多线程访问共享变量存在数据同时修改导致不一致问题,就需要锁来对共享数据的访问进行管理。
多个线程A B C 去竞争同一个锁L,存在线程获取锁的同步状态管理,排队获取锁,竞争获取锁,等待获取锁,释放锁唤醒其他等待中的线程问题。
Java中的synchronized关键字是一种锁的实现,隐式的管理多线程与锁的问题,由JVM实现。
JUC包下提供了显示锁来管理多线程和锁问题,Lock接口,队列同步器(AQS)AbstractQueuedSynchronizer分别定义了锁的操作接口和锁的实现基础模板。
AQS同步器的模板方法基本分为3类,独占式的获取与释放同步状态,共享式的获取与释放同步状态,查询等待队列中的等待线程情况。
独占锁获取了同步状态之后,其他独占和共享访问都会阻塞。 共享锁获取了同步状态之后,共享访问不会被阻塞,独占访问会被阻塞。
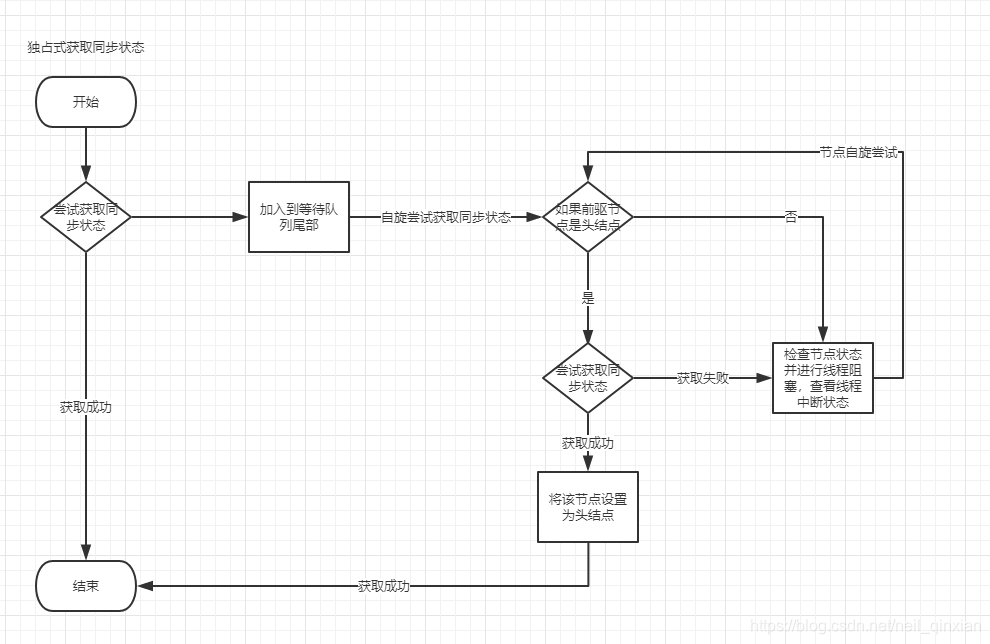
独占锁的获取过程
public final void acquire(int arg) {
if (!tryAcquire(arg) &&
acquireQueued(addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE), arg))
selfInterrupt();
}
// FairSync尝试获取同步状态
protected final boolean tryAcquire(int acquires) {
final Thread current = Thread.currentThread();
int c = getState();
// 当前状态为0 去尝试
if (c == 0) {
// 没有前驱节点并且获取成功 将当前线程设为持有锁的线程
if (!hasQueuedPredecessors() &&
compareAndSetState(0, acquires)) {
setExclusiveOwnerThread(current);
return true;
}
}
// 当前状态不为0 判断持有锁的线程是不是当前线程 是的话重新设置状态值 说明ReentrantLock.FairSync是可重入锁
else if (current == getExclusiveOwnerThread()) {
int nextc = c + acquires;
if (nextc < 0)
throw new Error("Maximum lock count exceeded");
setState(nextc);
return true;
}
return false;
}
}
// 尝试获取同步状态
final boolean acquireQueued(final Node node, int arg) {
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return interrupted;
}
// 获取失败 修改状态为等待装填
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
// 阻塞线程并检查中断状态
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
// 阻塞线程
private final boolean parkAndCheckInterrupt() {
// 阻塞线程
LockSupport.park(this);
return Thread.interrupted();
}
acquire();同步器的获取独占锁的方法,先尝试获取同步状态即获取锁tryAcquire(arg) ,获取失败去创建得带队列节点然后加入到等待队列addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE),等待队列节点自旋尝试去获取同步状态 acquireQueued()。获取同步状态失败之后阻塞该线程 LockSupport.park(this);。
private void doAcquireInterruptibly(int arg)
throws InterruptedException {
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return;
}
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
// 响应中断 抛出异常 和普通独占获取不一样的点
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
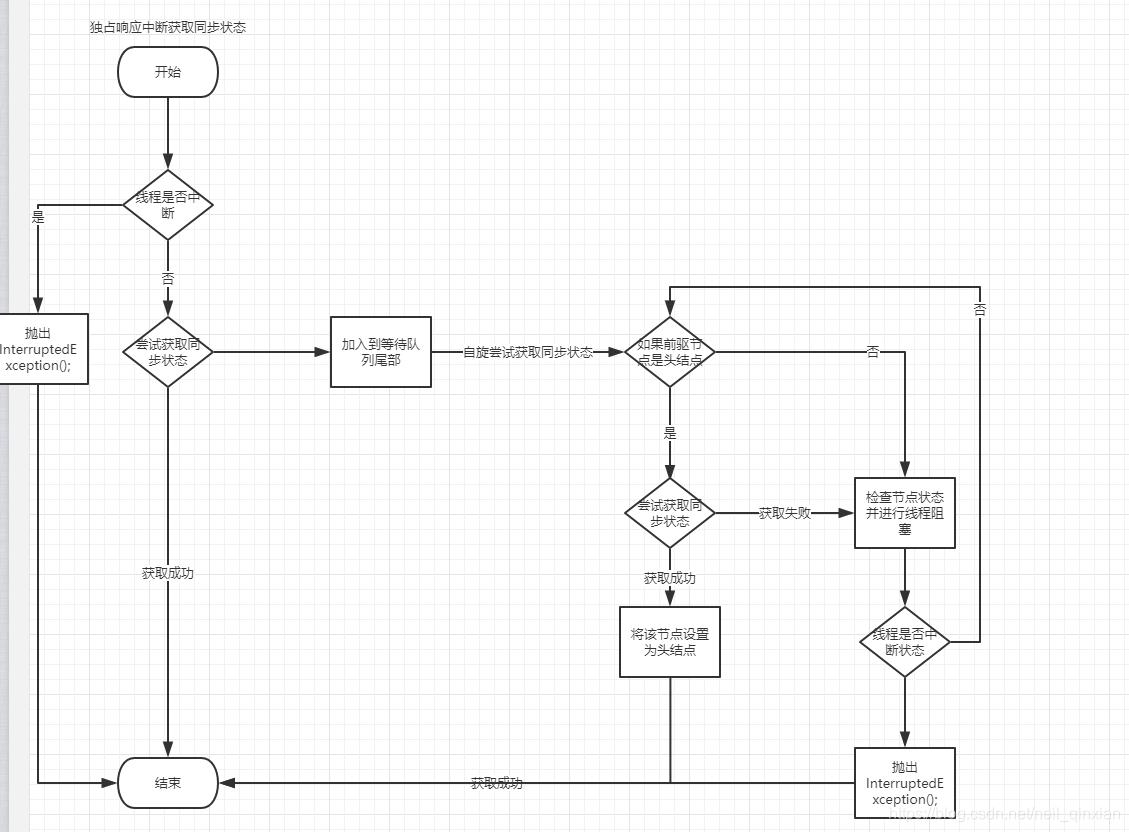
独占式获取,中断时仍然处于阻塞等待状态。如果是独占时中断响应式获取锁,中断后抛出异常InterruptedException();
private boolean doAcquireNanos(int arg, long nanosTimeout)
throws InterruptedException {
long lastTime = System.nanoTime();
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.EXCLUSIVE);
boolean failed = true;
try {
// 自旋尝试获取锁
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
// 前一节点是头结点尝试获取 都一样 独占式获取 独占响应中断式获取 独占超时获取
if (p == head && tryAcquire(arg)) {
setHead(node);
p.next = null; // help GC
failed = false;
return true;
}
// 到达超时时间 返回失败
if (nanosTimeout <= 0)
return false;
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
nanosTimeout > spinForTimeoutThreshold)
// 超时时间未到 阻塞超时时间
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanosTimeout);
// 重新计算超时时间
long now = System.nanoTime();
nanosTimeout -= now - lastTime;
lastTime = now;
// 如果中断 抛出异常
if (Thread.interrupted())
throw new InterruptedException();
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
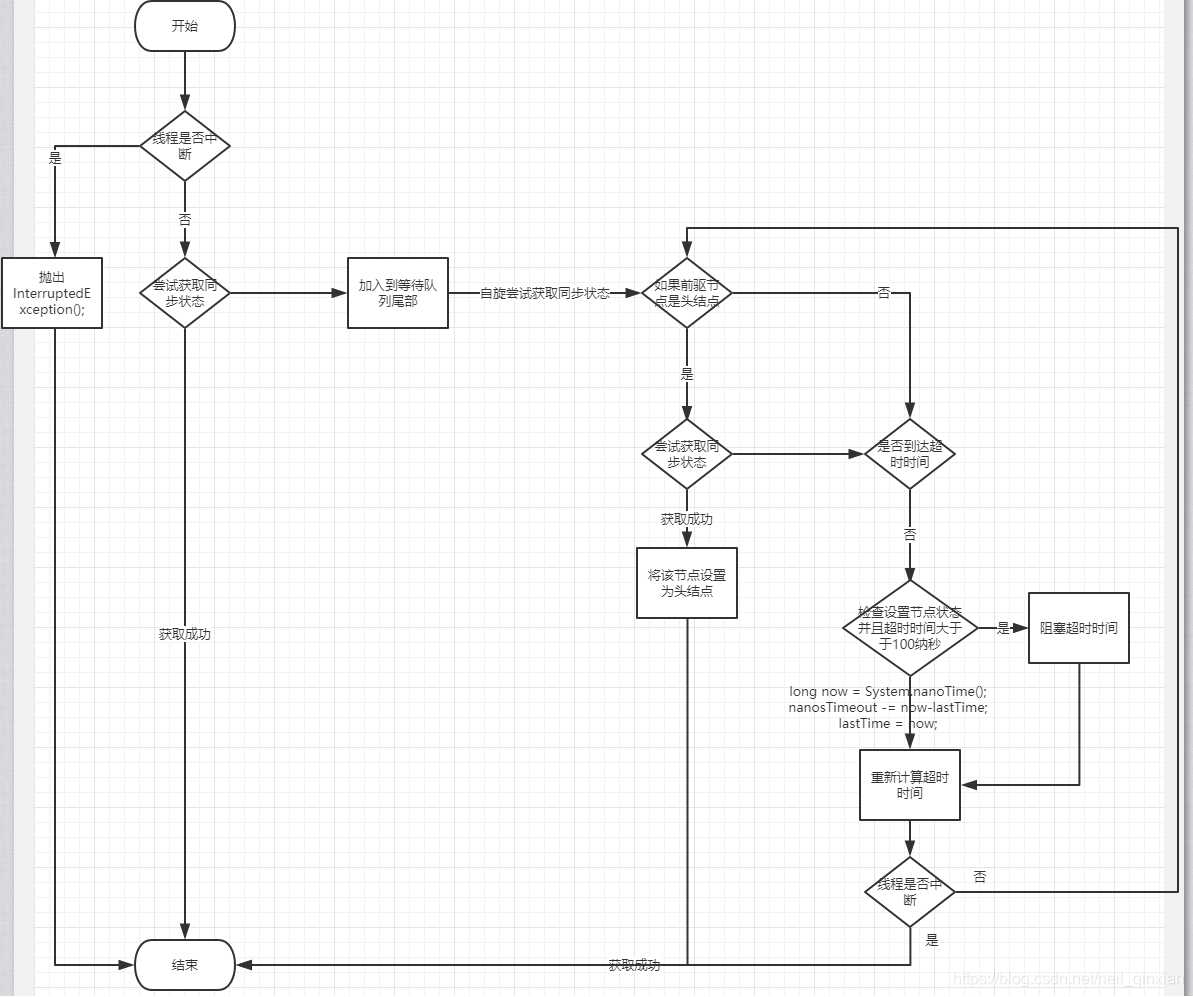
如果是超时获取锁,会在到达超时时间后直接返回false,如果该过程中中断仍然抛出异常InterruptedException();;
释放独占锁
public final boolean release(int arg) {
// 尝试释放锁
if (tryRelease(arg)) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h.waitStatus != 0)
// 唤醒后续节点的线程
unparkSuccessor(h);
return true;
}
return false;
}
// 释放锁 重入锁需要多次释放
protected final boolean tryRelease(int releases) {
int c = getState() - releases;
if (Thread.currentThread() != getExclusiveOwnerThread())
throw new IllegalMonitorStateException();
boolean free = false;
if (c == 0) {
free = true;
// 完全释放之后 持有锁的线程设为null
setExclusiveOwnerThread(null);
}
setState(c);
return free;
}
// 唤醒后续节点
private void unparkSuccessor(Node node) {
/*
* If status is negative (i.e., possibly needing signal) try
* to clear in anticipation of signalling. It is OK if this
* fails or if status is changed by waiting thread.
*/
int ws = node.waitStatus;
if (ws < 0)
compareAndSetWaitStatus(node, ws, 0);
/*
* Thread to unpark is held in successor, which is normally
* just the next node. But if cancelled or apparently null,
* traverse backwards from tail to find the actual
* non-cancelled successor.
*/
Node s = node.next;
if (s == null || s.waitStatus > 0) {
s = null;
for (Node t = tail; t != null && t != node; t = t.prev)
if (t.waitStatus <= 0)
s = t;
}
if (s != null)
// 唤醒后续节点
LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
}
release()同步器的释放锁方法。释放锁的时候 先去尝试释放锁成功之后去唤醒后续节点的线程 LockSupport.unpark(s.thread);
获取共享锁
public final void acquireShared(int arg) {
// 先尝试获取共享状态
if (tryAcquireShared(arg) < 0)
// 尝试获取共享状态失败 自旋去尝试获取
doAcquireShared(arg);
}
private void doAcquireShared(int arg) {
// 加入到等待队列
final Node node = addWaiter(Node.SHARED);
boolean failed = true;
try {
boolean interrupted = false;
for (;;) {
final Node p = node.predecessor();
if (p == head) {
// 前驱节点为头结点 尝试获取同步状态
int r = tryAcquireShared(arg);
if (r >= 0) {、
// 获取成功 将当前节点设为头结点
setHeadAndPropagate(node, r);
p.next = null; // help GC
if (interrupted)
selfInterrupt();
failed = false;
return;
}
}
// 获取失败 设置状态为等待并阻塞线程
if (shouldParkAfterFailedAcquire(p, node) &&
parkAndCheckInterrupt())
interrupted = true;
}
} finally {
if (failed)
cancelAcquire(node);
}
}
释放共享锁
public final boolean releaseShared(int arg) {
// 尝试释放 完全释放才会进行自旋尝试 唤醒后续线程
if (tryReleaseShared(arg)) {
// 共享锁尝试释放失败完全释放之后
doReleaseShared();
return true;
}
return false;
}
private void doReleaseShared() {
/*
* Ensure that a release propagates, even if there are other
* in-progress acquires/releases. This proceeds in the usual
* way of trying to unparkSuccessor of head if it needs
* signal. But if it does not, status is set to PROPAGATE to
* ensure that upon release, propagation continues.
* Additionally, we must loop in case a new node is added
* while we are doing this. Also, unlike other uses of
* unparkSuccessor, we need to know if CAS to reset status
* fails, if so rechecking.
*/
for (;;) {
Node h = head;
if (h != null && h != tail) {
int ws = h.waitStatus;
if (ws == Node.SIGNAL) {
if (!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, Node.SIGNAL, 0))
continue; // loop to recheck cases
unparkSuccessor(h);
}
else if (ws == 0 &&
!compareAndSetWaitStatus(h, 0, Node.PROPAGATE))
continue; // loop on failed CAS
}
if (h == head) // loop if head changed
break;
}
}





 本文探讨了多线程环境下如何使用锁来管理共享数据的访问,重点讲解了Java中synchronized关键字及JUC包下的Lock接口和AQS抽象队列同步器。独占锁在获取后会阻止其他线程(无论是独占还是共享)的访问,而共享锁则仅阻止独占访问。详细介绍了独占锁的获取(包括acquire方法、tryAcquire、addWaiter和acquireQueued等步骤)和释放过程,以及共享锁的相关操作。
本文探讨了多线程环境下如何使用锁来管理共享数据的访问,重点讲解了Java中synchronized关键字及JUC包下的Lock接口和AQS抽象队列同步器。独占锁在获取后会阻止其他线程(无论是独占还是共享)的访问,而共享锁则仅阻止独占访问。详细介绍了独占锁的获取(包括acquire方法、tryAcquire、addWaiter和acquireQueued等步骤)和释放过程,以及共享锁的相关操作。

















 273
273

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








