本文主要内容:
- 本文主要是对以下论文进行解读
《Xueyao Zhang, Juan Cao, Xirong Li, Qiang Sheng, Lei Zhong, and Kai Shu. 2021. Mining Dual Emotion for Fake News Detection. In Proceedings of the Web Conference 2021 (WWW '21). Association for Computing Machinery, New York, NY, USA, 3465–3476. DOI:https://doi.org/10.1145/3442381.3450004》 - 论文作者提供的代码
【https://github.com/RMSnow/WWW2021】 - 论文模型的主要任务
给定一则新闻TTT、该新闻是真实或虚假新闻的标签yyy、该则新闻的若干条评论M=[M1,M2,...,Mi,...,MLM]M=[M_1,M_2,...,M_i,...,M_{L_M}]M=[M1,M2,...,Mi,...,MLM]。现在需要设计出一个模型,基于TTT、MMM来预测出y^\hat{y}y^,使得yyy和y^\hat{y}y^一致。
模型整体思路
目前的模型大多是仅关注新闻文本所体现的Publisher Emotion,而忽略了该则新闻的评论所体现的Social Emotion。本文分别对新闻文本和新闻评论,各提取出情感特征。并将这两种特征同时添加入以往的fake news detector分类器(BI-GRU、BERT)中。实验结果表明,添加了这两种特征,能显著提升分类效果。
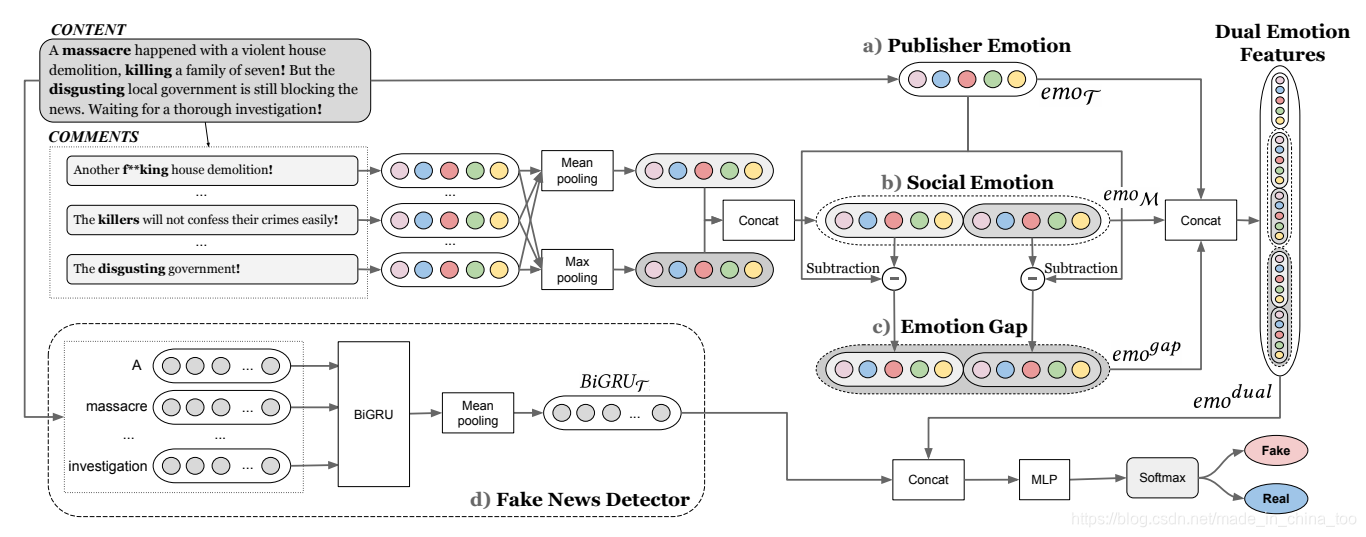
Publisher Emotion
给定含有LLL个单词的文本 T=[t1,t2,...,ti,...,tL]T=[ t_1, t_2,...,t_i,...,t_L ]T=[t1,t2,...,ti,...,tL],及一个情感分类器f()f()f(),
得到分类结果的概率为emoTcate∈Rdfemo_T^{cate} \in R^{d_f}emoTcate∈Rdf,其中dfd_fdf是情感的种类数量:
emoTcate=f(T)(1)emo_T^{cate}=f(T) \tag{1}emoTcate=f(T)(1)
假设Emotional Lexicon里共有ded_ede种情感,记E={e1,e2,...,ede}E=\{ e_1,e_2,...,e_{d_e} \}E={e1,e2,...,ede}。针对每种情感都有一个字典ϵe={we,1,we,2,...,we,Le}\epsilon_e=\{ w_{e,1},w_{e,2},...,w_{e,L_e} \}ϵe={we,1,we,2,...,we,Le}。
使用每种情感的字典ϵe\epsilon_eϵe,去遍历文本TTT中的每个单词tit_iti,可以得到文本TTT中各单词在每种情感下的得分:
{e1:[s(t1,e1),s(t2,e1),...,s(tL,e1)]e2:[s(t1,e2),s(t2,e2),...,s(tL,e2)]⋅⋅⋅ede:[s(t1,ede),s(t2,ede),...,s(tL,ede)](2) \begin{cases} e_1:[s(t_1,e_1),s(t_2,e_1),...,s(t_L,e_1)] \\ e_2:[s(t_1,e_2),s(t_2,e_2),...,s(t_L,e_2)] \\ \cdot \\ \cdot \\ \cdot \\ e_{d_e}:[s(t_1,e_{d_e}),s(t_2,e_{d_e}),...,s(t_L,e_{d_e})] \end{cases} \tag{2} ⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧e1:[s(t1,e1),s(t2,e1),...,s(tL,e1)]e2:[s(t1,e2),s(t2,e2),...,s(tL,e2)]⋅⋅⋅ede:[s(t1,ede),s(t2,ede),...,s(tL,ede)](2)
在一个情感eie_iei下,对于文本TTT中各个单词tit_iti的得分相加,得到文本TTT在不同情感eie_iei下的得分s(T,ei)s(T,e_i)s(T,ei):
{e1:s(T,e1)e2:s(T,e2)⋅⋅⋅ede:s(T,ede)(3)
\begin{cases}
e_1:s(T,e_1)\\
e_2:s(T,e_2)\\
\cdot \\
\cdot \\
\cdot \\
e_{d_e}:s(T,e_{d_e})
\end{cases} \tag{3}
⎩⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎨⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎪⎧e1:s(T,e1)e2:s(T,e2)⋅⋅⋅ede:s(T,ede)(3)
将文本TTT在不同情感eie_iei下的得分s(T,ei)s(T,e_i)s(T,ei)拼接成一个ded_ede维的向量,其包含了文本TTT在不同情感下的倾向信息:
emoTlex=s(T,e1)⊕s(T,e2)⊕⋯⊕s(T,ede) emo_T^{lex}=s(T,e_1) \oplus s(T,e_2) \oplus \cdots \oplus s(T,e_{d_e}) emoTlex=s(T,e1)⊕s(T,e2)⊕⋯⊕s(T,ede)
例如在考虑情感happy时,单词esctatic比单词joyful更强烈,因此需要考虑单词的情感强度int(ti)int(t_i)int(ti),其可以通过情感字典计算得到。intensity-aware text-level scores为:
s′(T,e)=∑i=1Ls′(ti,e)=∑i=1Lint(ti)s(ti,e),∀e∈E
s'(T,e)=\sum\limits_{i=1}^{L} s'(t_i,e) = \sum\limits_{i=1}^{L} int(t_i)s(t_i,e), \forall e \in E
s′(T,e)=i=1∑Ls′(ti,e)=i=1∑Lint(ti)s(ti,e),∀e∈E
将文本TTT在ded_ede种情感下的intensity-aware text-level scores进行拼接,得到情感强度特征emotint∈Rdeemo_t^{int} \in R^{d_e}emotint∈Rde:
emotint=s′(T,e1)⊕s′(T,e2)⊕⋯⊕s′(T,ede)
emo_t^{int}=s'(T,e_1) \oplus s'(T,e_2) \oplus \cdots \oplus s'(T,e_{d_e})
emotint=s′(T,e1)⊕s′(T,e2)⊕⋯⊕s′(T,ede)
除了上文提到的emotion-level特征,此处根据sentiment dictionary或public toolkits可以得到coarse-grained的情感得分,即非负则正的情感极性emoTsenti∈Rdsemo_T^{senti} \in R^{d_s}emoTsenti∈Rds ,通常ds=1d_s=1ds=1
另外,情感符号、标点符号、大写字母等也能表达情绪。假设共有dad_ada种特征,本文根据下表可以得到额外的辅助特征emoTaux∈Rdaemo_T^{aux} \in R^{d_a}emoTaux∈Rda:

最终,文本TTT的Publisher Emotion为emoT∈Rdf+2de+ds+daemo_T \in R^{df+2d_e+d_s+d_a}emoT∈Rdf+2de+ds+da:
emoT=emoTcate⊕emoTlex⊕emoTint⊕emoTsenti⊕emoTaux emo_T=emo_T^{cate} \oplus emo_T^{lex} \oplus emo_T^{int} \oplus emo_T^{senti} \oplus emo_T^{aux} emoT=emoTcate⊕emoTlex⊕emoTint⊕emoTsenti⊕emoTaux
Social Emotion
假设一则新闻共有LML_MLM条评论,M=[M1,M2,...,Mi,...,MLM]M=[M_1,M_2,...,M_i,...,M_{L_M}]M=[M1,M2,...,Mi,...,MLM],则根据上文的计算过程,将这LML_MLM条评论的特征汇聚,得到social emotion特征 emoM‾∈RLM×d\overline{emo_M} \in R^{L_M \times d}emoM∈RLM×d:
emoM‾=emoM1T⊕emoM2T⊕⋯⊕emoMLMT \overline{emo_M} = emo^T_{M_1} \oplus emo^T_{M_2} \oplus \cdots \oplus emo^T_{M_{L_M}} emoM=emoM1T⊕emoM2T⊕⋯⊕emoMLMT
使用Mean pooling计算情感的平均信号emoMmean∈Rdemo_M^{mean} \in R^demoMmean∈Rd,使用max pooling计算情感的极端信号emoMmax∈Rdemo_M^{max} \in R^demoMmax∈Rd:
emoMmean=mean(emoM‾)emoMmax=max(emoM‾) emo_M^{mean} = mean(\overline{emo_M}) emo_M^{max} = max(\overline{emo_M}) emoMmean=mean(emoM)emoMmax=max(emoM)
最后Social Emotion表达为emoM∈R2demo_M \in R^{2d}emoM∈R2d:
emoM=emoMmean⊕emoMmax
emo_M = emo_M^{mean} \oplus emo_M^{max}
emoM=emoMmean⊕emoMmax
Emotion Gap
为了特显Publisher Emotion和Social Emotion的不同之处,计算特征emoMmean∈R2demo_M^{mean} \in R^{2d}emoMmean∈R2d:
emogap=(emoT−emoMmean)⊕(emoT−emoMmax)
emo^{gap} = (emo_T-emo_M^{mean}) \oplus (emo_T-emo_M^{max})
emogap=(emoT−emoMmean)⊕(emoT−emoMmax)
Dual Emotion Features
emodual=emoT⊕emoM⊕emogap emo^{dual} = emo_T \oplus emo_M \oplus emo^{gap} emodual=emoT⊕emoM⊕emogap
Fake News Detection
假设现在BiGRU是虚假新闻分类器,则BiBURTBiBUR_TBiBURT是其输出的特征,现在将BiBURTBiBUR_TBiBURT与emodualemo^{dual}emodual进行拼接,再放到MLP、Softmax中进行最终分类,得到新闻的虚实预测结果y^\hat{y}y^:
y^=Softmax(MLP([BiGRUT,emodual]))
\hat{y} = Softmax(MLP([BiGRU_T,emo^{dual}]))
y^=Softmax(MLP([BiGRUT,emodual]))










 本文探讨了一种新型模型,该模型在虚假新闻检测任务中结合了出版商情绪(PublisherEmotion)和社交情绪(SocialEmotion)。通过情感分析,从新闻文本和评论中提取情绪特征,并利用BiGRU或BERT作为基础分类器。实验结果显示,这种双情感特征的加入显著提升了分类性能。模型包括情绪词典得分、情感强度、情感极性等特征,并通过平均池化和最大池化处理评论情绪,形成情绪差距(EmotionGap)。最后,这些特征被用于增强分类器的输入,以提高预测准确性。
本文探讨了一种新型模型,该模型在虚假新闻检测任务中结合了出版商情绪(PublisherEmotion)和社交情绪(SocialEmotion)。通过情感分析,从新闻文本和评论中提取情绪特征,并利用BiGRU或BERT作为基础分类器。实验结果显示,这种双情感特征的加入显著提升了分类性能。模型包括情绪词典得分、情感强度、情感极性等特征,并通过平均池化和最大池化处理评论情绪,形成情绪差距(EmotionGap)。最后,这些特征被用于增强分类器的输入,以提高预测准确性。
















 1031
1031

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








