解题报告 之 HDU5325 Crazy Bobo
Description
Bobo has a tree,whose vertices are conveniently labeled by 1,2,...,n.Each node has a weight 
 .
All the weights are distrinct.
.
All the weights are distrinct.
A set with m nodes
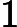


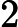






 is
a Bobo Set if:
is
a Bobo Set if:
- The subgraph of his tree induced by this set is connected.
- After we sort these nodes in set by their weights in ascending order,we get
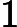


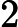






 ,(that
is,
,(that
is,







 for
i from 1 to m-1).For any node
for
i from 1 to m-1).For any node  in
the path from
in
the path from 
 to
to 


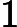 (excluding
(excluding 
 and
and 


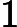 ),should
satisfy
),should
satisfy 




 .
.
Your task is to find the maximum size of Bobo Set in a given tree.

 .
All the weights are distrinct.
.
All the weights are distrinct. A set with m nodes

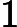


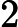






 is
a Bobo Set if:
is
a Bobo Set if: - The subgraph of his tree induced by this set is connected.
- After we sort these nodes in set by their weights in ascending order,we get

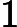


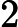






 ,(that
is,
,(that
is,







 for
i from 1 to m-1).For any node
for
i from 1 to m-1).For any node  in
the path from
in
the path from 
 to
to 


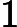 (excluding
(excluding 
 and
and 


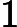 ),should
satisfy
),should
satisfy 




 .
. Your task is to find the maximum size of Bobo Set in a given tree.
Input
The input consists of several tests. For each tests:
The first line contains a integer n (



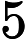




 ).
Then following a line contains n integers
).
Then following a line contains n integers 
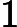


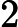






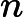 (
(






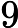 ,all
the
,all
the 
 is
distrinct).Each of the following n-1 lines contain 2 integers
is
distrinct).Each of the following n-1 lines contain 2 integers 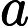
 and
and 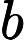
 ,denoting
an edge between vertices
,denoting
an edge between vertices 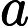
 and
and 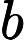
 (
(

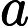


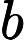


 ).
).
The sum of n is not bigger than 800000.
The first line contains a integer n (




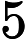




 ).
Then following a line contains n integers
).
Then following a line contains n integers 
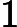


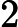






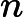 (
(






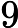 ,all
the
,all
the 
 is
distrinct).Each of the following n-1 lines contain 2 integers
is
distrinct).Each of the following n-1 lines contain 2 integers 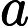
 and
and 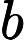
 ,denoting
an edge between vertices
,denoting
an edge between vertices 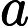
 and
and 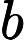
 (
(

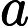


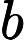


 ).
). The sum of n is not bigger than 800000.
Output
For each test output one line contains a integer,denoting the maximum size of Bobo Set.
Sample Input
7 3 30 350 100 200 300 400 1 2 2 3 3 4 4 5 5 6 6 7
Sample Output
5
分析:因为这个子图任意权重相邻的点都要满足这个条件,所以这个子图一定连通(否则一定存在权值相邻的点之间没有连通path)。然后注意到这个条件,这个子图任意权重相邻点之间的路要么是没有点,要么一定是呈现山谷状的,即两边最高,向中间递减。那么从图中的一个点开始,以它为最低点,向两边较高的扩展,然后再以同样的方式去搜索这两个较高点。那么任意两个权值相邻的点,往回找通路的时候一定都是呈现山谷状的。那么问题就转换成了,从某个点出发,去找到它能够扩展到的最大点数,深搜一次即可。
上代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<cstring>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstdio>
#pragma comment(linker, "/STACK:1024000000,1024000000")
using namespace std;
const int MAXN = 5e6+10;
struct Edge
{
int to, nxt;
};
Edge edge[MAXN];
int head[MAXN];
int w[MAXN];
int num[MAXN];
int cnt, ans;
void addedge( int from, int to )
{
edge[cnt].to = to;
edge[cnt].nxt = head[from];
head[from] = cnt++;
}
int dfs( int u )
{
if(num[u]) return num[u];
num[u] = 1;
for(int i = head[u]; i != -1; i = edge[i].nxt)
{
int v = edge[i].to;
num[u]+=dfs( v );
}
return num[u];
}
int main()
{
int n;
while(scanf( "%d", &n ) == 1)
{
cnt = 0;
memset( num, 0, sizeof num );
memset( head, -1, sizeof head );
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
scanf( "%d", &w[i] );
for(int i = 0; i < n - 1; i++)
{
int u, v;
scanf( "%d%d", &u, &v );
if(w[u] < w[v])
addedge( u, v );
else
addedge( v, u );
}
ans = 0;
for(int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
ans = max( ans, dfs( i ) );
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}嗯就是这样!











 本文介绍了解决HDU5325 Crazy Bobo问题的方法,该问题是寻找一棵树中满足特定条件的最大子集。通过分析问题特点,采用深度优先搜索算法实现了高效求解。
本文介绍了解决HDU5325 Crazy Bobo问题的方法,该问题是寻找一棵树中满足特定条件的最大子集。通过分析问题特点,采用深度优先搜索算法实现了高效求解。
















 666
666

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








