80~触发器和锁存器
- 80.D flip-flop (Dff)
- 81.D flip-flops
- 82.DFF with reset (Dff8r)
- 83.DFF with reset value
- 84.DFF with asynchronous reset
- 85.DFF with byte enable
- 86.D latch(D锁存器)
- 87.DFF(异步)
- 88.DFF(同步)
- 89.DFF+gate
- 90.Mux and DFF
- 91.Mux and DFF
- 92.DFFS and gates
- 93.Create circuit from truth table
- 94.Detect an Edge
- 95.Detect both edges
- 96.Edge capture register
- 97.Dual-edge triggered flip-flop(没咋看懂)
强烈建议大家去看看HDLBits 中文导学,原文在知乎
链接: link.
从这里开始就要正式进入时序逻辑啦,难点来了;
80.D flip-flop (Dff)
D触发器:
- t1时刻: d -> 0;
- t2时刻: clk->1 上升沿到来,触发器存储的数据变成 0,输出 q 保持为存储的值:0,直到下一个时钟上升沿到来;
- t3时刻: d -> 1(d:我变了),q 仍保持 0 不动摇(时钟沿还没来呢);
- t4时刻: clk->1 上升沿到来,q->1(q:时钟沿来了,我该变身了)
module top_module(
input clk,
input d,
output reg q);
// Use non-blocking assignment for edge-triggered always blocks
always @(posedge clk)
q <= d;//非阻塞赋值
// Undefined simulation behaviour can occur if there is more than one edge-triggered
// always block and blocking assignment is used. Which always block is simulated first?
endmodule
81.D flip-flops
一样的
always@(posedge clk)begin
q<=d;
end
82.DFF with reset (Dff8r)
添加了一个复位信号
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
q<=8'b0;
else
q<=d;
end
83.DFF with reset value
always@(negedge clk)begin
if(reset)
q<=8'h34;
else
q<=d;
end
84.DFF with asynchronous reset
asynchronous reset:异步复位;
同步复位:当同步复位事件发生时,等到下一个时钟上升沿才会得到响应,响应的速度比较慢。
异步复位:响应很快,异步复位有效的时刻,复位响应就会发生,好像戳破气球一般。
直接将areset加入敏感元器件表中,
always@(posedge clk or posedge areset)begin
if(areset)
q <= 8'b0;
else
q <= d;
end
85.DFF with byte enable
这一题其实还是有一点复杂的,直接照搬题目:
本题中需要创建一个 16 路 D触发器。使能端 ena 信号有效时,触发器在时钟上升沿工作。
byteena 使能信号以 byte 为单位管理 8 路触发器在时钟边沿触发与否。byteena [1] 作为 d[15:8] 高位字节的使能端,byteena [0] 则控制 d 的低位字节。
resetn 为同步,低电平有效复位信号。
所有的触发器在时钟上升沿被触发
module top_module (
input clk,
input resetn,
input [1:0] byteena,
input [15:0] d,
output [15:0] q
);
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(~resetn)begin
q<=16'd0;
end
else if(byteena[0]||byteena[1])begin //这里的else必须要加,不加的话前面的复位信号不起作用
if(byteena[0])
q[7:0]<=d[7:0];
if(byteena[1]) //这里不能写else语句,这个并不是二选一的语句,是可以同时成立的
q[15:8]<=d[15:8];
end
end
endmodule
这里主要就是一个语句的结构层次的问题,复位和使能语句是并列二选一的,只能有一个同时生效,而使能语句下的高低位使能的语句是可以并列的;
86.D latch(D锁存器)
锁存器锁存的触发事件发生于使能端 ena 的电平;
module top_module (
input d,
input ena,
output q);
always@(*)
if(ena)
q<=d;
endmodule
87.DFF(异步)
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input ar, // asynchronous reset
output q);
always@(posedge clk or posedge ar)//将异步复位信号直接加入到敏感器件列表中
if(ar)
q<=1'b0;
else
q<=d;
endmodule
88.DFF(同步)
module top_module (
input clk,
input d,
input r, // synchronous reset
output q);
always@(posedge clk )
if(r)
q<=1'b0;
else
q<=d;
endmodule
89.DFF+gate
always@(posedge clk)
out<=in^out;
90.Mux and DFF
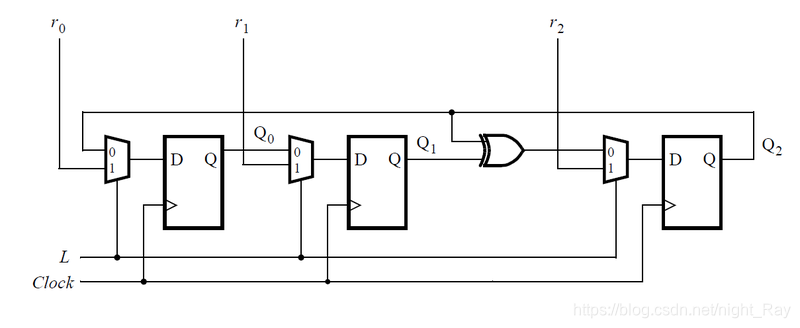
这一题只是让实现其中的一个选择器加触发器的子模块
module top_module (
input clk,
input L,
input r_in,
input q_in,
output reg Q);
always@(posedge clk)
Q<=L?r_in:q_in;
endmodule
91.Mux and DFF

module top_module (
input clk,
input w, R, E, L,
output Q
);
wire m1,m2;
assign m1= E?w:Q;
assign m2= L?R:m1;
/* always@(posedge clk)
m1= E?w:Q;
Q<= L?R:m1;
直接用两个非阻塞赋值就会报错,不知道为什么
*/
always@(posedge clk)
Q<=m2;
endmodule
92.DFFS and gates
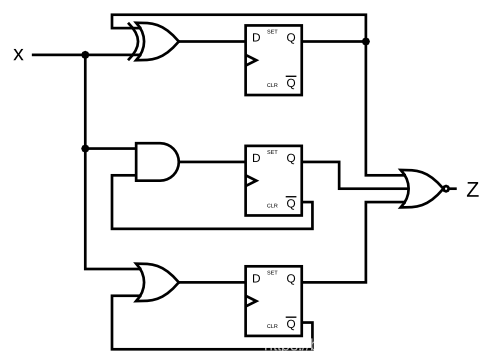
module top_module (
input clk,
input x,
output z
);
reg q1=0,q2=0,q3=0; //开始用的wire,会报错
always@(posedge clk)
q1<=q1^x;
always@(posedge clk)
q2<=x&(~q2);
always@(posedge clk)
q3<=x|(~q3);
assign z=~(q1|q2|q3);
endmodule
93.Create circuit from truth table
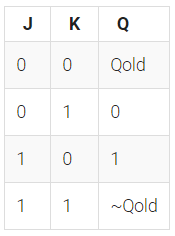
module top_module (
input clk,
input j,
input k,
output Q);
always@(posedge clk)
case({j,k})
2'b00:Q<=Q;
2'b01:Q<=0;
2'b10:Q<=1;
2'b11:Q<=!Q;
endcase
endmodule
94.Detect an Edge
link.
边沿检测:说实话,看了几遍,看的不是太懂。大概的意思就是,引入一个寄存器,这个寄存器的输入信号是上一个时钟信号的输入,然后输出是这个时钟的输入,然后比较的话,因为有延迟,这个时钟的信号在上个时钟之后变成0,就是下降沿。
module top_module (
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] pedge
);
reg[7:0] temp; //寄存器类型的信号
always@(posedge clk)
begin
temp <=in;
//temp在时钟到来的时候时钟保存上个时钟的in
pedge <= ~temp & in;
//如果这个时钟为1,上个时钟为0,说明上升沿
end
//这边的begin,end没加会报错,不清楚是什么原因
endmodule
95.Detect both edges
只要时钟信号和上个时钟不一样,就可以0判断,直接用异或就行;
module top_module (
input clk,
input [7:0] in,
output [7:0] anyedge
);
reg [7:0] temp;
always@(posedge clk)
begin
temp <=in;
anyedge <=temp^in;
end
endmodule
96.Edge capture register
capture:捕获的意思就是,当获取到摸个信号之后保持不变,
module top_module (
input clk,
input reset,
input [31:0] in,
output [31:0] out
);
reg[31:0] temp;
reg[31:0] pos;//上升沿捕获标志
//先来判断上升沿
always@(posedge clk)
begin
temp<=in;
end
assign pos=temp &~in;
//这里是看了解析才发现的,如果将这三个写在一个时序里会发生时序错误,
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(reset)
out<=0;
else
for(int i=0;i<=31;i++)
if(pos[i]==1)
//这里必须要用一个for循环来判断pos的每一个位是否为1
out[i]<=1;
end
endmodule
97.Dual-edge triggered flip-flop(没咋看懂)
这个时序图压根就看不懂;经过我的观察,应该是这样的,
时钟上升的时候q和d相反,时钟下降,q和d相同;
link看了一点这个,还是不怎么明白;所以就直接先过了;





 本文详细介绍了数字电路中的各种触发器与锁存器,包括D触发器、带复位功能的触发器、锁存器等,并通过Verilog代码示例展示了其工作原理与应用。还探讨了异步与同步复位的区别,以及如何使用触发器进行边沿检测。
本文详细介绍了数字电路中的各种触发器与锁存器,包括D触发器、带复位功能的触发器、锁存器等,并通过Verilog代码示例展示了其工作原理与应用。还探讨了异步与同步复位的区别,以及如何使用触发器进行边沿检测。
















 1698
1698

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








