案例准备
前端页面准备:GET.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#result{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 1px #90b;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>点击发送请求</button>
<div id="result"></div>
</body>
</html>
服务器页面准备:GET.js
// 1.引入express
const express = require('express');
// 2.创建应用对象
const app = express();
// 3.创建路由规则
// 如果请求行的路径是/server就会执行回调韩式里面的内容
app.get('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX')
})
// 4.监听端口启动服务
app.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('服务已经启动,8000端口监听中……')
})
启动GET.js
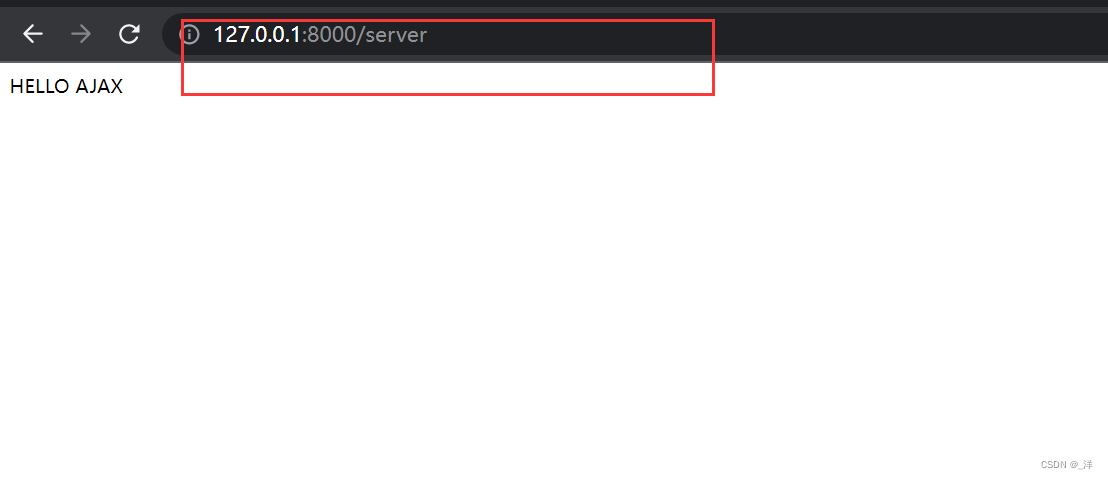
AJAX发送get请求
- 创建AJAX对象:
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest(); - 初始化 设置请求方法和url(向谁发送请求):
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server')
——请求行 - 发送请求:
xhr.send() - 事件绑定,处理服务端返回的结果:
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (){
}
- on:当…的时候
- readystate是xhr对象中的属性,表示状态:
0(未初始化)
1(open方法调用完毕)
2(send方法调用完毕)
3(服务端返回了部分结果)
4(服务端返回了所有结果) - change 改变
处理结果:行 头 空行 体:
// 1.响应行
console.log(xhr.status);//状态码
console.log(xhr.statusText)//状态字符串
//2.响应头
console.log(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders)
// 3.响应体
console.log(xhr.response)
eg:实际应用:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#result{
width: 200px;
height: 100px;
border: solid 1px #90b;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<button>点击发送请求</button>
<div id="result"></div>
<script>
// 获取button
const btn=document.getElementsByTagName('button')[0];
btn.onclick = function (){
// 创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest()
// 初始化 设置请求方法和url(向谁发送请求)
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server')
// 发送请求
xhr.send()
// 事件绑定,处理服务端返回的结果
// on:当...的时候
// readystate是xhr对象中的属性
// 表示状态:0(未初始化) 1(open方法调用完毕) 2(send方法调用完毕) 3(服务端返回了部分结果) 4(服务端返回了所有结果)
// change 改变
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
// 判断响应状态码 200(成功) 404 403 401 500
// 2开头的都是成功
if(xhr.status >=200 && xhr.status<300){
// 处理结果:行 头 空行 体
// 1.响应行
console.log(xhr.status);//状态码
console.log(xhr.statusText)//状态字符串
//2.响应头
console.log(xhr.getAllResponseHeaders)
// 3.响应体
console.log(xhr.response)
// 将相应结果放到页面上
const result = document.getElementById('result')
result.innerHTML = xhr.response
}else{
}
}
}
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
运行结果:

点击后:

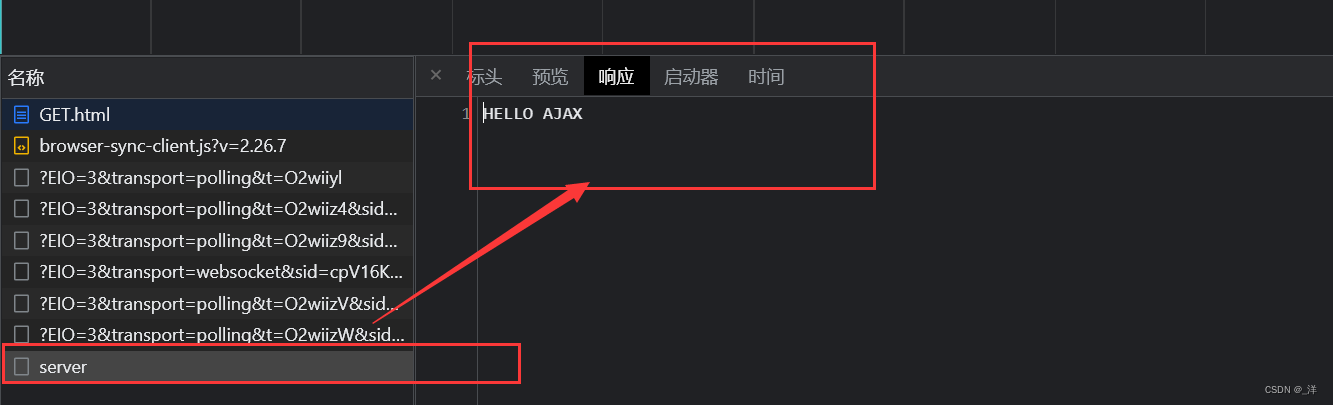
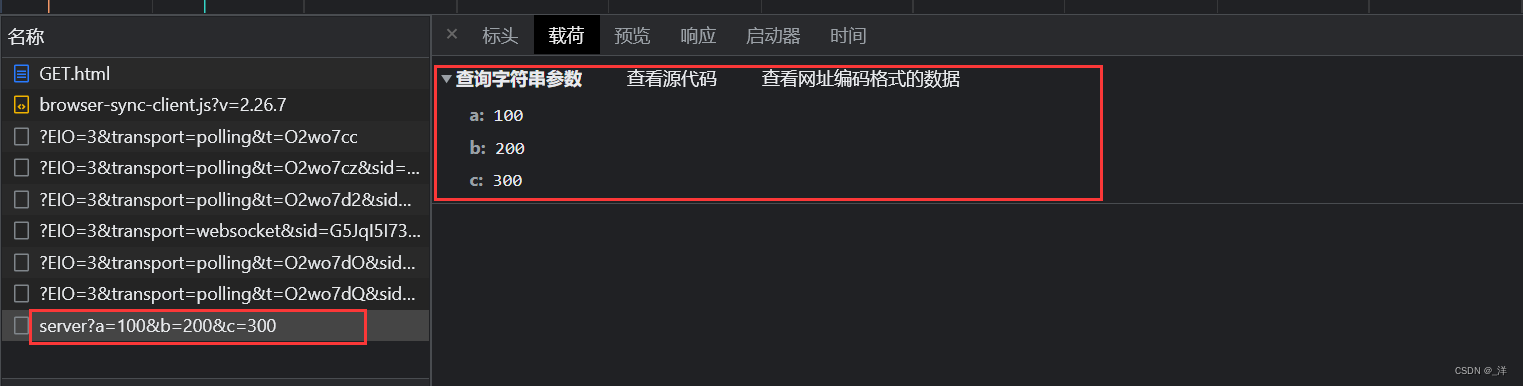
AJAX的get请求设置参数——(请求体)
ajax传递参数值需要在url后面添加参数即可。
格式 :url?参数名 = 参数值&参数名 = 参数值
url和参数之间使用?分隔,多个参数之间使用&分隔。
eg:
xhr.open('GET','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server?a=100&b=200&c=300')
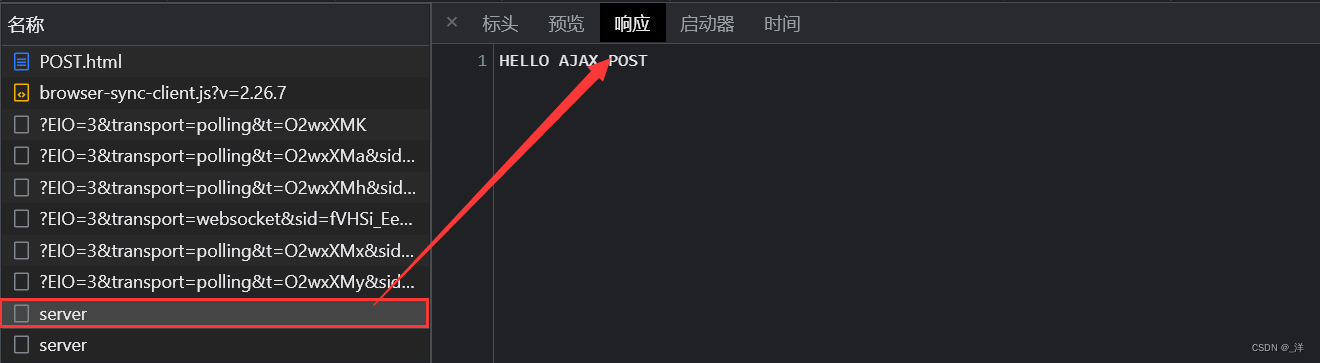
AJAX发送post请求
和发送get请求类似,将get换成post
post.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#result{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 1px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id = 'result'></div>
<script>
// 获取元素
const result = document.getElementById('result')
// 绑定事件
result.addEventListener('mouseover',function (){
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. 初始化类型与URL
xhr.open('POST','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server')
// 3.发送
xhr.send()
// 4.事件绑定
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >=200 && xhr.status<300){
// 处理返回结果
result.innerHTML = xhr.response
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
server.js
// 1.引入express
const express = require('express');
// 2.创建应用对象
const app = express();
// 3.创建路由规则
// 如果请求行的路径是/server的GET请求就会执行回调函数里面的内容
app.get('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX GET')
})
// 如果请求行的路径是/server的POST请求就会执行回调函数里面的内容
app.post('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX POST')
})
// 4.监听端口启动服务
app.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('服务已经启动,8000端口监听中……')
})
输出:

AJAX的post请求设置参数
post请求是在send中1进行设置的
格式:xhr.send('参数名=参数值&参数名=参数值')
或者xhr.send('参数名:参数值&参数名:参数值')
eg:
xhr.send('a=100&b=200&c=300')
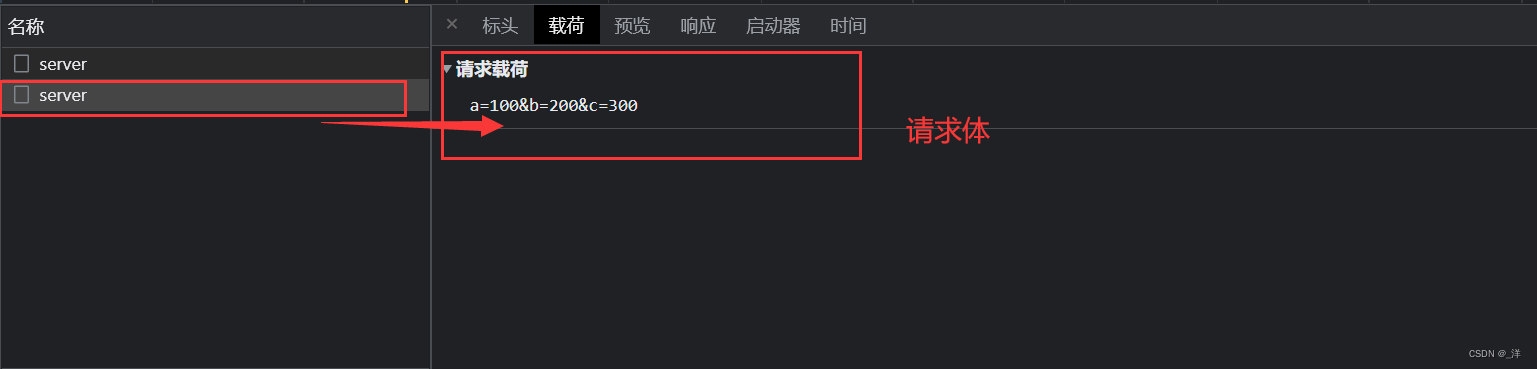
AJAX请求头的设置
在open后面设置请求头。
设置请求头格式:setRequestHeader('头的名字','头的值')
我们一般把身份校验的信息放到头信息中,传递到后端进行验证
eg:预定义的响应头
// 设置请求头(setRequestHeader('头的名字','头的值'))
// Content-Type请求体类型
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
POST.HTML
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#result{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 1px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id = 'result'></div>
<script>
// 获取元素
const result = document.getElementById('result')
// 绑定事件
result.addEventListener('mouseover',function (){
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. 初始化类型与URL
xhr.open('POST','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server')
// 设置请求头(setRequestHeader('头的名字','头的值'))
// Content-Type请求体类型
xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
// 3.发送
xhr.send('a=100&b=200&c=300')
// 4.事件绑定
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >=200 && xhr.status<300){
// 处理返回结果
result.innerHTML = xhr.response
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
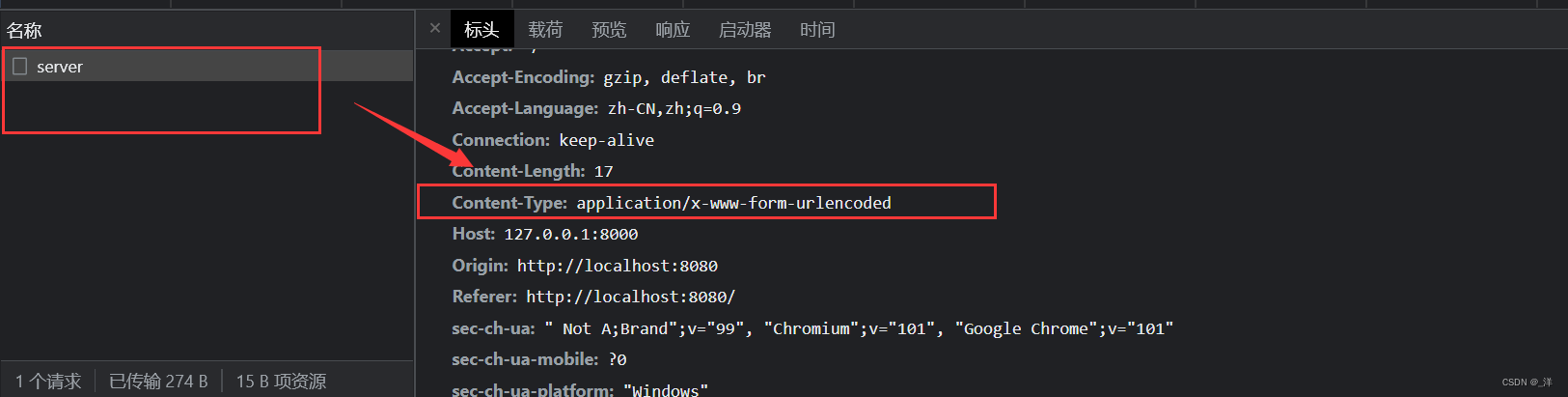
eg:自定义的响应头
自定义的响应头浏览器的安全检验机制会检验出来,所以需要对server.js的post请求做如下修改(修改成all,表示接受所有请求)
// 如果请求行的路径是/server的POST请求就会执行回调函数里面的内容
app.all('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 响应头(接受所有响应头信息)
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers','*')
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX POST')
})
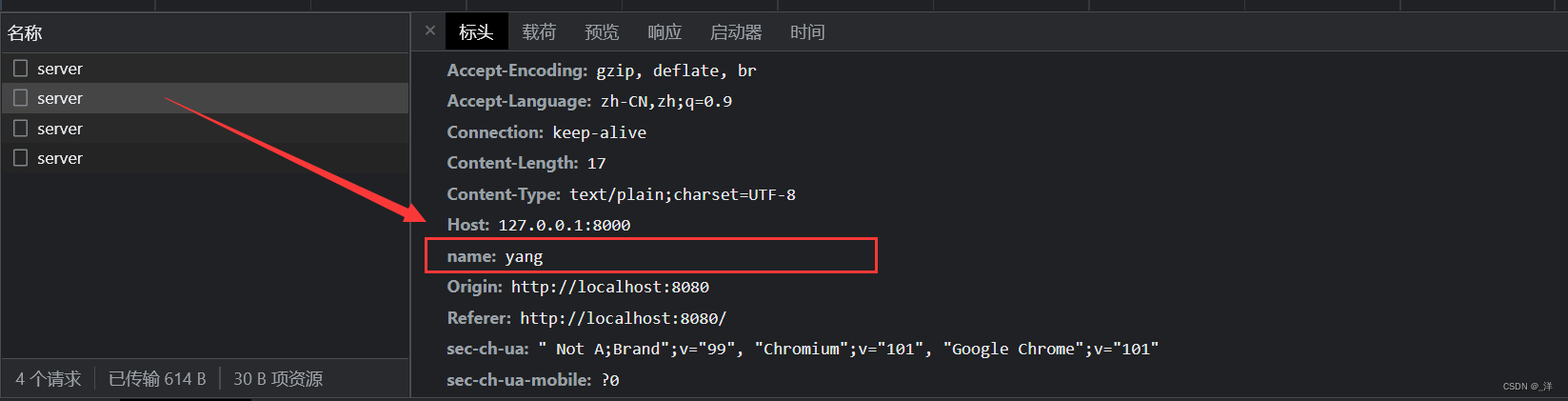
前端设置响应头
xhr.setRequestHeader('name','yang')
重新启动server.js
浏览器显示如下:
完整代码:
post.html
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta http-equiv="X-UA-Compatible" content="IE=edge">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<style>
#result{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
border: solid 1px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id = 'result'></div>
<script>
// 获取元素
const result = document.getElementById('result')
// 绑定事件
result.addEventListener('mouseover',function (){
// 1.创建对象
const xhr = new XMLHttpRequest();
// 2. 初始化类型与URL
xhr.open('POST','http://127.0.0.1:8000/server')
// 设置请求头(setRequestHeader('头的名字','头的值'))
// Content-Type请求体类型
// xhr.setRequestHeader('Content-Type','application/x-www-form-urlencoded')
xhr.setRequestHeader('name','yang')
// 3.发送
xhr.send('a=100&b=100&c=100')
// 4.事件绑定
xhr.onreadystatechange = function (){
if(xhr.readyState === 4){
if(xhr.status >=200 && xhr.status<300){
// 处理返回结果
result.innerHTML = xhr.response
}
}
}
})
</script>
</body>
</html>
server.js
// 1.引入express
const express = require('express');
// 2.创建应用对象
const app = express();
// 3.创建路由规则
// 如果请求行的路径是/server的GET请求就会执行回调函数里面的内容
app.get('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX GET')
})
// 如果请求行的路径是/server的POST请求就会执行回调函数里面的内容
app.all('/server', (request, response) => {
// 设置响应头 设置允许跨越
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Origin', '*');
// 响应头(接受所有响应头信息)
response.setHeader('Access-Control-Allow-Headers','*')
// 设置响应体
response.send('HELLO AJAX POST')
})
// 4.监听端口启动服务
app.listen(8000, () => {
console.log('服务已经启动,8000端口监听中……')
})








 本文详细介绍了AJAX的基础知识,包括如何使用XMLHttpRequest对象发送GET和POST请求,以及设置请求参数和请求头。通过实例展示了在前端页面和服务器端的交互过程,帮助理解AJAX在数据传输中的应用。
本文详细介绍了AJAX的基础知识,包括如何使用XMLHttpRequest对象发送GET和POST请求,以及设置请求参数和请求头。通过实例展示了在前端页面和服务器端的交互过程,帮助理解AJAX在数据传输中的应用。
















 3189
3189

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








