days) {
set.add(v);
}
return dp(1);
}
public int dp(int i) {
if (i > ed) return 0;
if (f[i] != null) return f[i];
if (!set.contains(i)) f[i] = dp(i + 1);
else
f[i] = Math.min(dp(i + 1) + costs[0],
Math.min(dp(i + 7) + costs[1], dp(i + 30) + costs[2]));
return f[i];
}
}
2020.5.7 572. 另一个树的子树
递归问题,首先递归找到s的所有子树,然后对于每一个子树都与t进行比较看是否完全相同。
/**
* Definition for a binary tree node.
* public class TreeNode {
* int val;
* TreeNode left;
* TreeNode right;
* TreeNode(int x) { val = x; }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public TreeNode t;
public boolean isSubtree(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) {
this.t = t;
return dfs(s);
}
public boolean dfs(TreeNode s) { // 递归找所有的子树
if (s == null) return false;
boolean succ = dfs_1(s, t);
if (succ) return succ;
else return dfs(s.left) || dfs(s.right);
}
public boolean dfs_1(TreeNode s, TreeNode t) { // 看子树s是否与t完全相同
if (s == null && t == null) return true;
if (s == null && t != null || s != null && t == null) return false;
if (s.val != t.val) return false;
return dfs_1(s.left, t.left) && dfs_1(s.right, t.right);
}
}
2020.5.8 221. 最大正方形
动态规划 时间复杂度: O ( n m ) O(nm) O(nm)
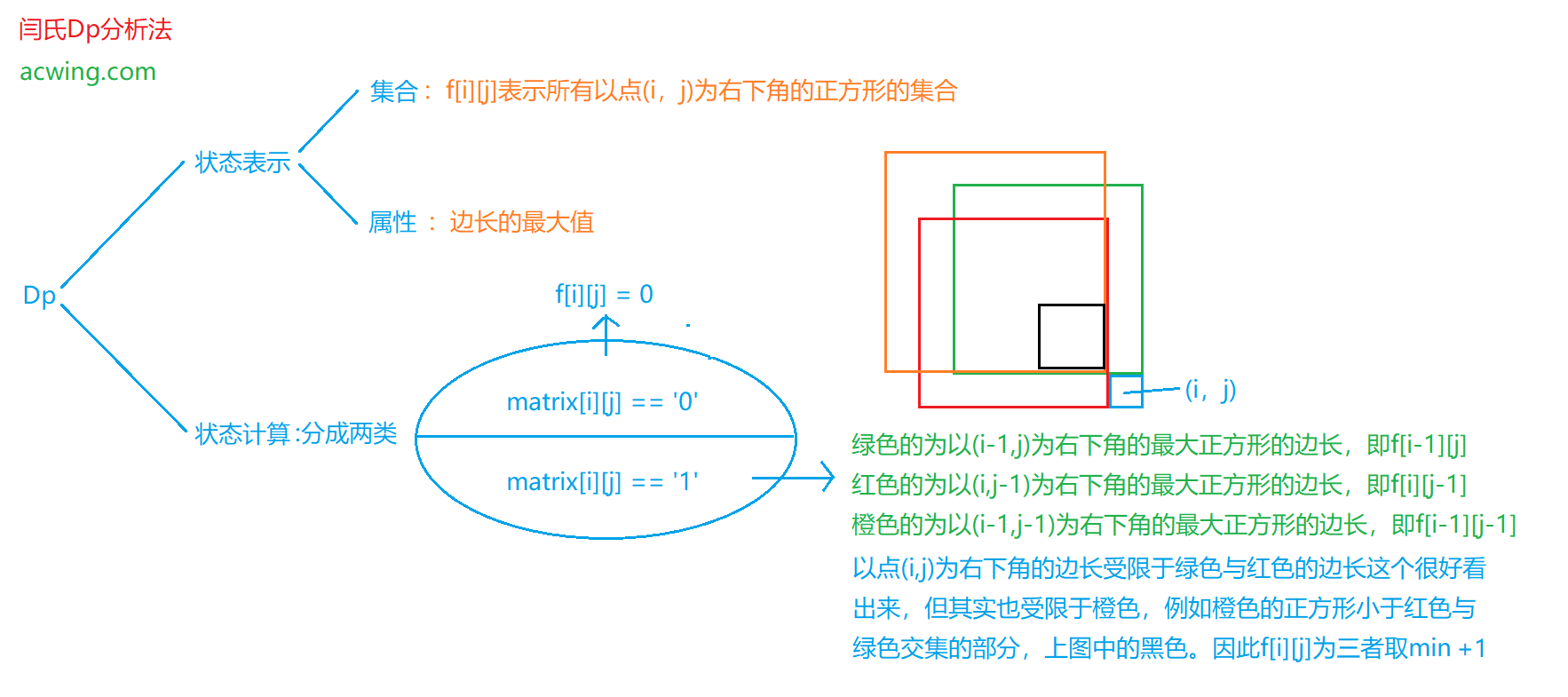
代码
因为在计算过程出现了下标减一:f[i-1][j],f[i][j-1],f[i-1][j-1],为了减少边界的处理,在计算时将横坐标与纵坐标+1
class Solution {
public int maximalSquare(char[][] matrix) {
int n = matrix.length;
if (n == 0) return 0;
int m = matrix[0].length;
int[][] f = new int[n + 1][m + 1];
int ans = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
for (int j = 0; j < m; j++) {
int u = i + 1, v = j + 1;
if (matrix[i][j] == '0') f[u][v] = 0;
else {
f[u][v] = Math.min(f[u - 1][v - 1], Math.min(f[u - 1][v], f[u][v - 1])) + 1;
ans = Math.max(ans, f[u][v]);
}
}
return ans * ans;
}
}
2020.5.9 69. x 的平方根
简单二分,注意爆int
class Solution {
public int mySqrt(int x) {
int l = 0, r = x;
while (l < r) {
int mid = (int)(((long)l + r + 1) >> 1);
if ((long)mid * mid <= x) l = mid;
else r = mid - 1;
}
return l;
}
}
 经典算法题解
经典算法题解























 806
806

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








