本篇内容主要是把wiki上的CNN(英文版)结合自己理解,翻译了一下,wiki中文版太粗糙了...而且访问还得翻墙
In deep learning, a convolutional neural network (CNN, or ConvNet) is a class of deep neural networks, most commonly applied to analyzing visual imagery.
CNNs use a variation of multilayer perceptrons designed to require minimal preprocessing.[1] They are also known as shift invariant or space invariant artificial neural networks (SIANN), based on their shared-weights architecture and translation invariance characteristics.[2][3]
Convolutional networks were inspired by biological processes[4] in that the connectivity pattern between neurons resembles the organization of the animal visual cortex. Individual cortical neurons respond to stimuli only in a restricted region of the visual field known as the receptive field. The receptive fields of different neurons partially overlap such that they cover the entire visual field.
CNNs use relatively little pre-processing compared to other image classification algorithms. This means that the network learns the filters that in traditional algorithms were hand-engineered. This independence from prior knowledge and human effort in feature design is a major advantage.
They have applications in image and video recognition, recommender systems,[5] image classification, medical image analysis, and natural language processing.[6]
在深度学习中,卷积神经网络(CNN或ConvNet)是一类深度神经网络,最常用于分析视觉图像。
CNN使用多层感知器的变体设计,需要最少的预处理。[1]它们也被称为移位不变或空间不变人工神经网络(SIANN),基于它们的共享权重架构和平移不变性特征。[2] [3]
Multilayer perceptron:多层感知器,即多层网络(至少三层,包含input layer、output layer和一层或多层hide layer ),在每层之间由权重和激活函数相连接
卷积网络被启发由生物工艺[4]在之间的连接图案的神经元类似于动物的组织视觉皮层。个体皮层神经元仅在被称为感受野的视野的受限区域中对刺激作出反应。不同神经元的感受野部分重叠,使得它们覆盖整个视野。
与其他图像分类算法相比,CNN使用相对较少的预处理。这意味着网络学习传统算法中手工设计的过滤器。这种与特征设计中的先前知识和人力的独立性是一个主要优点。
它们可用于图像和视频识别,推荐系统,[5] 图像分类,医学图像分析和自然语言处理。[6]
Design[edit]
A CNN consists of an input and an output layer, as well as multiple hidden layers. The hidden layers of a CNN typically consist of convolutional layers, RELU layer i.e. activation function, pooling layers, fully connected layers and normalization layers.[7]
Description of the process as a convolution in neural networks is by convention. Mathematically it is a cross-correlation rather than a convolution (although cross-correlation is a related operation). This only has significance for the indices in the matrix, and thus which weights are placed at which index.
设计
CNN由输入和输出层以及多个隐藏层组成。CNN的隐藏层通常包括卷积层,RELU层(非线性层)、激活函数,池化层,完全连接层和归一化层组成。[7]
神经网络中的卷积只是一种描述惯例,在数学上它是互相关而不是卷积(尽管互相关是一个和卷积相像的操作)。这仅对矩阵中的指数具有重要性,因此权重放在哪个指数处。
Convolutional[edit]
Convolutional layers apply a convolution operation to the input, passing the result to the next layer. The convolution emulates the response of an individual neuron to visual stimuli.[8]
Each convolutional neuron processes data only for its receptive field. Although fully connected feedforward neural networks can be used to learn features as well as classify data, it is not practical to apply this architecture to images. A very high number of neurons would be necessary, even in a shallow (opposite of deep) architecture, due to the very large input sizes associated with images, where each pixel is a relevant variable. For instance, a fully connected layer for a (small) image of size 100 x 100 has 10000 weights for each neuron in the second layer. The convolution operation brings a solution to this problem as it reduces the number of free parameters, allowing the network to be deeper with fewer parameters.[9] For instance, regardless of image size, tiling regions of size 5 x 5, each with the same shared weights, requires only 25 learnable parameters. In this way, it resolves the vanishing or exploding gradients problem in training traditional multi-layer neural networks with many layers by using backpropagation.[citation needed]
卷积
卷积层对输入做卷积运算,将结果传递给下一层。卷积模拟个体神经元对视觉刺激的反应。[8]
每个卷积神经元仅处理其感受野的数据。尽管可以使用完全连接的前馈神经网络来学习特征以及对数据进行分类,但是将该架构应用于图像是不实际的。由于与图像相关联的非常大的输入尺寸,每个像素是相关变量,因此即使在浅(深的相反)架构中也需要非常多的神经元。例如,尺寸为100×100的(小)图像的完全连接层对于第二层中的每个神经元具有10000个权重。卷积操作为这个问题带来了解决方案,因为它减少了自由参数的数量,允许网络更深,参数更少。[9] 例如,无论图像大小如何,大小为5 x 5的平铺区域(每个都具有相同的共享权重)仅需要25个可学习的参数。通过这种方式,它通过使用反向传播来解决训练具有多层的传统多层神经网络中的消失或爆炸梯度问题。[ 引证需要 ]
Pooling[edit]
Convolutional networks may include local or global pooling layers,[clarification needed] which combine the outputs of neuron clusters at one layer into a single neuron in the next layer.[10][11] For example, max pooling uses the maximum value from each of a cluster of neurons at the prior layer.[12] Another example is average pooling, which uses the average value from each of a cluster of neurons at the prior layer.[13]
池化
卷积网络可以包括局部或全局池化层,其作用为将一层神经元簇的输出组合成下一层中的单个神经元(将上一层的多个输出合并为下一层的单个输入,使得运算量减小)。[10] [11]例如,max pooling使用前一层神经元簇中每个神经元的最大值。[12]另一个例子是平均池,其使用在现有层从每个神经元的群集的平均值。[13]
Fully connected[edit]
Fully connected layers connect every neuron in one layer to every neuron in another layer. It is in principle the same as the traditional multi-layer perceptron neural network (MLP).
完全连接层
完全连接层将一层中的每个神经元连接到另一层中的每个神经元。它原则上与传统的多层感知器神经网络(MLP)相同。
Weights[edit]
Each neuron in a neural network computes an output value by applying some function to the input values coming from the receptive field in the previous layer. The function that is applied to the input values is specified by a vector of weights and a bias (typically real numbers). Learning in a neural network progresses by making incremental adjustments to the biases and weights. The vector of weights and the bias are called a filter and represents some feature of the input (e.g., a particular shape). A distinguishing feature of CNNs is that many neurons share the same filter. This reduces memory footprint because a single bias and a single vector of weights is used across all receptive fields sharing that filter, rather than each receptive field having its own bias and vector of weights.[1]
Receptive field[edit]
In neural networks, each neuron receives input from some number of locations in the previous layer. In a fully connected layer, each neuron receives input from every element of the previous layer. In a convolutional layer, neurons receive input from only a restricted subarea of the previous layer. Typically the subarea is of a square shape (e.g., size 5 by 5). The input area of a neuron is called its receptive field. So, in a fully connected layer, the receptive field is the entire previous layer. In a convolutional layer, the receptive area is smaller than the entire previous layer.
感受野(滤波器/卷积核的范围)
在神经网络中,每个神经元接收来自前一层中某些位置的输入。在完全连接的层中,每个神经元接收来自前一层的每个元素的输入。在卷积层中,神经元仅从前一层的受限区域接收输入。通常,子区域具有正方形形状(例如,尺寸5乘5)。神经元的输入区域称为其感受野(窗口)。因此,在完全连接层中,感受野是整个前一层。在卷积层中,接收区域小于整个前一层。
权重W
神经网络中的每个神经元通过来自前一层中的感受野的输入值来进行一些函数运算计算输出值。应用于输入值的函数由权重W向量和偏差B(通常为实数)指定。在神经网络中进行学习,就是对相应的偏差和权重进行调整。权重和偏差的矢量被称为滤波器(卷积核)并且表示输入的一些特征(例如,特定形状)。CNN的一个显着特征是许多神经元共享相同的滤波器(卷积核)。这减少了内存占用因为在共享该过滤器的所有感受野中使用单个偏差和单个权重向量,而不是每个感受野具有其自身的偏差和权重向量。[1]
Pooling layer[edit]
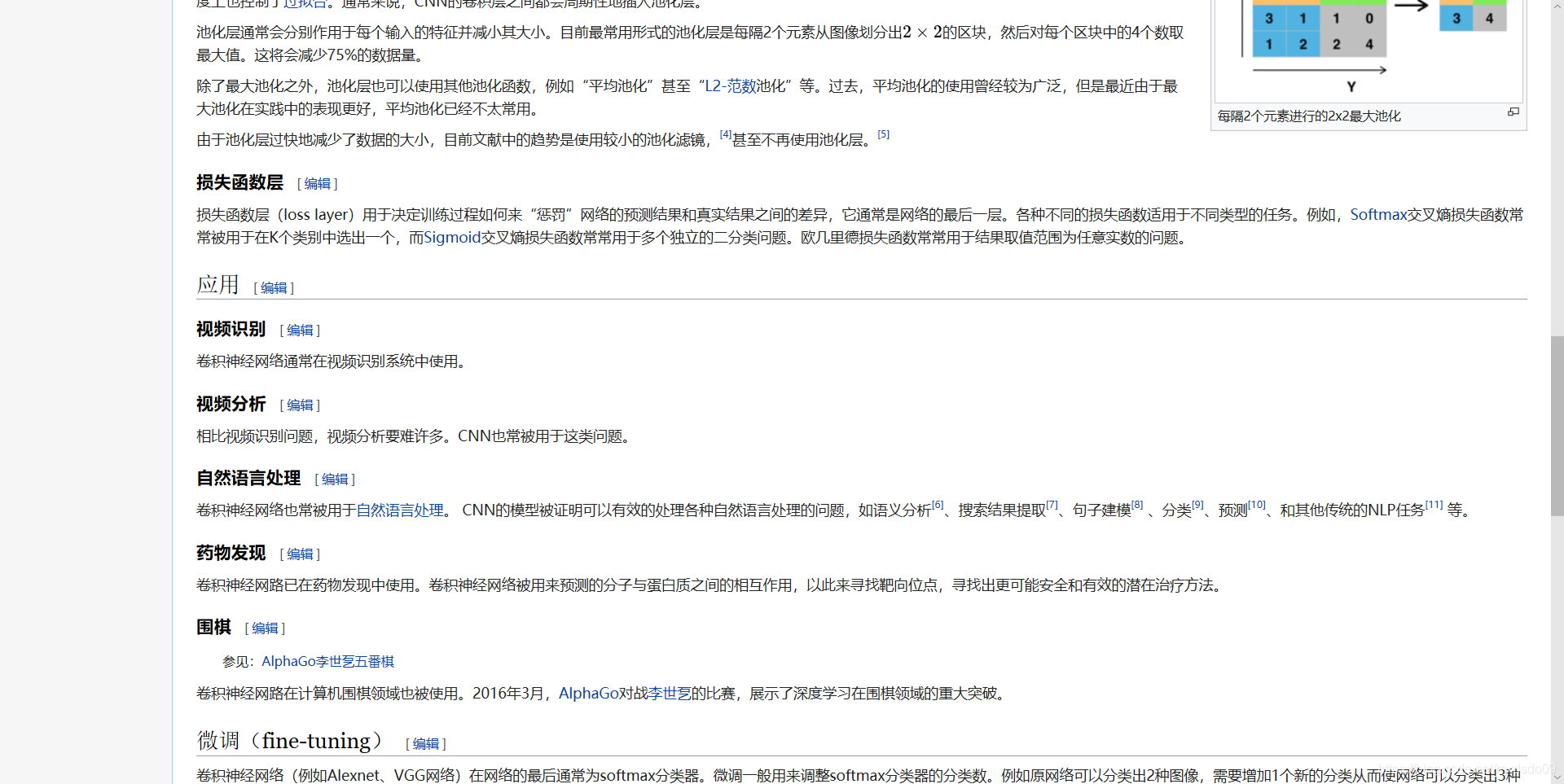
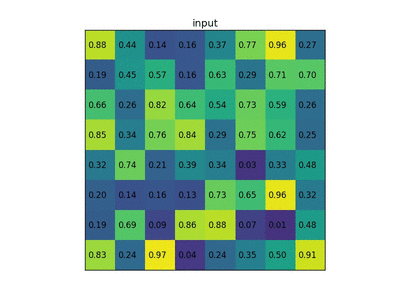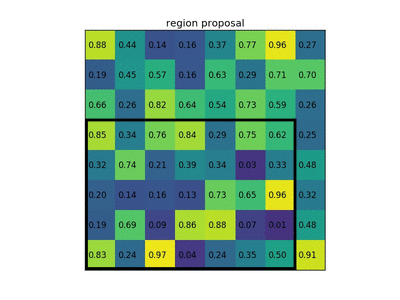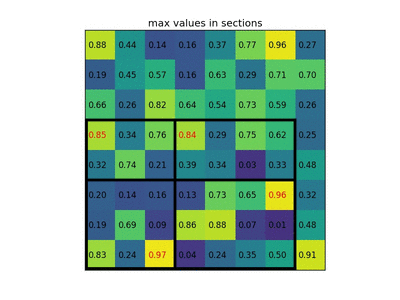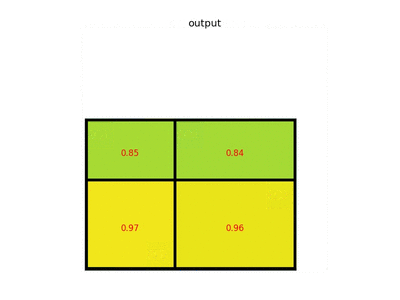
Max pooling with a 2x2 filter and stride = 2Another important concept of CNNs is pooling, which is a form of non-lineardown-sampling. There are several non-linear functions to implement pooling among whichmax poolingis the most common. Itpartitionsthe input image into a set of non-overlapping rectangles and, for each such sub-region, outputs the maximum.Intuitively, the exact location of a feature is less important than its rough location relative to other features. This is the idea behind the use of pooling in convolutional neural networks. The pooling layer serves to progressively reduce the spatial size of the representation, to reduce the number of parameters,memory footprintand amount of computation in the network, and hence to also controloverfitting. It is common to periodically insert a pooling layer between successive convolutional layers in a CNN architecture.[citation needed]The pooling operation provides another form of translation invariance.The pooling layer operates independently on every depth slice of the input and resizes it spatially. The most common form is a pooling layer with filters of size 2×2 applied with a stride of 2 downsamples at every depth slice in the input by 2 along both width and height, discarding 75% of the activations. In this case, everymax operationis over 4 numbers. The depth dimension remains unchanged.In addition to max pooling, pooling units can use other functions, such asaveragepooling orℓ2-normpooling. Average pooling was often used historically but has recently fallen out of favor compared to max pooling, which performs better in practice.[42]Due to the aggressive reduction in the size of the representation,[which?]there is a recent trend towards using smaller filters[43]or discarding pooling layers altogether.[44]
RoI pooling to size 2x2. In this example region proposal (an input parameter) has size 7x5."Region of Interest" pooling (also known as RoI pooling) is a variant of max pooling, in which output size is fixed and input rectangle is a parameter.[45]Pooling is an important component of convolutional neural networks forobject detectionbased on Fast R-CNN[46]architecture.
池化层(相当于下采样,减少参数)
使用2x2过滤器和stride = 2进行最大池化CNN的另一个重要概念是汇集,这是一种非线性下采样。有几个非线性函数来实现池化,其中最常见的池化是最常见的。它分割所述输入图像划分成一组非重叠矩形的,并且对于每个这样的子区域中,输出最大。直观地,特征的确切位置不如其相对于其他特征的粗略位置重要。这是在卷积神经网络中使用汇集的理念。池化层用于逐渐减小表示的空间大小,以减少参数的数量,存储器占用空间和网络中的计算量,并因此还控制过度拟合。通常在CNN架构中的连续卷积层之间周期性地插入池化层。[ 引证需要 ]汇集操作提供了另一种形式的翻译不变性。汇集层在输入的每个深度切片上独立操作,并在空间上调整其大小。最常见的形式是具有2×2大小的过滤器的池化层,在输入中的每个深度切片处沿着宽度和高度施加2个下行样本的步幅,丢弃75%的激活。在这种情况下,每个最大操作都超过4个数字。深度维度保持不变。除了最大池,池单元可以使用其他功能,如平均池或ℓ 2范数池。平均汇集通常在历史上使用,但最近已经失宠,而最大汇集在实践中表现更好。[42]由于表现形式的大幅减少,[ 哪个?]存在朝向使用较小的过滤器最近的趋势[43]或完全丢弃池层。[44]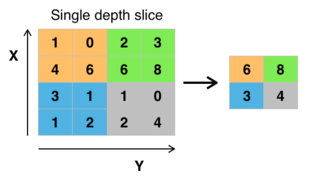
RoI汇集到2x2的大小。在此示例中,区域提议(输入参数)的大小为7x5。“ 感兴趣区域 ”池(也称为RoI池)是最大池的变体,其中输出大小是固定的,输入矩形是参数。[45]汇聚是基于快速R-CNN [46]架构的用于对象检测的卷积神经网络的重要组成部分。
ReLU layer
ReLU is the abbreviation ofrectified linear unit, which applies the non-saturatingactivation functionf(x)=max(0,x){\textstyle f(x)=\max(0,x)}.[47]Effectively, it removes negative values from an activation map by setting them to zero. It increases thenonlinear propertiesof thedecision functionand of the overall network without affecting the receptive fields of the convolution layer.Other functions are also used to increase nonlinearity, for example the saturatinghyperbolic tangentf(x)=tanh(x){\displaystyle f(x)=\tanh(x)},f(x)=|tanh(x)|{\displaystyle f(x)=|\tanh(x)|}, and thesigmoid functionσ(x)=(1+e−x)−1{\textstyle \sigma (x)=(1+e^{-x})^{-1}}. ReLU is often preferred to other functions because it trains the neural network several times faster without a significant penalty togeneralizationaccuracy.[48]
ReLU层(增加网络的非线性特性)
ReLU是整流线性单元的缩写,它应用非饱和激活功能 {\ textstyle f(x)= \ max(0,x)}。[47]实际上,它通过将激活图设置为零来从激活图中删除负值。它增加了决策函数和整个网络的非线性特性,而不会影响卷积层的感知域。其他函数也用于增加非线性,例如饱和双曲正切 {\ displaystyle f(x)= \ tanh(x)}, {\ displaystyle f(x)= | \ tanh(x)|},以及sigmoid功能 {\ textstyle \ sigma(x)=(1 + e ^ { - x})^ { - 1}}。ReLU通常比其他功能更受欢迎,因为它可以更快地训练神经网络几次而不会对泛化精度造成重大损失。[48]
Fully connected layer
Finally, after several convolutional and max pooling layers, the high-level reasoning in the neural network is done via fully connected layers. Neurons in a fully connected layer have connections to all activations in the previous layer, as seen in regular (non-convolutional) artificial neural networks. Their activations can thus be computed as an affine transformation, with matrix multiplication followed by a bias offset (vector addition of a learned or fixed bias term).
完全连接层(在最后输出之前,然后统计分数)
最后,在几个卷积和最大池化层之后,神经网络中的高级推理是通过完全连接的层完成的。完全连接层中的神经元与前一层中的所有激活具有连接,如常规(非卷积)人工神经网络中所见。因此,它们的激活可以作为仿射变换来计算,其中矩阵乘法后跟偏置偏移(学习或固定偏置项的向量相加)。
参考





 本文深入探讨了卷积神经网络(CNN)的基本原理,包括其在视觉图像分析中的应用,设计架构,如卷积层、池化层、全连接层等,以及CNN如何通过减少参数数量实现深层网络的学习。
本文深入探讨了卷积神经网络(CNN)的基本原理,包括其在视觉图像分析中的应用,设计架构,如卷积层、池化层、全连接层等,以及CNN如何通过减少参数数量实现深层网络的学习。

















 2913
2913

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








