- 注解概念


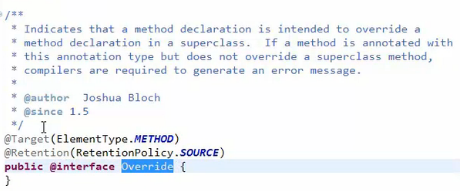
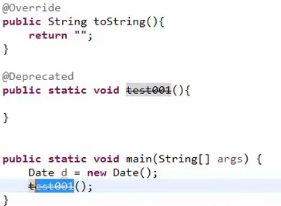
- @Override 表示重写父类方法
Interface 修饰
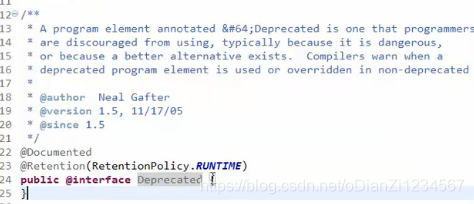
@Deperated 表示废弃。过时不建议使用,但是还可以使用。
@SuppressWarnings 表示抑制编译时的警告信息。

添加 @SuppressWarining 后:
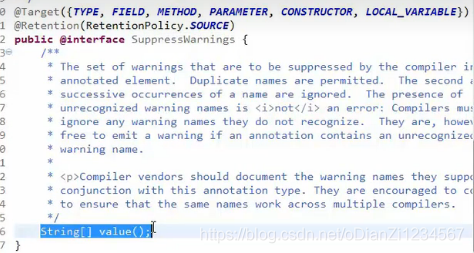
多了属性的定义:String[] value(); String[]表示参数类型,value表示参数名称。

自定义注解:


@Traget

Target内部:
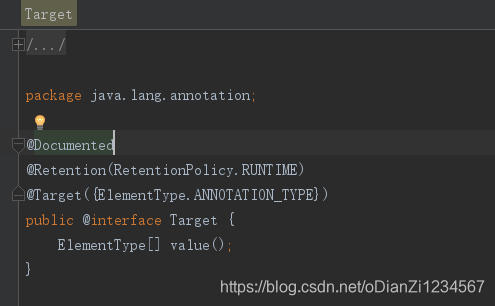
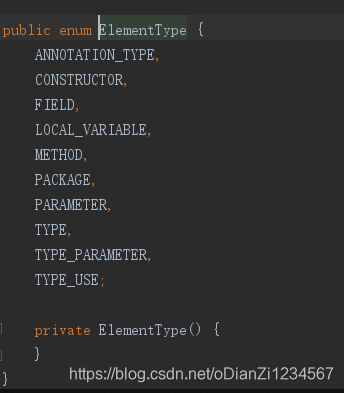
ElementType:内部是枚举类型
@Retention 注解的生命周期。



String[] schools() default{“ www”,”aaaa”} ;//数组
使用:
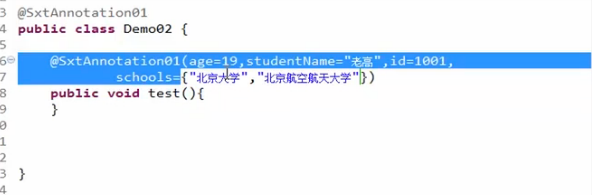
Annotation1:
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
//@Target(ElementType.METHOD)//Merhod 表示只能用在方法前面。
//数组表示可以用于类 方法
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
// 可以被反射读取 一般会用RUNTIME
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation {
String StudentName() default ""; //StudentName表示参数名称 default 表示默认值
int age() default 0;
int id() default -1;// -1 表示不存在
String[] schools() default {"1111","2222"};
}
Annotation2:
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
@Target(value = {ElementType.METHOD,ElementType.TYPE})
// 可以被反射读取 一般会用RUNTIME
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyAnnotation2 {
String value();//如果只用一个参数一般是 value()
}
使用:
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
//使用 ()赋值
@MyAnnotation
public class Demo01 {
@MyAnnotation(age = 112,StudentName = "zeng",id=123,schools = {"ssss","ddddd"})
public void test01(){
}
@MyAnnotation2(value = "一个值")
public void test2(){
}
}
反射读取注解:

一个注解的使用步骤:
- 定义注解
- 在类里面使用这个注解
- 写解析程序读出注解。
定义Filed 注解类:
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
@Target(ElementType.FIELD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SxtField {
String columName();//列名
String type();//数据类型
int length();//长度
}
定义 SxtTable注解 类
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import java.lang.annotation.ElementType;
import java.lang.annotation.Retention;
import java.lang.annotation.RetentionPolicy;
import java.lang.annotation.Target;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
@Target(ElementType.TYPE)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface SxtTable {
String value();
}
使用 SxtStudent 注解
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
@SxtTable("tb_student")
public class SxtStudent {
@SxtField(columName ="id",type ="int",length = 10)
private int id;
@SxtField(columName ="sname",type ="varchar",length = 10)
private String studentname;
@SxtField(columName ="age",type ="int",length = 3)
private int age ;
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public int getId() {
return id;
}
public String getStudentname() {
return studentname;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
public void setId(int id) {
this.id = id;
}
public void setStudentname(String studentname) {
this.studentname = studentname;
}
}
解析类:
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import java.lang.annotation.Annotation;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
public class Demo03 {
public String test(){
String allannotations=null;
try{
//按照完整路径获取类
Class clazz =Class.forName("com.example.zengjx.myjavabase.SxtStudent") ;//完整路径
//获得类的所有注解
Annotation[] annotations= clazz.getAnnotations();
StringBuffer sb=new StringBuffer();
for(Annotation a:annotations){
sb.append(a);
}
allannotations=sb.toString();
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.getMessage();
}
return allannotations;
}
public void test2(){
//获得类指定注解的值
try {
Class clazz =Class.forName("com.example.zengjx.myjavabase.SxtStudent") ;
SxtTable sxtTable =(SxtTable) clazz.getAnnotation(SxtTable.class);
System.out.println("sxtTable.value()"+sxtTable.value());//sxtTable.value()tb_student
//获得类属性值其中 的 studentname ,id 类似
Field f = clazz.getDeclaredField("studentname");
SxtField sxtField=f.getAnnotation(SxtField.class);
// 获取 studentname :snamevarchar 10
System.out.println("获取 studentname :"+sxtField.columName()+ ""+sxtField.type()+" "+sxtField.length());
}catch (ClassNotFoundException e){
e.getMessage();
}catch (NoSuchFieldException e){
e.getMessage();
}
}
}
junit测试 :
package com.example.zengjx.myjavabase;
import org.junit.After;
import org.junit.Before;
import org.junit.Test;
import static org.junit.Assert.*;
/**
* Created by zengjx on 2019/2/1.
*/
public class Demo03Test {
Demo03 demo03 ;
@Before
public void setUp() throws Exception {
demo03 =new Demo03();
}
@After
public void tearDown() throws Exception {
}
@Test
public void test1() throws Exception {
//反射:@com.example.zengjx.myjavabase.SxtTable(value=tb_student)
String s= demo03.test();
System.out.println("反射:"+s);
}
@Test
public void test2() throws Exception{
demo03.test2();
}
}
输出:1.反射:@com.example.zengjx.myjavabase.SxtTable(value=tb_student)
2. sxtTable.value()tb_student
获取 studentname :sname varchar 10







 本文详细介绍了Java注解的概念及应用,包括@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings等常见注解的含义,自定义注解的创建步骤,以及如何通过反射读取类上的注解信息。
本文详细介绍了Java注解的概念及应用,包括@Override、@Deprecated、@SuppressWarnings等常见注解的含义,自定义注解的创建步骤,以及如何通过反射读取类上的注解信息。
















 1049
1049

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








