jsoncpp的配置和使用
json的全称为:JavaScript Object Notation,是一种轻量级的数据交互格式。它基于 ECMAScript (欧洲计算机协会制定的js规范)的一个子集,采用完全独立于编程语言的文本格式来存储和表示数据。【以上来自于百度百科】
简单来说:json就是一种在各个编程语言中流通的数据格式,负责不同编程语言中的数据传递和交互。
1. 下载和编译
Jsoncpp 是个跨平台的 C++ 开源库,提供的类为我们提供了很便捷的操作,而且使用的人也很多。在使用之前我们首先要从 github 仓库下载源码
https://github.com/open-source-parsers/jsoncpp



下载的文件中,包含一个cmakelist的txt文件,因为对于大型的项目而言,不能够通过vs直接打开源码,需要通过cmake进行工程的构建并且在vs中进行编译动态库
下载 cmake 工具
CMake 工具的官方下载地址如下:
https://cmake.org/download/










jsoncpp 的使用
jsoncpp 库中的类被定义到了一个 Json 命名空间中,建议在使用这个库的时候先声明这个命名空间:
using namespace Json;
使用 jsoncpp 库解析 json 格式的数据,我们只需要掌握三个类:
Value 类:将 json 支持的数据类型进行了包装,最终得到一个 Value 类型
FastWriter类:将 Value 对象中的数据序列化为字符串
Reader类:反序列化,将 json 字符串 解析成 Value 类型
Value 类
这个类可以看做是一个包装器,它可以封装 Json 支持的所有类型,

构造函数
// 因为Json::Value已经实现了各种数据类型的构造函数
Value(ValueType type = nullValue);
Value(Int value);
Value(UInt value);
Value(Int64 value);
Value(UInt64 value);
Value(double value);
Value(const char* value);
Value(const char* begin, const char* end);
Value(bool value);
Value(const Value& other);
Value(Value&& other);
检测保存的数据类型
// 检测保存的数据类型
bool isNull() const;
bool isBool() const;
bool isInt() const;
bool isInt64() const;
bool isUInt() const;
bool isUInt64() const;
bool isIntegral() const;
bool isDouble() const;
bool isNumeric() const;
bool isString() const;
bool isArray() const;
bool isObject() const;
将 Value 对象转换为实际类型
Int asInt() const;
UInt asUInt() const;
Int64 asInt64() const;
UInt64 asUInt64() const;
LargestInt asLargestInt() const;
LargestUInt asLargestUInt() const;
JSONCPP_STRING asString() const;
float asFloat() const;
double asDouble() const;
bool asBool() const;
const char* asCString() const;
对 json 数组的操作
ArrayIndex size() const;
Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index);
Value& operator[](int index);
const Value& operator[](ArrayIndex index) const;
const Value& operator[](int index) const;
Value get(ArrayIndex index, const Value& defaultValue) const;
Value& append(const Value& value);
const_iterator begin() const;
const_iterator end() const;
iterator begin();
iterator end();
对 json 对象的操作
Value& operator[](const char* key);
const Value& operator[](const char* key) const;
Value& operator[](const JSONCPP_STRING& key);
const Value& operator[](const JSONCPP_STRING& key) const;
Value& operator[](const StaticString& key);
// 通过key, 得到value值
Value get(const char* key, const Value& defaultValue) const;
Value get(const JSONCPP_STRING& key, const Value& defaultValue) const;
Value get(const CppTL::ConstString& key, const Value& defaultValue) const;
// 得到对象中所有的键值
typedef std::vector<std::string> Members;
Members getMemberNames() const;
将 Value 对象数据序列化为 string
// 序列化得到的字符串有样式 -> 带换行 -> 方便阅读
// 写配置文件的时候
std::string toStyledString() const;
FastWriter 类
// 将数据序列化 -> 单行
// 进行数据的网络传输
std::string Json::FastWriter::write(const Value& root);
Reader 类
bool Json::Reader::parse(const std::string& document,
Value& root, bool collectComments = true);
参数:
- document: json格式字符串
- root: 传出参数, 存储了json字符串中解析出的数据
- collectComments: 是否保存json字符串中的注释信息
// 通过begindoc和enddoc指针定位一个json字符串
// 这个字符串可以是完成的json字符串, 也可以是部分json字符串
bool Json::Reader::parse(const char* beginDoc, const char* endDoc,
Value& root, bool collectComments = true);
// write的文件流 -> ofstream
// read的文件流 -> ifstream
// 假设要解析的json数据在磁盘文件中
// is流对象指向一个磁盘文件, 读操作
bool Json::Reader::parse(std::istream& is, Value& root, bool collectComments = true);
VS 的配置


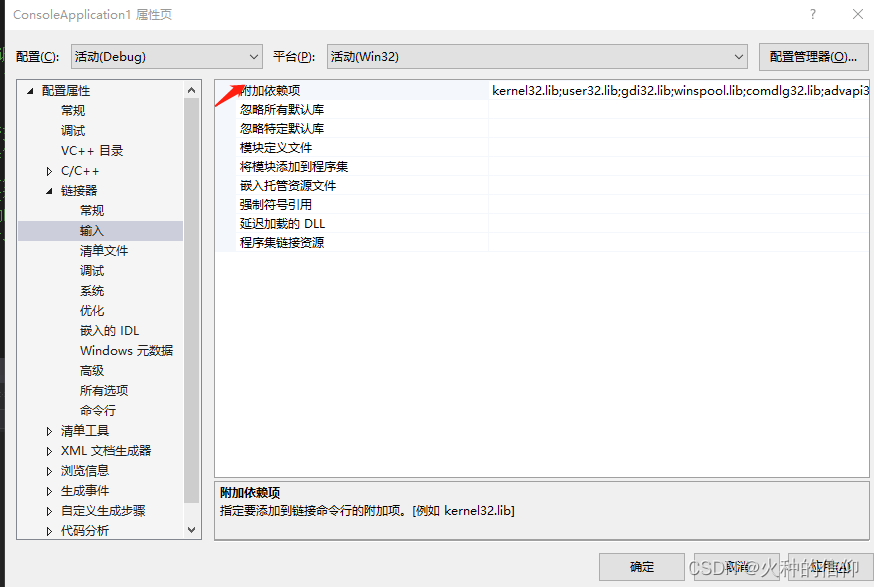

示例代码
[
12,
12.34,
true,
"tom",
["jack", "ace", "robin"],
{"sex":"man", "girlfriend":"lucy"}
]
#include <json/json.h>
#include <fstream>
using namespace Json;
int main()
{
writeJson();
readJson();
}
void writeJson()
{
// 将最外层的数组看做一个Value
// 最外层的Value对象创建
Value root;
// Value有一个参数为int 行的构造函数
root.append(12); // 参数进行隐式类型转换
root.append(12.34);
root.append(true);
root.append("tom");
// 创建并初始化一个子数组
Value subArray;
subArray.append("jack");
subArray.append("ace");
subArray.append("robin");
root.append(subArray);
// 创建并初始化子对象
Value subObj;
subObj["sex"] = "woman"; // 添加键值对
subObj["girlfriend"] = "lucy";
root.append(subObj);
// 序列化
#if 1
// 有格式的字符串
string str = root.toStyledString();
#else
FastWriter f;
string str = f.write(root);
#endif
// 将序列化的字符串写磁盘文件
ofstream ofs("test.json");
ofs << str;
ofs.close();
}
void readJson()
{
// 1. 将磁盘文件中的json字符串读到磁盘文件
ifstream ifs("test.json");
// 2. 反序列化 -> value对象
Value root;
Reader r;
r.parse(ifs, root);
// 3. 从value对象中将数据依次读出
if (root.isArray())
{
// 数组, 遍历数组
for (int i = 0; i < root.size(); ++i)
{
// 依次取出各个元素, 类型是value类型
Value item = root[i];
// 判断item中存储的数据的类型
if (item.isString())
{
cout << item.asString() << ", ";
}
else if (item.isInt())
{
cout << item.asInt() << ", ";
}
else if (item.isBool())
{
cout << item.asBool() << ", ";
}
else if (item.isDouble())
{
cout << item.asFloat() << ", ";
}
else if (item.isArray())
{
for (int j = 0; j < item.size(); ++j)
{
cout << item[j].asString() << ", ";
}
}
else if (item.isObject())
{
// 对象
// 得到所有的key
Value::Members keys = item.getMemberNames();
for (int k = 0; k < keys.size(); ++k)
{
cout << keys.at(k) << ":" << item[keys[k]] << ", ";
}
}
}
cout << endl;
}
}








 本文介绍了Jsoncpp库的下载、编译过程,并详细讲解了如何在C++中使用Jsoncpp进行JSON数据的序列化和反序列化,包括Value类、FastWriter类和Reader类的使用。还给出了一个完整的示例代码,展示了如何创建和解析JSON数据。
本文介绍了Jsoncpp库的下载、编译过程,并详细讲解了如何在C++中使用Jsoncpp进行JSON数据的序列化和反序列化,包括Value类、FastWriter类和Reader类的使用。还给出了一个完整的示例代码,展示了如何创建和解析JSON数据。

















 803
803

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








