Linked List in Binary Tree (M)
Given a binary tree root and a linked list with head as the first node.
Return True if all the elements in the linked list starting from the head correspond to some downward path connected in the binary tree otherwise return False.
In this context downward path means a path that starts at some node and goes downwards.
Example 1:

Input: head = [4,2,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: true
Explanation: Nodes in blue form a subpath in the binary Tree.
Example 2:
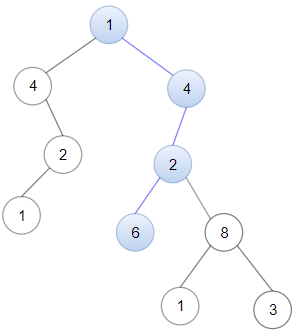
Input: head = [1,4,2,6], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: true
Example 3:
Input: head = [1,4,2,6,8], root = [1,4,4,null,2,2,null,1,null,6,8,null,null,null,null,1,3]
Output: false
Explanation: There is no path in the binary tree that contains all the elements of the linked list from head.
Constraints:
1 <= node.val <= 100for each node in the linked list and binary tree.- The given linked list will contain between
1and100nodes. - The given binary tree will contain between
1and2500nodes.
题意
判断一个链表是否是一个二叉树的一部分。
思路
dfs处理,遍历所有树结点,每次都将它当作链表的起点与链表进行比较
代码实现
class Solution {
public boolean isSubPath(ListNode head, TreeNode root) {
// head一定不为null
if (root == null) {
return false;
}
// 递归处理三种情况:
// 1. 当前结点是链表起点;2. 左子树根结点是链表起点;3. 右子树根结点是链表起点
return judge(head, root) || isSubPath(head, root.left) || isSubPath(head, root.right);
}
private boolean judge(ListNode head, TreeNode root) {
if (head == null) {
return true;
} else if (root == null || head.val != root.val) {
return false;
}
return judge(head.next, root.left) || judge(head.next, root.right);
}
}

























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








