先给自己打个广告,本人的微信公众号正式上线了,搜索:张笑生的地盘,主要关注嵌入式软件开发,股票基金定投,足球等等,希望大家多多关注,有问题可以直接留言给我,一定尽心尽力回答大家的问题

本系列文章是为记录在学习韦东山老师的嵌入式开发教程中的课程笔记,并整理一个比较详细的课堂笔记,方便一起学习的同学们参考。
如果还没有购买韦老师的教学视频,或者不知道去哪里购买的,我这里给大家一个小程序链接


一 why
我们为什么要研究字符驱动设备程序的另一种写法呢?问这个问题之前,先看我们之前的字符设备驱动程序是如何写的,如何初始化的呢?
static int third_drv_init(void)
{
major = register_chrdev(0, "my_third_drv", &third_drv_fops);
thirddrv_class = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "mythirddrv");
thirddrv_class_dev = class_device_create(thirddrv_class, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "buttons"); /* /dev/xyz */
gpfcon = (volatile unsigned long *)ioremap(0x56000050, 16);
gpfdat = gpfcon + 1;
gpgcon = (volatile unsigned long *)ioremap(0x56000060, 16);
gpgdat = gpgcon + 1;
return 0;
}
关注语句:major = register_chrdev(0, "my_third_drv", &third_drv_fops);,这个注册字符设备有什么不妥的地方呢?我们跟踪这个函数,发现它会将次设备号从0到255都对应结构体third_drv_fops,显然这很浪费资源,
static inline int register_chrdev(unsigned int major, const char *name,
const struct file_operations *fops)
{
return __register_chrdev(major, 0, 256, name, fops);
}
正确的做法是,我们只需要指定一个次设备号,或者几个此设备号对应结构体third_drv_fops就可以了,所以我们需要重新写字符设备驱动程序
二 how
展开register_chrdev,发现它实际上是用了好几个接口来注册,我们参照这几个函数的用法即可,这几个函数是
register_chrdev_region / alloc_chrdev_region
register_chrdev_region : 从(主,次)到(主,次+n)都对应这个file_operations
cdev_init
cdev_add
a. 初始化函数如下
static int hello_init(void)
{
dev_t devid;
#if 0
register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hellp_fops); /* (major, 0 ) ~ (major, 255)都对应hellp_fops */
#else
if (major){
devid = MKDEV(major, 0); /* 0表示次设备号的base从0开始 */
register_chrdev_region(devid, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0~1)对应hellp_fops, (major,2~255)不对应hellp_fops */
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, HELLO_CNT, "hello");
major = MAJOR(devid);
}
cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hellp_fops);
cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devid, HELLO_CNT);
#endif
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello");
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello0"); /* /dev/hello0 */
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 1), NULL, "hello1"); /* /dev/hello1 */
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 2), NULL, "hello2"); /* /dev/hello2 */
return 0;
}
b. 对应的,退出函数如下
static void hello_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0));
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 1));
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 2));
class_destroy(cls);
cdev_del(&hello_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), HELLO_CNT);
}
完整代码如下:
#include <linux/module.h>
#include <linux/version.h>
#include <linux/init.h>
#include <linux/fs.h>
#include <linux/interrupt.h>
#include <linux/irq.h>
#include <linux/sched.h>
#include <linux/pm.h>
#include <linux/sysctl.h>
#include <linux/proc_fs.h>
#include <linux/delay.h>
#include <linux/platform_device.h>
#include <linux/input.h>
#include <linux/kernel.h>
#include <linux/device.h>
#include <linux/cdev.h>
#include <asm/uaccess.h>
#include <asm/io.h>
#define HELLO_CNT 2
/* 1. 确定主设备号 */
static int major;
static struct class *cls;
static struct cdev hello_cdev;
static int hello_open (struct inode *inode, struct file *file)
{
printk("hello_open\n");
return 0;
}
/* 2. 构造file_operation结构体 */
static struct file_operations hellp_fops = {
.owner = THIS_MODULE,
.open = hello_open,
};
static int hello_init(void)
{
dev_t devid;
#if 0
register_chrdev(0, "hello", &hellp_fops); /* (major, 0 ) ~ (major, 255)都对应hellp_fops */
#else
if (major){
devid = MKDEV(major, 0); /* 0表示次设备号的base从0开始 */
register_chrdev_region(devid, HELLO_CNT, "hello"); /* (major,0~1)对应hellp_fops, (major,2~255)不对应hellp_fops */
} else {
alloc_chrdev_region(&devid, 0, HELLO_CNT, "hello");
major = MAJOR(devid);
}
cdev_init(&hello_cdev, &hellp_fops);
cdev_add(&hello_cdev, devid, HELLO_CNT);
#endif
cls = class_create(THIS_MODULE, "hello");
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 0), NULL, "hello0"); /* /dev/hello0 */
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 1), NULL, "hello1"); /* /dev/hello1 */
device_create(cls, NULL, MKDEV(major, 2), NULL, "hello2"); /* /dev/hello2 */
return 0;
}
static void hello_exit(void)
{
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 0));
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 1));
device_destroy(cls, MKDEV(major, 2));
class_destroy(cls);
cdev_del(&hello_cdev);
unregister_chrdev_region(MKDEV(major, 0), HELLO_CNT);
}
module_init(hello_init);
module_exit(hello_exit);
MODULE_LICENSE("GPL");
c. 为了验证我们的猜想,我们准备一个测试程序,如下:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <fcntl.h>
#include <stdio.h>
/*
* hello_test <dev>
*/
void print_usage(char *file)
{
printf("%s <dev>\n", file);
}
int main(int argc, char **argv)
{
int fd;
if (argc != 2)
{
print_usage(argv[0]);
return 0;
}
fd = open(argv[1], O_RDWR);
if (fd < 0)
printf("can't open %s\n", argv[1]);
else
printf("can open %s\n", argv[1]);
return 0;
}
三 测试
a. 分别将驱动和测试程序编译上传至nfs服务器
b. 加载驱动 insmod
c. 运行测试程序
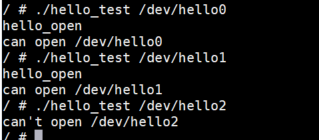
因为我们的驱动程序中,定义了次设备号0,1对应file operation结构体,次设备号2没有对应结构体,所以/dev/hello2就没有对应的open函数,所以会提示can’t open





















 346
346

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








