定位概述
- 定位(position)
定位是一种更加高级的布局手段
通过定位可以将元素摆放到页面的任意位置,而且不会对其他元素产生影响。 - 使用position属性来设置定位
可选值:
static默认值,元素是静止的没有开启定位
relative开启元素的相对定位
absolute开启元素的绝对定位
fixed开启元素的固定定位
sticky开启元素的粘滞定位
偏移量(offset)
当元素开启了定位以后,可以通过偏移量来设置元素的位置
- top:定位元素和定位位置上边的距离
- bottom:定位元素和定位位置下边的距离
定位元素垂直方向的位置由top和bottom两个属性来控制,通常情况下我们只会使用其中一个
top值越大,定位元素越向下移动
bottom值越大,定位元素越向上移动 - left:定位元素和定位位置的左侧距离
- right:定位元素和定位位置的右侧距离
定位元素水平方向的位置由left和right两个属性控制
通常情况下只会使用一个
left越大元素越靠右
right越大元素越靠左
坐标及方向
在页面中坐标的样式:
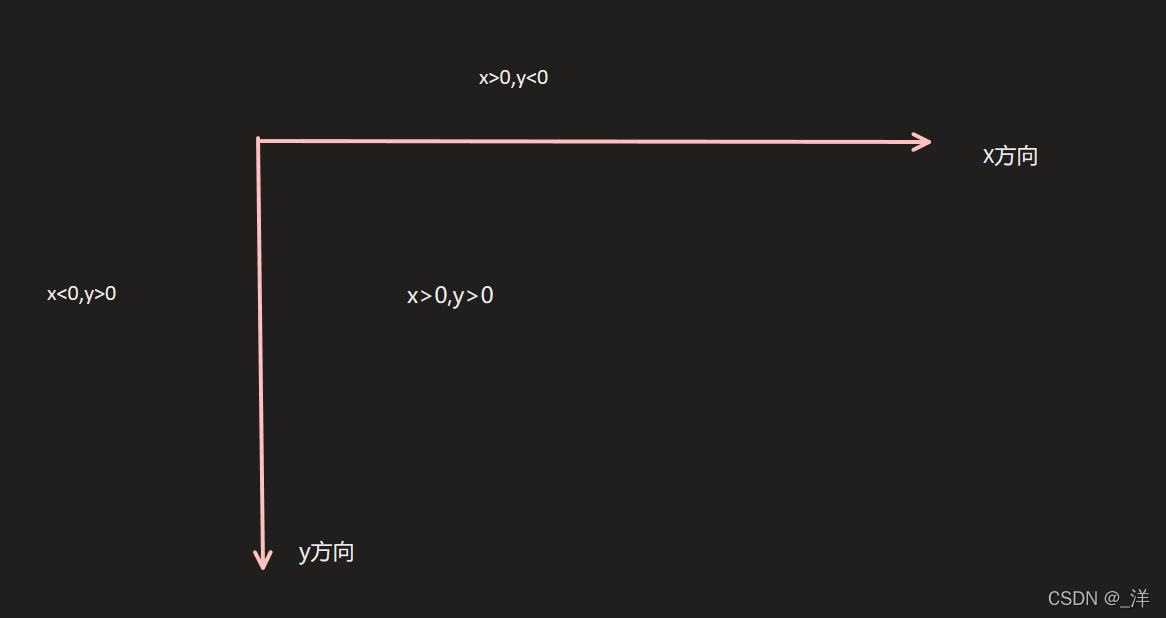
相对定位——position
相对定位:
当元素的position属性值设置为relative时则开启了元素的相对定位
- 相对定位的特点:
1.元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化
2.相对定位是参照于元素在文档流中的位置进行定位的
3.相对定位会提升元素的层级
4.相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
5.相对定位不会改变元素的性质块还是块,行内还是行内
eg:元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1,.box2,.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.box1{
background-color: teal;
}
.box2{
background-color: tomato;
position: relative;
}
.box3{
background-color:rgb(236, 233, 61);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>

eg:相对定位是参照于元素自己在文档流中的位置进行定位的
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1,.box2,.box3{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
}
.box1{
background-color: teal;
}
.box2{
background-color: tomato;
position: relative;
left: 100px;
top: -100px
}
.box3{
background-color:rgb(236, 233, 61);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
<div class="box3"></div>
</body>
</html>

eg:提升元素的层级
.box2{
background-color: tomato;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: -100px
}

绝对定位——absolute
- 当元素的position属性值设置为
absolute时,则开启了元素的绝对定位 - 绝对定位的特点:
1.开启绝对定位后,如果不设置偏移量元素的位置不会发生变化
2.开启绝对定位后,元素会从文档流中脱离
3.行内元素:行内元素脱离文档流以后会变成块元素,特点和块元素一样。
4.块元素:块元素不再独占页面的一行;如果没有设置宽度和高度,脱离文档流以后,块元素的宽度和高度默认都被内容撑开;如果设置了宽度和高度,就按设置的来。
5.绝对定位会使元素提升一个层级
6.绝对定位元素是相对于其包含块进行定位的
包含块( containing block ): - 正常情况下:
包含块就是离当前元素最近的祖先块元素
<div> <div></div> </div>div的包含块就是div
<div><span><em>hello</em></span></div>em的包含块也是div,因为span是行内元素 - 绝对定位的包含块:
包含块就是离它最近的开启了定位(即position不是static即可)的祖先元素,
如果所有的祖先元素都没有开启定位,则根元素(html)就是它的包含块 - 初始包含块:html(根元素)
eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
body{
font-size: 50px;
}
.box0{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(52, 78, 102);
}
.box1 {
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: teal;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: tomato;
position:absolute;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(236, 233, 61);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box0">0</div>
<div class="box1">1
<div class="box3">3<div class="box2">2</div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
输出:

如果开启2的定位:
.box1 {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: teal;
}
输出:

如果开启3的定位:
.box3 {
position: relative;
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(236, 233, 61);
}

固定定位 ——fixed
固定定位:
- 将元素的position属性设置为fixed则开启了元素的固定定位
- 固定定位也是一种绝对定位(absoult),所以固定定位的大部分特点都和绝对定位一样:
1.开启固定定位后,如果不设置偏移量元素的位置不会发生变化
2.开启固定定位后,元素会从文档流中脱离
3.固定定位会改变元素的性质,行内变成块,块的宽高被内容撑开
(也就是脱离文档流的特点)
4.固定定位会使元素提升一个层级
5.唯一不同的是固定定位永远参照于浏览器的视口(即窗口)进行定位。
即当滚动条滚动时,固定定位的元素的位置不会改变
eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<style>
body{
font-size: 50px;
height: 1500px;
}
.box0{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: rgb(52, 78, 102);
}
.box1 {
position: relative;
width: 400px;
height: 400px;
background-color: teal;
}
.box2 {
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: tomato;
position:fixed;
left: 0px;
top: 0px;
}
.box3 {
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: rgb(236, 233, 61);
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box0">0</div>
<div class="box1">1
<div class="box3">3<div class="box2">2</div></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

粘滞定位——sticky
该属性,浏览器的支持度不高
粘滞定位
- 当元素的position属性设置为sticky时则开启了元素的粘滞定位
- 粘滞定位和相对定位的特点基本一致
1.元素开启相对定位以后,如果不设置偏移量元素不会发生任何的变化
2.相对定位会提升元素的层级
3.相对定位不会使元素脱离文档流
4.相对定位不会改变元素的性质块还是块,行内还是行内
不同的是:
- 粘滞定位可以在元素到达某个位置时将其固定
2.粘滞定位是参照于body进行定位的
eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8" />
<link rel="stylesheet" href="../reset.css" />
<style>
.nav{
/* width: 1246px; */
width: 1250px;
height: 50px;
background-color: rgb(231,231,226);
margin: 50px auto;
position: sticky;
top:100px;
}
.nav li{
height:50px;
float: left;
/* 设置height=line-height可以使元素垂直居中 */
line-height: 48px;
}
.nav a{
display: block;
color: slategray;
text-decoration: none;
font-size: 18px;
padding: 0 42px;
}
.nav li:last-child a{
/* 这样写或者将nav的宽度修改为 width: 1246px; */
padding: 0 44px 0 44px;
}
.nav a:hover{
background-color: #3f3f3f;
color: white;
}
.box1{
width: 200px;
height: 1000px;
background-color: darksalmon;
}
body{
height: 2000px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<ul class="nav">
<li><a href="#">HTML/CSS</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Browser Side</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Server Side</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Programming</a></li>
<li><a href="#">XML</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Web Building</a></li>
<li><a href="#">Reference</a></li>
</ul>
<div class="box1"></div>
</body>
</html>

绝对定位对布局的影响
也是相对于自己的包含快进行分居中等位置操作
水平布局:
当我们开启了绝对定位后,水平方向的布局等式就需要添加left和right两个值,此时规则和之前一样只是多添加了两个值:
left + margin-left + border-left + padding-left + width + padding-rigth + border-right + margin-right + right = 包含块的内容宽度
当发生过度约束:
- 如果9个值中没有auto 则自动调整right值以使等式满足
如果有auto,则自动调整auto的值以使等式满足 - 可设置auto的值
margin width left right - 因为left和right的
值默认是auto,所以如果不指定left和right,则等式不满足时,会自动调整这两个值(着重调整right)
eg:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: darksalmon;
position: relative;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
/* 写不写都一样,因为默认值就是auto */
left: auto;
right: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

如果:width,right,left都为auto时就不会显示了
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
body{
background-color: darksalmon;
}
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color:rgba(253, 253, 253, 0.288);
position: relative;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
/* 写不写都一样,因为默认值就是auto */
width: auto;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
/* 写不写都一样,因为默认值就是auto */
left: auto;
right: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
输出:

水平居中方式:
要先指定 width,并且设置right = left = 0,水平居中才有效果
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
body{
background-color: darksalmon;
}
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color:rgba(253, 253, 253, 0.288);
position: relative;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin-left: auto;
margin-right: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
输出:

垂直方向
垂直方向布局的等式的也必须要满足
top + margin-top/bottom + padding-top/bottom + border-top/border-bottom + height + bottom = 包含块的内容高度
所以可以利用这一特性,使元素垂直居中:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
body{
background-color: darksalmon;
}
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color:rgba(253, 253, 253, 0.288);
position: relative;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
margin-top: auto;
margin-bottom: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

所以利用绝对定位可以使元素垂直水平居中
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="zh">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<style>
body{
background-color: darksalmon;
}
.box1{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color:rgba(253, 253, 253, 0.288);
position: relative;
}
.box2{
position: absolute;
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: darkseagreen;
top: 0;
bottom: 0;
left: 0;
right: 0;
margin: auto;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<div class="box2"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>

























 4846
4846

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








