/**
* Definition of Interval:
* classs Interval {
* int start, end;
* Interval(int start, int end) {
* this->start = start;
* this->end = end;
* }
* }
*/
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(const Interval &a, const Interval &b){
return (a.start<b.start);
}
vector<Interval> merge(vector<Interval> &intervals) {
if (intervals.size()==0) return intervals;
sort(intervals.begin(),intervals.end(),cmp);
int head=intervals[0].start;
int tail=intervals[0].end;
int index=0;
int i=1;
while (i<intervals.size())
{
if (intervals[i].start<=tail)
if (intervals[i].end<=tail) intervals.erase(intervals.begin()+i);
else
{
tail=intervals[i].end;
intervals[index].end=tail;
intervals.erase(intervals.begin()+i);
}
else
{
index=i;
head=intervals[i].start;
tail=intervals[i].end;
i++;
}
}
return intervals;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
int addDigits(int num) {
while (num>=10)
{
int tmp=0;
while (num>0)
{
tmp+=num%10;
num=num/10;
}
num=tmp;
}
return num;
}
};1360. 对称树
1.打印中序遍历,看一下是不是对称
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> order;
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode * root) {
if(root==NULL)return true;
midorder(root);
for (int i=0;i<order.size()/2;i++)
if (order[i]!=order[order.size()-1-i]) return false;
return true;
}
void midorder(TreeNode * root){
if (root==NULL) {order.push_back(INT_MIN);return;}
midorder(root->left);
order.push_back(root->val);
midorder(root->right);
}
};2.分治,对称树的特点是左子树的左子树=右子树的右子树&&左子树的右子树==右子树的左子树。
class Solution {
public:
bool isSymmetric(TreeNode * root) {
if(root==NULL)return true;
return helper(root->left,root->right);
}
bool helper(TreeNode * left,TreeNode * right){
if (left==NULL) return right==NULL;
if (right==NULL) return left==NULL;
if (left->val!=right->val) return false;
return helper(left->left,right->right) && helper(left->right,right->left);
}
};class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string &s) {
vector<int> rec(255,0);
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
rec[s[i]]++;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
if (rec[s[i]]==1) return i;
return -1;
}
};451. 两两交换链表中的节点
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85243994
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * swapPairs(ListNode * head) {
if (head==NULL) return head;
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(0);
dummy->next=head;
ListNode* prev=dummy;
ListNode* cur=head;
while (prev->next!=NULL && prev->next->next!=NULL) {
prev->next=cur->next;
cur->next=cur->next->next;
prev->next->next=cur;
prev=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};453. 将二叉树拆成链表
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85274891
13. 字符串查找
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85610373
这里注意特殊情况:""是任何字符串的子串
class Solution {
public:
int strStr(string &source, string &target) {
if (source.length()<target.length()) return -1;
if (target=="") return 0;
for (int i=0;i<source.length()-target.length()+1;i++) {
int j=0;
while (j<target.size() && source[i+j]==target[j]) j++;
if (j==target.size()) return i;
}
return -1;
}
};1334. 旋转数组
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85164803
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> levelOrder(TreeNode * root) {
vector<vector<int>> res;
queue<TreeNode*> h;
if (root==NULL) return res;
h.push(root);
while (!h.empty())
{
vector<int> tmp;
int i = h.size();
for (int j = 0; j < i; j++)
{
tmp.push_back(h.front()->val);
if (h.front()->left != NULL) h.push(h.front()->left); //注意判断是否为空!
if (h.front()->right!= NULL) h.push(h.front()->right);
h.pop();
}
res.push_back(tmp);
}
return res;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int countPrimes(int n) {
vector<bool> num(n,true);
int res=0;
for (int i=2;i<=sqrt(n);i++)
if (num[i])
{
int k=2;
while (k*i<n)
{
num[k*i]=false;
k++;
}
}
for (int i=2;i<n;i++)
if (num[i]) res++;
return res;
}
};844. 数对统计
class Solution {
public:
int pairNumbers(vector<Point> &p) {
int x,y,z,w;
x=y=z=w=0;
for (int i=0;i<p.size();i++)
if (p[i].x%2==1)
{
if (p[i].y%2==0) x++;
else y++;
}
else {if (p[i].y%2==1) z++;
else w++;}
return x*(x-1)/2+y*(y-1)/2+z*(z-1)/2+w*(w-1)/2;
}
};class Solution {
public:
string concatenetedString(string &s1, string &s2) {
unordered_set<char> t1;
unordered_set<char> t2;
for (int i=0;i<s1.length();i++) t1.insert(s1[i]);
for (int i=0;i<s2.length();i++) t2.insert(s2[i]);
string res="";
for (int i=0;i<s1.length();i++)
if (t2.find(s1[i])==t2.end()) res=res+s1[i];
for (int i=0;i<s2.length();i++)
if (t1.find(s2[i])==t1.end()) res=res+s2[i];
return res;
}
};class Solution {
public:
int maxSubArray(vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.size()==1) return nums[0];
int subsum=0;
int minsubsum=0;
int res=INT_MIN;
for (int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
subsum=subsum+nums[i];
res=max(res,subsum-minsubsum);
minsubsum=min(minsubsum,subsum);
}
return res;
}
}; class Solution {
public:
ListNode * reverse(ListNode * head) {
// write your code here
if (head == NULL || head->next == NULL) return head;
ListNode* prev=head;
ListNode* cur=head->next;
while (cur!=NULL) {
ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
cur->next=prev;
prev=cur;
cur=tmp;
}
head->next=NULL;
return prev;
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int> &numbers, int target) {
vector<int> copy = numbers;
// write your code here
sort(numbers.begin(), numbers.end());
int i = 0;
int j = numbers.size()-1;
while (numbers[i]+numbers[j]!=target)
{
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] > target) j--;
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] < target) i++;
}
vector<int> res;
for (int k = 0; k < numbers.size();k++)
if (copy[k] == numbers[i] || copy[k] == numbers[j])
res.push_back(k);
return res;
}
};100. 删除排序数组中的重复数字
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85273856
class Solution {
public:
int numIslands(vector<vector<bool>> &grid) {
if (grid.size()==0 || grid[0].size()==0) return 0;
int count=0;
for (int i=0;i<grid.size();i++)
for (int j=0;j<grid[i].size();j++) {
if (grid[i][j]) {
count++;
BFShelper(grid,i,j);
}
}
return count;
}
void BFShelper(vector<vector<bool>> &grid,int i,int j) {
queue<pair<int,int>> h;
h.push(make_pair(i,j));
grid[i][j]=0;
while (!h.empty()){
int x=h.front().first;
int y=h.front().second;
h.pop();
if (in_bound(grid,x-1,y)&&grid[x-1][y]) { h.push(make_pair(x-1,y)); grid[x-1][y]=false;}
if (in_bound(grid,x+1,y)&&grid[x+1][y]) { h.push(make_pair(x+1,y)); grid[x+1][y]=false;}
if (in_bound(grid,x,y-1)&&grid[x][y-1]) { h.push(make_pair(x,y-1)); grid[x][y-1]=false;}
if (in_bound(grid,x,y+1)&&grid[x][y+1]) { h.push(make_pair(x,y+1)); grid[x][y+1]=false;}
}
}
bool in_bound(vector<vector<bool>> &grid,int i,int j) {
int m=grid.size()-1;
int n=grid[0].size()-1;
if (i>=0 && i<=m && j>=0 && j<=n) return true;
return false;
}372. 在O(1)时间复杂度删除链表节点
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/72897816
class Solution {
public:
int titleToNumber(string &s) {
int sum=0;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
sum=sum*26+s[i]-'A'+1;
return sum;
}
};class Solution {
public:
string convertToTitle(int n) {
vector<char> table={'A','B','C','D','E','F','G','H','I','J','K','L','M','N','O','P','Q','R','S','T','U','V','W','X','Y','Z'};
string res="";
do {
res=table[(n-1)%26]+res;
n=(n-1)/26;
} while(n>0);
return res;
}
}class Solution {
public:
string compress(string &originalString) {
string str = "";
int i = 0, n = originalString.size();
while(i < n){
int j = i;
while(j < n && originalString[j] == originalString[i]){
j++;
}
str.push_back(originalString[i]);
str += to_string(j - i);
i = j;
}
return (str.size() >= n)?originalString:str;
//比较压缩后的字符串是不是更短
}
};64. 合并排序数组
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/83382343
class Solution {
public:
int firstUniqChar(string &s) {
vector<int> rec(256,0);
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
rec[s[i]]++;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
if (rec[s[i]]==1) return s[i];
return -1;
}
};class Solution {
public:
ListNode * mergeTwoLists(ListNode * l1, ListNode * l2) {
// write your code here
if (l1==NULL) return l2;
if (l2==NULL) return l1;
ListNode* dummy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* cur=dummy;
while (l1!=NULL &&l2!=NULL) {
if (l1->val<=l2->val) {
cur->next=l1;
l1=l1->next;
}
else {
cur->next=l2;
l2=l2->next;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
if (l1==NULL && l2!=NULL) cur->next=l2;
if (l2==NULL && l1!=NULL) cur->next=l1;
return dummy->next;
}
};900. 二叉搜索树中最接近的值
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85229404
1410. 矩阵注水
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85270348
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * addLists(ListNode * l1, ListNode * l2) {
ListNode * dummy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode * head=dummy;
int flag=0;
while(true)
{
if (l1==NULL && l2==NULL &&flag==0) break;
int sum=0;
if (l1!=NULL)
{
sum=sum+l1->val;
l1=l1->next;
}
if (l2!=NULL)
{
sum=sum+l2->val;
l2=l2->next;
}
sum+=flag;
flag=sum/10;
ListNode *tmp=new ListNode(sum%10);
head->next=tmp;
head=head->next;
}
return dummy->next;
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getAnswer(vector<int> &A, vector<int> &B) {
unordered_set<int> s;
int m=A.size();
int n=B.size();
for (int i=0;i<m;i++) s.insert(A[i]);
int cnt=0;
for (int j=0;j<n;j++) {
if (s.find(B[j])!=s.end()) cnt++;
}
vector<int> res;
res.push_back(m+n-cnt);
res.push_back(cnt);
res.push_back(m-cnt);
return res;
}
};53. 翻转字符串中的单词
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/83029702
1332. 判断一个整数中有多少个1
手动把int转化为二进制:
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(unsigned int n) {
int res=0;
while (n>0) {
if (n%2==1) res++;
n=n/2;
}
return res;
}
};通过右移和位运算计算:
class Solution {
public:
int hammingWeight(unsigned int n) {
int res=0;
while (n>0) {
res=res+(n&1);
n=n>>1;
}
return res;
}
};596. 最小子树
给一棵二叉树, 找到和为最小的子树, 返回其根节点。
方法一,使用全局变量:
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * res;
int sum;
TreeNode * findSubtree(TreeNode * root) {
if (root==NULL) return NULL;
sum=INT_MAX;
int sum=sumofSubtree(root);
return res;
}
int sumofSubtree(TreeNode * root){
if (root==NULL) return 0;
int left=sumofSubtree(root->left);
int right=sumofSubtree(root->right);
if (left+right+root->val<sum)
{sum=left+right+root->val;
res=root;}
return left+right+root->val;
}
};方法二,构造新的答案类型:
class ResultType {
public:
int minSum;
int sum;
TreeNode * node;
ResultType():minSum(INT_MAX),sum(0),node(NULL) {}
ResultType(int _minSum,int _sum, TreeNode * _node):minSum(_minSum),sum(_sum),node(_node) {}
};
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * findSubtree(TreeNode * root) {
if (root==NULL) return NULL;
return helper(root).node;
}
ResultType helper(TreeNode * root){
if (root==NULL) return ResultType();
ResultType left=helper(root->left);
ResultType right=helper(root->right);
ResultType res=ResultType(left.sum+right.sum+root->val,left.sum+right.sum+root->val,root);
if (left.minSum<res.minSum) {
res.minSum=left.minSum;
res.node=left.node;
}
if (right.minSum<res.minSum) {
res.minSum=right.minSum;
res.node=right.node;
}
return res;
}
};
1570. 二进制流
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> getOutput(string &s) {
vector<int> res;
long int sum=0;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
sum=sum*2+(s[i]-'0');
sum=sum%3;
if (sum==0) res.push_back(i+1);
}
return res;
}
};
class Solution {
public:
bool isValidParentheses(string &s) {
stack<char> res;
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++)
{
if (s[i]=='('||s[i]=='['||s[i]=='{') res.push(s[i]);
else
{
if (res.empty()) return false;
char tmp=res.top();
res.pop();
if (s[i]==')'&&tmp!='(') return false;
if (s[i]==']'&&tmp!='[') return false;
if (s[i]=='}'&&tmp!='{') return false;
}
}
if (!res.empty()) return false;
return true;
}
};67. 二叉树的中序遍历
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/84107660
842. 折纸
考虑找找规律,第一次是0,第二次在0两边分别添加0、1,第三次在三个数之间交替添加0、1,以此类推。写了一个模拟添加的程序,但是在大数的时候超时了。
class Solution {
public:
string getString(int n) {
string res="0";
bool flag=0;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) {
string tmp="";
for (int j=0;j<2*res.size()+1;j++) {
if (j%2==0) {//如果是偶数,是新添的数
if (!flag) tmp=tmp+'0';
else tmp=tmp+'1';
flag=!flag;
}else {//如果是奇数,是原来的数
tmp=tmp+res[(j-1)/2];
}
}
res=tmp;
}
return res;
}
};又考虑这个结构是一个左子树为0右子树为1的二叉树,可以手动构造一个二叉树再用中序遍历即可。但是也超时。
class Solution {
private:
string res;
class TreeNode {//由于测试系统内已有TreeNode类,写在外面会报错,所以写成私有类
public:
char val;
TreeNode* left;
TreeNode* right;
TreeNode (char _val, TreeNode* _left, TreeNode* _right):
val(_val), left(_left), right(_right) {}
};
public:
string getString(int n) {
TreeNode* root=new TreeNode('0',NULL,NULL);
buildTree(root,1,n);//构造
midOrderTraverse(root);//中序遍历
return res;
}
void buildTree(TreeNode* root,int now,int n) {
if (now==n) return;
root->left=new TreeNode('0',NULL,NULL);
root->right=new TreeNode('1',NULL,NULL);
buildTree(root->left,now+1,n);
buildTree(root->right,now+1,n);
}
void midOrderTraverse(TreeNode* root) {
if (root==NULL) return;
midOrderTraverse(root->left);
res=res+root->val;
midOrderTraverse(root->right);
}
};或者进一步简化,虚拟一颗树。依然超时。
class Solution {
private:
string res;
public:
string getString(int n) {
midOrderTraverse(1,n,0);
res=res+'0';
midOrderTraverse(1,n,1);
return res;
}
void midOrderTraverse(int now, int n,int direct) {
if (now==n) return;
midOrderTraverse(now+1,n,0);
if (direct==0) res=res+'0';
else res=res+'1';
midOrderTraverse(now+1,n,1);
}
};标准题解给出的规律是:设第 i - 1 次折纸的折痕为 s, 则第 i 次折纸的折痕为 s + "0" + s.reverse().flip()
其中 reverse 代表字符串前后反转, flip 代表字符串内01互换。
class Solution {
public:
string getString(int n) {
// Write your code here
string ans = "0";
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
int len=(1<<(i-1))-1;//上一次折叠的长度是len
ans.push_back('0');
for (int j=len-1; j>=0; j--) {
if (ans[j]=='0') ans.push_back('1');
else ans.push_back('0');
}
}
return ans;
}
};1568. 毒药测试
试验方法是:对N瓶水进行唯一的二进制编码,第i位代表第i只小白鼠有没有喝这瓶水。最后按照小白鼠的存活形成一个序列,就是水的序号。那么小白鼠的数量m必须足够能构建N个不同的二进制编码,即长度为m的二进制序列必须能产生N个不同的序列,即2^m>=N。
class Solution {
public:
int getAns(int n) {
int m=0;
int amount=1;
//0只小白鼠能鉴定1瓶水
while (amount<n) {
m++;
amount=amount*2;
//每增加一只小白鼠,能验证的水的数量*2
}
return m;
}
};728. 3个不同的因子
三个不同的因子只可能是1,它本身,它开平方(开方后不能有其他因子)。所以要找的数是一个质数平方数。
class Solution {
public:
bool isThreeDisctFactors(long long n) {
if (n<=3) return false;//特殊情况
long long a=sqrt(n);//sqrt返回一个float,注意转成long long
if (a*a==n)
if (isPrime(a)) return true;
else return false;
else return false;
}
bool isPrime(long long n) {
if (n<2) return false;
long long a=sqrt(n);
for (long long i=2;i<=a;i++) {
if (n%i==0) return false;
}
return true;
}
};421. 简化路径
用栈。当前路径不动,返回上一层则回弹,否则push当前进入的位置。
class Solution {
public:
string simplifyPath(string &path) {
stack<string> s;
int i=0;
while (i<path.length()) {
if (path[i]=='/') {
while (i<path.length() && path[i]=='/') i++;
}else {
string tmp="";
while (i<path.length() && path[i]!='/') {
tmp=tmp+path[i];
i++;
}
if (tmp==".") continue;
else if (tmp=="..") {
if (!s.empty()) s.pop();
//已经返回根目录,则返回上一层目录指令可以被忽略
}
else s.push(tmp);
}
}
string res="";
while (!s.empty()) {
res=s.top()+res;
s.pop();
res='/'+res;
}
if (res=="") return "/" ;//处理全都为空的特殊情况
return res;
}
};有点类似合并数组,但不同的是这里记录的归并后数组范围应该是xend最小的那个。
class Solution {
public:
static bool cmp(vector<int> a, vector<int> b) {
if (a[0]!=b[0]) return a[0]<b[0];
else return a[1]<b[1];
}
int findMinArrowShots(vector<vector<int>> &points) {
if (points.size()<=1) return points.size();
sort(points.begin(),points.end(),cmp);
int xend=points[0][1];
int res=1;
for (int i=1;i<points.size();i++) {
if (points[i][0]<=xend) {
xend=min(points[i][1],xend);
//需要记录同一组爆破中xend最靠前的气球
}else {
res++;
xend=points[i][1];
}
}
return res;
}
};1403. 最大乘积路径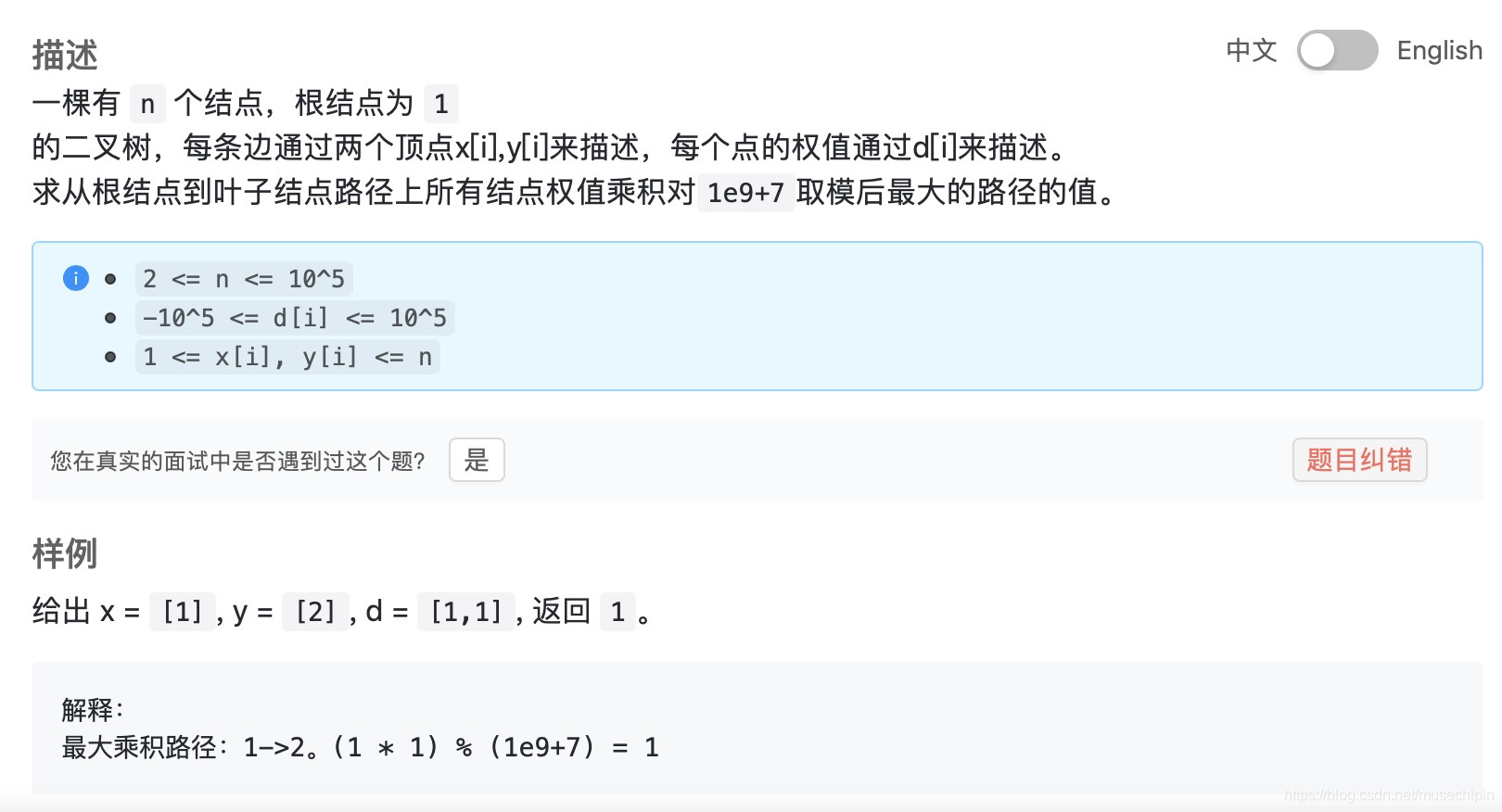
这个题把树的结构按照图的路径给出,按照图的遍历方法走一遍即可。注意是单向图。另外由于余数一定是正的,而%回出现负数结果,最后结果比较的时候应该+mod%mod保证结果为正。
class Solution {
public:
long long res;
int getProduct(vector<int> &x, vector<int> &y, vector<int> &d) {
long long mod=1e9+7;
unordered_map<int,unordered_set<int>> route;
for (int i=0;i<x.size();i++) {
//注意这里只保存x—>y,不保存y->x。因为树是单向的。
if (route.find(x[i])!=route.end()) route[x[i]].insert(y[i]);
else {
unordered_set<int> tmp;
tmp.insert(y[i]);
route[x[i]]=tmp;
}
}
res=INT_MIN;
dfs(route,d,1,d[0],mod);
return res;
}
void dfs(unordered_map<int,unordered_set<int>> &route,vector<int> &d,
int root,long long mul,long long mod) {
if (route.find(root)==route.end() || route[root].size()==0) {
res=max(res,(mul+mod)%mod); //这里把负数变为一个正数。
return;
}
for (auto n:route[root]) {
int tmp=mul;
mul=(mul*d[n-1])%mod; //为了防止过大,先mod一下,但是结果不一定对
//如-1%mod=-1,但是余数应该是一个正数。但这里先不处理,
//因为应该用最后的乘积进行处理
dfs(route,d,n,mul,mod);
mul=tmp;
}
}
};1409. 矩阵找数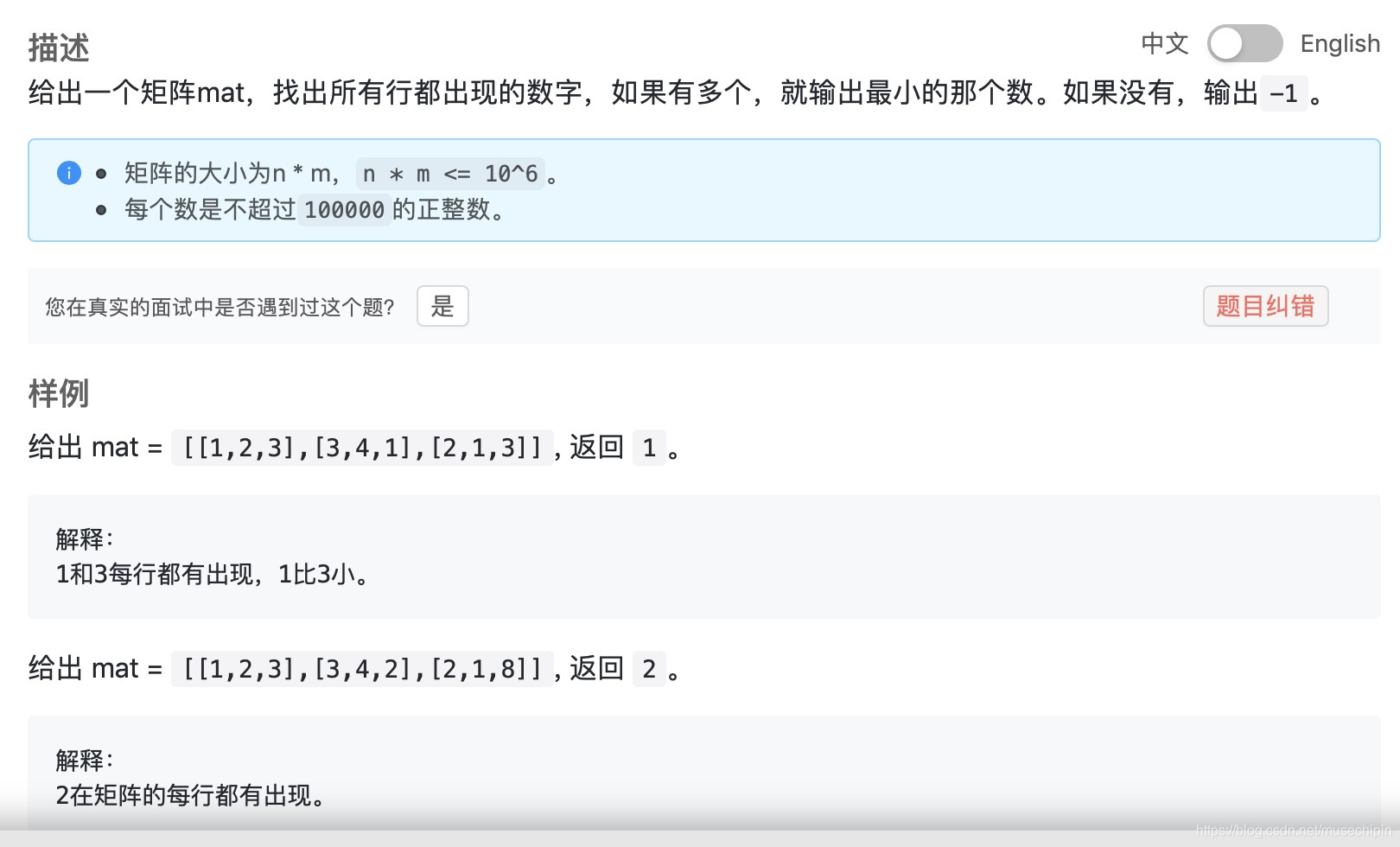
用map做,但是要注意每行会有重复数字的情况,这种情况下不能多加也不能少加。
class Solution {
public:
int findingNumber(vector<vector<int>> &mat) {
unordered_map<int,int> num;
for (int i=0;i<mat[0].size();i++) {
num[mat[0][i]]=1;
}
for (int i=1;i<mat.size();i++) {
for (int j=0;j<mat[i].size();j++)
if (num.find(mat[i][j])!=num.end()) {
if (num[mat[i][j]]==i) //严格保证每行的数字只加一次,且这个数字一定是之前的每行都有
num[mat[i][j]] ++;
}
}
int res=INT_MAX;
for (auto n=num.begin();n!=num.end();n++) {
if (n->second==mat.size()) res=min(res,n->first);
}
return res==INT_MAX?-1:res;
}
};1022. 合法的井字棋状态
限定了3X3的大小完全没有难度。如果棋盘大小不定可能需要搜索。
class Solution {
public:
bool validTicTacToe(vector<string> &board) {
if (board.size()!=3) return false;//棋盘大小非法
int x=0;
int o=0;
for (int i=0;i<3;i++) {
if (board[i].length()!=3) return false;//棋盘大小非法
if (board[i]=="XXX" || board[i]=="OOO") return false;
for (int j=0;j<3;j++) {
if (board[i][j]=='X') x++;
if (board[i][j]=='O') o++;
}
}
if (x<o) return false;//x的步数不能比o少
if (x-o>1) return false;//x和o的步数最多差1
for (int i=0;i<3;i++) {
if (board[0][i]!=' ' && board[0][i]==board[1][i] && board[2][i]==board[1][i])
return false; //纵向非法
}
//斜向非法
if (board[0][0]==board[1][1] && board[1][1]==board[2][2] &&board[0][0]!=' ')
return false;
if (board[0][2]==board[1][1] && board[1][1]==board[2][0] &&board[0][0]!=' ')
return false;
return true;
}
};1567. 可交换的最大子数组
这题第一反应是暴力循环每个交换然后查找最大子区间,时间负责度O(n^3)。但是重复计算了很多遍子区间的值。所以考虑以遍历交换点为核心,向左向右分别查找一个以其左右为起点的子区间,然后再尝试交换这个交换点,找到最大值。
class Solution {
public:
int getAnswer(vector<int> &a) {
vector<int> right(a.size(),0);
vector<int> left(a.size(),0);
int res=INT_MIN;
//算一个从左往右的子数组
int sub=0;
int rminsub=0;
for (int i=0;i<a.size();i++) {
sub+=a[i];
right[i]=sub;
}
//算一个从右往左的子数组
sub=0;
for (int i=a.size()-1;i>=0;i--) {
sub+=a[i];
left[i]=sub;
}
//遍历所有点作为交换点
for (int i=0;i<a.size();i++) {
//toRight找到最大子区间
int rindex=i;
int rmax=0;
for (int j=i+1;j<a.size();j++) {
if (right[j]-right[i]>rmax) {
rmax=right[j]-right[i];
rindex=j;
}
}
//toLeft找到最大子区间
int lindex=i;
int lmax=0;
for (int j=i-1;j>=0;j--) {
if (left[j]-left[i]>lmax) {
lmax=left[j]-left[i];
lindex=j;
}
}
int tmpres=lmax+rmax+a[i];
int tmpres2=tmpres;
//查找可交换的点(区间边界或者区间之外的点)
for (int j=0;j<a.size();j++) {
if (j>lindex && j<rindex) continue;
if (j==lindex || j==rindex)
tmpres2=max(tmpres2,tmpres-a[i]);//换边界点的特殊情况
else tmpres2=max(tmpres2,tmpres-a[i]+a[j]);//换其他点
}
res=max(res,tmpres2);
}
return res;
}
};123. 单词搜索
注意出口写法,找到一个就退出,否则会超时。
class Solution {
public:
vector<vector<int>> pace={{1,0,-1,0},{0,1,0,-1}};
bool res;
bool exist(vector<vector<char>> &board, string &word) {
if (board.size()==0) return false;
if (word.size()<=0) return true;
res=false;
for (int i=0;i<board.size();i++) {
for (int j=0;j<board[i].size(); j++) {
if (board[i][j]==word[0]) {
board[i][j]='%';
tryChar(board,i,j,word,1);
if (res) return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
void tryChar(vector<vector<char>> &board,int i,int j,string &word,int index) {
if (index==word.size()) res=true;
else if (!res) {
for (int k=0;k<4;k++)
if (isvalid(i+pace[0][k],j+pace[1][k],board.size(),board[0].size())
&& board[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]==word[index]) {
char tmp=word[index];
board[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]='%';
tryChar(board,i+pace[0][k],j+pace[1][k],word,index+1);
board[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]=tmp;
}
}
}
bool isvalid(int i,int j,int m,int n) {
return (i>=0 && i<m && j>=0 && j<n);
}
};class Solution {
public:
unordered_set <string> ans;
vector<vector<int>> pace={{1,0,-1,0},{0,1,0,-1}};
vector<string> wordSearchII(vector<vector<char>> &board, vector<string> &words) {
if (words.size()<=0 || board.size()==0) return vector<string>();
for (int i=0;i<board.size();i++)
for (int j=0;j<board[i].size();j++) {
for (int k=0;k<words.size();k++) {
if (board[i][j]==words[k][0] && ans.find(words[k])==ans.end() ){
vector<vector<bool>> visited(board.size(),vector<bool>(board[0].size(),true));
visited[i][j]=false;
tryChar(board,i,j,words[k],1,visited);
}
}
}
vector<string>res;
res.assign(ans.begin(),ans.end());
return res;
}
void tryChar(vector<vector<char>> &board,int i,int j,string &word,int index,vector<vector<bool>> &visited) {
if (index==word.size()) ans.insert(word);
else if (ans.find(word)==ans.end()) {
for (int k=0;k<4;k++)
if (isvalid(i+pace[0][k],j+pace[1][k],board.size(),board[0].size())
&& board[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]==word[index]
&& visited[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]) {
visited[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]=false;
tryChar(board,i+pace[0][k],j+pace[1][k],word,index+1,visited);
visited[i+pace[0][k]][j+pace[1][k]]=true;
}
}
}
bool isvalid(int i,int j,int m,int n) {
return (i>=0 && i<m && j>=0 && j<n);
}
};200. 最长回文子串
考虑单核和双核的情况,时间复杂度为O(n^2)。还有一个时间复杂度为O(n)的方法。
class Solution {
public:
string res;
string longestPalindrome(string &s) {
if (s.length()<=1) return s;
res=s[0];
for (int i=0;i<s.length();i++) {
findLongest(s,i,i);
findLongest(s,i,i+1);
}
return res;
}
void findLongest(string &s,int i,int j) {
while (i>=0 && j<s.length() && s[i]==s[j] ) {
i--;
j++;
}
i++; j--;
if (j-i+1 > res.length()) res=s.substr(i,j-i+1);
}
};162. 矩阵归零
我想到的方法是用两个set记录为0的行和列,空间复杂度接近O(m+n).
class Solution {
public:
void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.size()<=0) return ;
unordered_set<int> row;
unordered_set<int> col;
for (int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)
for (int j=0;j<matrix[0].size();j++) {
if (matrix[i][j]==0) {
row.insert(i);
col.insert(j);
}
}
for (int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)
for (int j=0;j<matrix[0].size();j++) {
if (row.find(i)!=row.end() || col.find(j)!=col.end())
matrix[i][j]=0;
}
}
};还有常数级的空间复杂度方法:使用第一行第一列分别记录为0的情况,再使用两个常数记录这一行一列是否为0.
class Solution {
public:
void setZeroes(vector<vector<int>>& matrix) {
if (matrix.size()<=0) return ;
bool row=true;
bool col=true;
for (int i=0;i<matrix[0].size();i++)
if (matrix[0][i]==0) row=false;
for (int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++)
if (matrix[i][0]==0) col=false;
for (int i=1;i<matrix.size();i++)
for (int j=1;j<matrix[0].size();j++) {
if (matrix[i][j]==0) {
matrix[0][j]=0;
matrix[i][0]=0;
}
}
for (int i=1;i<matrix.size();i++)
for (int j=1;j<matrix[0].size();j++)
if (matrix[0][j]==0 || matrix[i][0]==0)
matrix[i][j]=0;
if (!row)
for (int i=0;i<matrix[0].size();i++) matrix[0][i]=0;
if (!col)
for (int i=0;i<matrix.size();i++) matrix[i][0]=0;
}
};843. 数字翻转
class Solution {
public:
/**
* @param nums: the array
* @return: the minimum times to flip digit
*/
int flipDigit(vector<int> &nums) {
if (nums.size()<=1) return 0;
int ones=0;
for (int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
if (nums[i]==1) ones++;
//最多只要把所有1反转成0即可
int res=ones;
int tmp=0;//记录已经数了多少1
for (int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) {
if (nums[i]==1) tmp++;
res=min(res, i+1-tmp +ones-tmp); //前半段是有几个0要变成1,后面是有几个1要变成0
}
return res;
}
};975. 只有2个按键的键盘
class Solution {
public:
int minSteps(int n) {
// Write your code here
vector<int> f(n+1,INT_MAX);
f[0]=0;
f[1]=1;
for (int i=2;i<=n;i++) {
f[i]=i;
for (int j=1;j<i;j++) {
if (i%j==0)
f[i]=min(f[i],f[j]+i/j);
}
}
return f[n];
}
};867. 四键键盘
https://blog.youkuaiyun.com/musechipin/article/details/85332708
class Solution {
public:
int maxA(int N) {
vector<int> res(N+1,0);
for (int i=1;i<=N;i++)
{
res[i]=i;
for (int j=i-3;j>=1;j--)
res[i]=max(res[i],res[j]*(i-j-1));
}
return res[N];
}
};class Solution {
public:
vector<int> productExceptSelf(vector<int> &nums) {
vector<int> res(nums.size(),1);
//把自己之前的乘积求出来
for (int i=1;i<nums.size();i++)
res[i]=res[i]*res[i-1]*nums[i-1];
int multi=1;
//把自己之后的算出来,乘起来
for (int i=nums.size()-2;i>=0;i--){
multi=multi*nums[i+1];
res[i]=res[i]*multi;
}
return res;
}
};1106. 最大二叉树
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * constructMaximumBinaryTree(vector<int> &nums) {
TreeNode * root=findmax(nums,0,nums.size()-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode * findmax(vector<int> &nums,int h, int t) {
if (h>t) return NULL;
int mid=h;
int maxval=nums[h];
for (int i=h;i<=t;i++)
if (nums[i]>maxval) {
maxval=nums[i];
mid=i;
}
TreeNode * root=new TreeNode(maxval);
root->left=findmax(nums,h,mid-1);
root->right=findmax(nums,mid+1,t);
return root;
}
};还有个单调栈的做法
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * maxTree(vector<int> &A) {
stack<TreeNode*> s;//维护一个根的直单调递减的栈,栈内的树只有左子树
for (int i=0;i<A.size();i++) {
TreeNode* tmp=new TreeNode(A[i]);
//如果没有元素,往里加
if (s.empty()) {s.push(tmp);continue;}
//如果当前数比栈顶树根大,说明还没找到最大的值,栈顶的树还能再往上添根
//把这个树取出来添上当前的树做根
//如[3,2,1,5] 2进入的时候已经和3连好了,所以5先连2再连3不影响
while (!s.empty() && A[i]>s.top()->val) {
tmp->left=s.top();
s.pop();
}
//栈内如果还有树,此树的根值一定大于当前数,当前数是这个根的右孩子,连上
if (!s.empty()) {
s.top()->right=tmp;
}
s.push(tmp);
}
//由于是根单调递减的栈,栈底的那个是根
while (s.size()>1) s.pop();
return s.top();
}
};class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * buildTree(vector<int> &preorder, vector<int> &inorder) {
if (preorder.size()==0 && inorder.size()==0)
return NULL;
TreeNode * root=help(preorder,0,preorder.size()-1,inorder,0,inorder.size()-1);
return root;
}
TreeNode * help( vector<int> &preorder,int prestart, int preend,
vector<int> &inorder, int instart, int inend) {
if ((instart>inend)||(prestart>preend)) return NULL;
TreeNode* root= new TreeNode(preorder[prestart]);
int i;
for (i=instart;i<=inend;i++)
if (inorder[i]==root->val)
break;
int l_length=i-instart;
int r_length=inend-i;
root->left=help(preorder,prestart+1,prestart+l_length,inorder,instart,i-1);
root->right=help(preorder,preend-r_length+1,preend,inorder,i+1,inend);
return root;
}
};103. 带环链表 II
快慢指针问题。画个图,非环的长度为l,环起始到相遇的长度为a,相遇到环起始的长度为b,有l+a+b+a=2(a+l),得到b=l,即两个指针分别从相遇的位置和链头出发,相遇的位置就是环首。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * detectCycle(ListNode * head) {
if (head==NULL) return NULL;
ListNode * fast=head;
ListNode * slow=head;
while (fast->next!=NULL && fast->next->next!=NULL) {
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if (slow==fast) {
ListNode * pace=head;
while (pace!=fast) {
pace=pace->next;
fast=fast->next;
}
return fast;
}
}
return NULL;
}
};1311. 二叉搜索树的最近公共祖先
是二叉搜索树就比较简单,只要判断要找的两个数和当前根的大小关系即可。
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode* lowestCommonAncestor(TreeNode* root, TreeNode* p, TreeNode* q) {
if ((p->val-root->val)*(q->val-root->val)<=0)
return root;
if (p->val > root->val) return lowestCommonAncestor(root->right,p,q);
else return lowestCommonAncestor(root->left,p,q);
}
};221. 链表求和 II
和链表求和不一样的是这个题的数字是和自然数字一个顺序,要从后往前加。我一开始的想法就是把它都变成int型加起来再改成链表,但是好像数据范围不够。比较好的方法是用栈。注意进位问题。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * addLists2(ListNode * l1, ListNode * l2) {
if (l1==NULL) return l2;
if (l2==NULL) return l1;
stack<int> s1;
stack<int> s2;
while (l1!=NULL) {
s1.push(l1->val);
l1=l1->next;
}
while (l2!=NULL) {
s2.push(l2->val);
l2=l2->next;
}
int count=0;
int num=0;
ListNode* nextnode=NULL;
while (!s1.empty() || !s2.empty() || count!=0) {
int a=0;
int b=0;
if (!s1.empty()) {
a=s1.top();
s1.pop();
}
if (!s2.empty()) {
b=s2.top();
s2.pop();
}
num=(a+b+count)%10;
count=(a+b+count)/10;
ListNode* cur=new ListNode(num);
cur->next=nextnode;
nextnode=cur;
}
return nextnode;
}
};149. 买卖股票的最佳时机
其他股票买卖问题 这个是最简单的问题,找到最低点和最低点之后的最高点即可。
class Solution {
public:
int maxProfit(vector<int> &prices) {
int res=0;
if (prices.size()<=1) return 0;
int lowest=prices[0];
for (int i=1;i<prices.size();i++) {
if (prices[i]-lowest>res) res=prices[i]-lowest;
if (prices[i]<lowest) lowest=prices[i];
}
return res;
}
};448. 二叉查找树的中序后继
写个一个很丑陋的代码,倒中序遍历二叉查找树(右中左),找到p时跳出,返回prev值。丑陋的地方在于为了找到结果就停止,每一步都要判断到底找没找到结果(!flag)。一些比较漂亮的做法:https://www.cnblogs.com/grandyang/p/5306162.html
class Solution {
public:
TreeNode * prev;
int flag;
TreeNode * inorderSuccessor(TreeNode * root, TreeNode * p) {
if (root==NULL) return NULL;
prev=NULL;
flag=0;
inorder(root,p);
return prev;
}
void inorder(TreeNode * root, TreeNode *p) {
if (flag==1) return;
if (root->right!=NULL && !flag) inorder(root->right,p);
if (root==p) {flag=1; return;}
if (!flag) prev=root;
if (root->left!=NULL && !flag) inorder(root->left,p);
}
};1197. 寻找树中最左下结点的值
简单的层次遍历,每次记下队首元素即可。
class Solution {
public:
int findBottomLeftValue(TreeNode * root) {
queue<TreeNode *> q;
q.push(root);
TreeNode* res;
while (!q.empty()) {
int l=q.size();
res=q.front();
for (int i=0;i<l;i++) {
TreeNode* cur=q.front();
q.pop();
if (cur->left!=NULL) q.push(cur->left);
if (cur->right!=NULL) q.push(cur->right);
}
}
return res->val;
}
};1069. 删除注释
这个问题的解决的重点在于要分清楚不是每一行是一个循环,而是每一段注释结束后进入下一个循环段落。用i和j控制字符的计入与否。注意各种特殊情况。
class Solution {
public:
vector<string> removeComments(vector<string> &source) {
vector<string> res;
if (source.size()==0) return res;
int para=0;
int l=source.size();
int i=0;
int j=0;
string s="";
while (i<l){
if (para==0) {
//判断空行的问题
if (source[i].size()==0) {i+=1; continue;}
while (j<source[i].length()-1 && !(source[i][j]=='/' &&(source[i][j+1]=='/' || source[i][j+1]=='*'))) {
s=s+source[i][j];
j+=1;
}
//如果到了行末或此行全部注释,则后面全部忽略,开始下一行
if ((j==source[i].length()-1) || (j+1<source[i].length() && source[i][j]=='/' && source[i][j+1]=='/')) {
//把最后一个字符加上
if (j==source[i].length()-1) s=s+source[i][j];
if (s!="") res.push_back(s);
i+=1;
j=0;
s="";
}
else if (j+1<source[i].length() && source[i][j]=='/' && source[i][j+1]=='*') {
//如果此行开始块注释,则记下来,找块结尾标志
//s不更新!因为要一直计到注释块结束的那一行内容
para=1;
j+=2;
if (j>=source[i].length()) {
i+=1;
j=0;
}
}
}
//para=1说明还在注释中,忽略所有内容找块结束标志
else {
//判断空行的问题
if (source[i].size()==0) {i+=1; continue;}
while (j<source[i].length()-1 && !(source[i][j]=='*' && source[i][j+1]=='/')) {
j+=1;
}
if (j==source[i].length()-1) {
i=i+1;
j=0;
}
//找到块结尾,一切重新开始
else if (j<source[i].length()-1 && source[i][j]=='*' && source[i][j+1]=='/') {
para=0;
j=j+2;
//如果段落正好结束完就重新计算,
//否则还在原行继续找 有可能有....*/....//....的情况
if (j>=source[i].length()) {
if (s!="") res.push_back(s);
i+=1;
j=0;
s="";
}
}
}
}
return res;
}
};这道问题其实可以转换为有一个很大的容器,我们有两个杯子,容量分别为x和y,问我们通过用两个杯子往里倒水,和往出舀水,问能不能使容器中的水刚好为z升。那么我们可以用一个公式来表达:
z = m * x + n * y (关于为什么能成立https://pastebin.com/yzNXrJAi)
其中m,n为舀水和倒水的次数,正数表示往里舀水,负数表示往外倒水,那么题目中的例子可以写成: 4 = (-2) * 3 + 2 * 5,即3升的水罐往外倒了两次水,5升水罐往里舀了两次水。那么问题就变成了对于任意给定的x,y,z,存不存在m和n使得上面的等式成立。根据裴蜀定理,ax + by = d的解为 d = gcd(x, y),那么我们只要只要z % d == 0,上面的等式就有解,所以问题就迎刃而解了,我们只要看z是不是x和y的最大公约数的倍数就行了,别忘了还有个限制条件x + y >= z,因为x和y不可能称出比它们之和还多的水。
class Solution {
public:
bool canMeasureWater(int x, int y, int z) {
if (z>x+y || z<0 || x==0 && y==0 && z>0) return false;
if (x>y) swap(x,y);
while (y%x!=0) {
y=y%x;
swap(x,y);
}
return (z%x==0);
}
};292. 奇偶链表
使用两个dummy会比较清晰。
class Solution {
public:
ListNode * oddEvenList(ListNode * head) {
if (head==NULL || head->next==NULL) return head;
ListNode* odd_dummy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* even_dummy=new ListNode(0);
ListNode* odd=odd_dummy;
ListNode* even=even_dummy;
int flag=1;
while (head!=NULL) {
if (flag){
odd->next=head;
odd=odd->next;
}
else {
even->next=head;
even=even->next;
}
head=head->next;
flag=1-flag;
}
odd->next=even_dummy->next;
even->next=NULL;
return odd_dummy->next;
}
};1255. 移除K位
想要获得最小的数字,就要让开头的数字尽量小。所以按照一个原则:如果后一个数小于当前数,说明后一个数更适合做高位,将当前这位删掉,否则后一个数删掉。维护一个单调递增栈即可。记得最后把开头的0去掉。
class Solution {
public:
string removeKdigits(string &num, int k) {
if (num.length()<=k) return "0";
stack<char> s;
int i=0;
while (k>0) {
if (s.empty() || num[i]>=s.top())
{
s.push(num[i]);
i++;
}
else {
s.pop();
k--;
}
}
string res="";
while (!s.empty()) {
res=s.top()+res;
s.pop();
}
while (i<num.length()) {
res=res+num[i];
i++;
}
i=0;
while (res[i]=='0') i++;
return res.substr(i,res.length());
}
};1707. 骑士拨号器
一开始想用回溯做,后来发现因为是很小的棋盘,每个位置能跳到的位置很少,甚至枚举即可。同时回溯会超时。注意1.为了防止溢出,每次相加都要取模 2.要求不能原地跳,所以5的位置只能在第一次按出,后面都不可能了。
class Solution {
public:
int knightDialer(int N) {
if (N==0) return 0;
if (N==1) return 10;
vector<vector<long>> pace(10,vector<long>(N+1,0));
for (int i=0;i<=9;i++) pace[i][1]=1;
for (int i=2;i<=N;i++) {
pace[0][i]=(pace[4][i-1]+pace[6][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[1][i]=(pace[8][i-1]+pace[6][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[2][i]=(pace[7][i-1]+pace[9][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[3][i]=(pace[4][i-1]+pace[8][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[4][i]=(pace[3][i-1]+pace[9][i-1]+pace[0][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[5][i]=0;
pace[6][i]=(pace[1][i-1]+pace[7][i-1]+pace[0][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[7][i]=(pace[2][i-1]+pace[6][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[8][i]=(pace[1][i-1]+pace[3][i-1])%1000000007;
pace[9][i]=(pace[2][i-1]+pace[4][i-1])%1000000007;
}
long res=0;
for (int i=0;i<=9;i++) {
res=(res+pace[i][N])%1000000007;
}
return res;
}
};1301. 生命游戏
用两位数记录前后两个状态即可。
class Solution {
public:
void gameOfLife(vector<vector<int>> &board) {
if (board.size()==0) return;
vector<int> x={-1,-1,-1, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1};
vector<int> y={-1, 0, 1,-1, 1,-1, 0, 1};
int m=board.size();
int n=board[0].size();
for (int i=0; i<m;i++)
for (int j=0;j<n;j++) {
int live=0;
for (int k=0;k<8;k++)
if (isvalid(i+x[k],j+y[k],m,n)) {
if (board[i+x[k]][j+y[k]]%10==1) live++;
}
if (board[i][j]==1 && live<2) board[i][j]=0*10+1;
else if (board[i][j]==1 && (live==2 || live==3)) board[i][j]=1*10+1;
else if (board[i][j]==1 && live >3) board[i][j]=0*10+1;
else if (board[i][j]==0 && live==3) board[i][j]=1*10+0;
else board[i][j]=0*10+0;
}
for (int i=0; i<m; i++)
for (int j=0;j<n; j++)
board[i][j]=board[i][j]/10;
}
bool isvalid(int i, int j, int x, int y) {
return (i<x && i>=0 && j<y && j>=0);
}
};
1084. “马”在棋盘上的概率
和1707相同,只不过棋盘变成变量,所以要加两重循环遍历棋盘。跳K次,每次有8种选择,所以一共有8^K种走法,统计出有效的走法相除即可。但是注意会溢出,所以改成每次加之前*0.125。另外注意C++不支持^,要使用pow()。
class Solution {
public:
double knightProbability(int N, int K, int r, int c) {
if (K==0) return 1;
if (N==0) return 0;
vector<int> x={-2, -2, -1, -1, 1, 1, 2,2};
vector<int> y={-1, 1, -2, 2,-2, 2,-1,1};
vector<vector<vector<float>>> dp(N,vector<vector<float>>(N,vector<float>(K+1,0)));
dp[r][c][0]=1;
for (int s=1;s<=K;s++)
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
for (int j=0;j<N; j++) {
for (int p=0;p<8;p++)
if (isvalid(i+x[p],j+y[p],N)) dp[i][j][s]+=dp[i+x[p]][j+y[p]][s-1]*0.125;
}
float res=0;
for (int i=0;i<N;i++)
for (int j=0;j<N;j++)
res+=dp[i][j][K];
return res;
}
bool isvalid(int i,int j,int N) {
return(i>=0 && i<N && j>=0 &&j<N);
}
};362. 滑动窗口的最大值
这个题的最大问题在于不知道当前窗口的最大值什么时候滑出去,所以一开始我想的是标记每个窗口的最大值并把下一个值与此值比较的方法是错误的。正确方法是维护一个单调递减的双端队列(如果当前值大于队列里的值说明前面的值全部作废不可能是最大值,全部弹出。又因为要求空间复杂度为O(k),不可以用栈或者数组先把所有的可能的最大值存下来),这样队首的值永远都是最大的,记录的时候记录下标,当当前下标和队首下标差值大于K时说明队首的元素已经出滑动框了。
class Solution {
public:
vector<int> maxSlidingWindow(vector<int> &nums, int k) {
vector<int> res;
if (nums.size()<k || k<1) return res;
if (k==1) return nums;
deque<int> index;
for (int i=0;i<nums.size();i++) {
//最大的数可能已经超出滑窗范围了,处理
//放在最前面是因为保证空间复杂度O(k)
while (!index.empty() && i-index.front()>=k) index.pop_front();
//处理初始情况,如果没有数字先放进去
if (index.empty()) index.push_back(i);
else {
//从后往前比较,从离当前数最近的数字开始,比当前数字小的全都取掉
//即维护一个降序队列,保证前面的是最大的
//注意等于的也pop出去,保证最大的是更靠后的
while (!index.empty() && nums[index.back()]<=nums[i])
index.pop_back();
//当前的数放进去
index.push_back(i);
}
//前k-1个数不足k,没有结果
if (i>=k-1) res.push_back(nums[index.front()]);
}
return res;
}
};







 本文主要探讨了多个LeetCode中的算法问题,包括合并区间、对称树的判断、字符串查找、旋转数组、二叉树的层次遍历以及矩阵注水等。文章提供了详细的问题解析和解决方案,涉及二叉树遍历、链表操作、字符串处理和数组操作等多种算法思想。
本文主要探讨了多个LeetCode中的算法问题,包括合并区间、对称树的判断、字符串查找、旋转数组、二叉树的层次遍历以及矩阵注水等。文章提供了详细的问题解析和解决方案,涉及二叉树遍历、链表操作、字符串处理和数组操作等多种算法思想。
















 2270
2270

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








