随机链表的复制
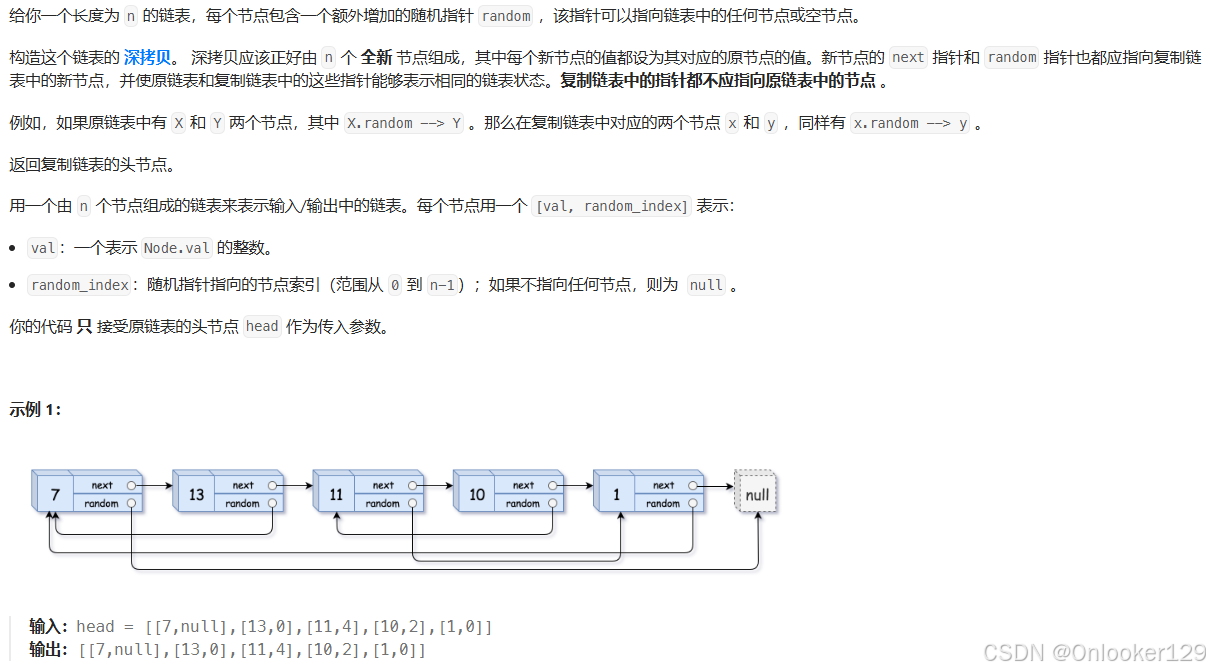
为了在 O(n) 时间复杂度内解决这个问题,并且使用 O(1) 的额外空间,可以利用以下技巧:
- 将新节点插入到原节点后面:我们可以将复制节点插入到原节点后面。例如,如果链表是
A -> B -> C,我们将链表改为A -> A' -> B -> B' -> C -> C',其中A'、B'、C'是A、B、C的拷贝节点。 - 复制
random指针:因为复制节点与原节点紧挨在一起,我们可以直接利用原节点的random指针,来为新节点复制random指针。 - 拆分链表:最后,我们将原链表和复制链表拆分成两个独立的链表。
/*
// Definition for a Node.
class Node {
int val;
Node next;
Node random;
public Node(int val) {
this.val = val;
this.next = null;
this.random = null;
}
}
*/
class Solution {
public Node copyRandomList(Node head) {
if(head == null){
return null;
}
//插入新节点到原节点后面
Node cur = head;
while(cur != null){
Node copy = new Node(cur.val);//创建新节点
copy.next = cur.next;//新节点的next指向原节点的next
cur.next = copy;//原节点的next指向新节点
cur = copy.next;//移动到原节点的下一个节点
}
//复制random节点
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
if(cur.random != null){
cur.next.random = cur.random.next;//新节点的random指向原节点random对应的新节点
}
cur = cur.next.next;//跳到下一个原节点
}
//拆分链表,恢复原链表并生成新链表
Node newHead = head.next;
Node copyCur = newHead;
cur = head;
while(cur != null){
cur.next = cur.next.next;//恢复原链表
if(copyCur.next != null){
copyCur.next = copyCur.next.next;//更新新链表的next指针
copyCur = copyCur.next;
}
cur = cur.next;
}
return newHead;
}
}




 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 322
322

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








