题目:
Given an m x n matrix of positive integers representing the height of each unit cell in
a 2D elevation map, compute the volume of water it is able to trap after raining.
Note:
Both m and n are less than 110. The height of each unit cell is greater than 0 and is less than 20,000.
Example:
Given the following 3x6 height map: [ [1,4,3,1,3,2], [3,2,1,3,2,4], [2,3,3,2,3,1] ] Return 4.

The above image represents the elevation map [[1,4,3,1,3,2],[3,2,1,3,2,4],[2,3,3,2,3,1]] before
the rain.
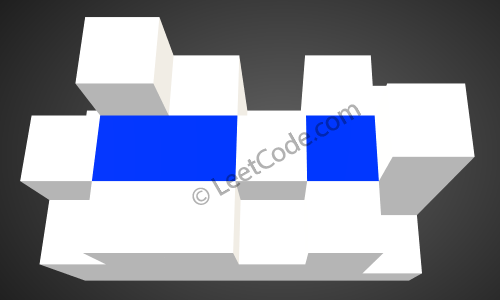
After the rain, water are trapped between the blocks. The total volume of water trapped is 4.
思路:
我记得Leetcode中好像有Trapping Rain Water I这道题目,我也贴出来解题报告了。其实这道题目就是将一维的情况扩展到了二维上,但是基本思路还是一样的:在一维中我们只需要从两个端点中选一个较低者即可,而在二维中可选的点就扩大成了整个矩形的四个边。根据上一道题目知道,我们每次应该先选取边界最小的高度,所以很自然的可以想到优先队列或者小顶堆来保存周围边界。在我们访问过了一个点之后,要继续在矩形的内部遍历,所以还需要保存一个点的位置信息(注意下面的代码将二维位置信息映射到了一维上)。为了防止再次访问已经访问过的点,还需要用一个数组来标记每个点的访问状态。
由于优先队列中的元素个数可达m*n个,所以该算法的时间复杂度应该是O(m*n*log(m*n)),空间复杂度是O(m*n)。
代码:
class Solution {
public:
int trapRainWater(vector<vector<int>>& heightMap) {
if(heightMap.size() == 0) {
return 0;
}
priority_queue<pair<int, int>, vector<pair<int, int>>, greater<pair<int, int>>> que; // smallest height in front
int row = heightMap.size(), col = heightMap[0].size();
vector<vector<int>> visited(row, vector<int>(col, 0));
int ans = 0, Max = INT_MIN;
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++) {
for(int j = 0; j < col; j++) {
if(!(i == 0 || i == row - 1 || j == 0 || j == col - 1)) { // boundary grid
continue;
}
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[i][j], i * col + j)); // put all the bounary grid in the que
visited[i][j] = 1;
}
}
vector<vector<int>> dir{{1, 0}, {-1, 0}, {0, 1}, {0, -1}};
while(!que.empty()) {
auto val = que.top();
que.pop();
int height = val.first, x = val.second / col, y = val.second % col;
Max = max(Max, height);
for(auto d: dir) { // for each direction
int x2 = x + d[0], y2 = y + d[1];
if(x2 >= row || x2 < 0 || y2 < 0 || y2 >= col || visited[x2][y2]) {
continue;
}
visited[x2][y2] = 1;
if(heightMap[x2][y2] < Max) {
ans += (Max - heightMap[x2][y2]);
}
que.push(make_pair(heightMap[x2][y2], x2 * col + y2));
}
}
return ans;
}
};




 这篇博客主要解析Leetcode的407题,即二维地形图在下雨后的积水体积计算。通过扩展一维问题的思路,利用边界上的最小高度,采用优先队列(小顶堆)来处理。博主详细介绍了算法的思路,指出每次选择边界上的最小高度,并用堆来更新,同时避免重复访问已检查的单元格,确保算法的正确性。最终,算法的时间复杂度为O(m*n*log(m*n)),空间复杂度为O(m*n)。
这篇博客主要解析Leetcode的407题,即二维地形图在下雨后的积水体积计算。通过扩展一维问题的思路,利用边界上的最小高度,采用优先队列(小顶堆)来处理。博主详细介绍了算法的思路,指出每次选择边界上的最小高度,并用堆来更新,同时避免重复访问已检查的单元格,确保算法的正确性。最终,算法的时间复杂度为O(m*n*log(m*n)),空间复杂度为O(m*n)。
















 427
427

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








