目录
一. 栈的概念和结构
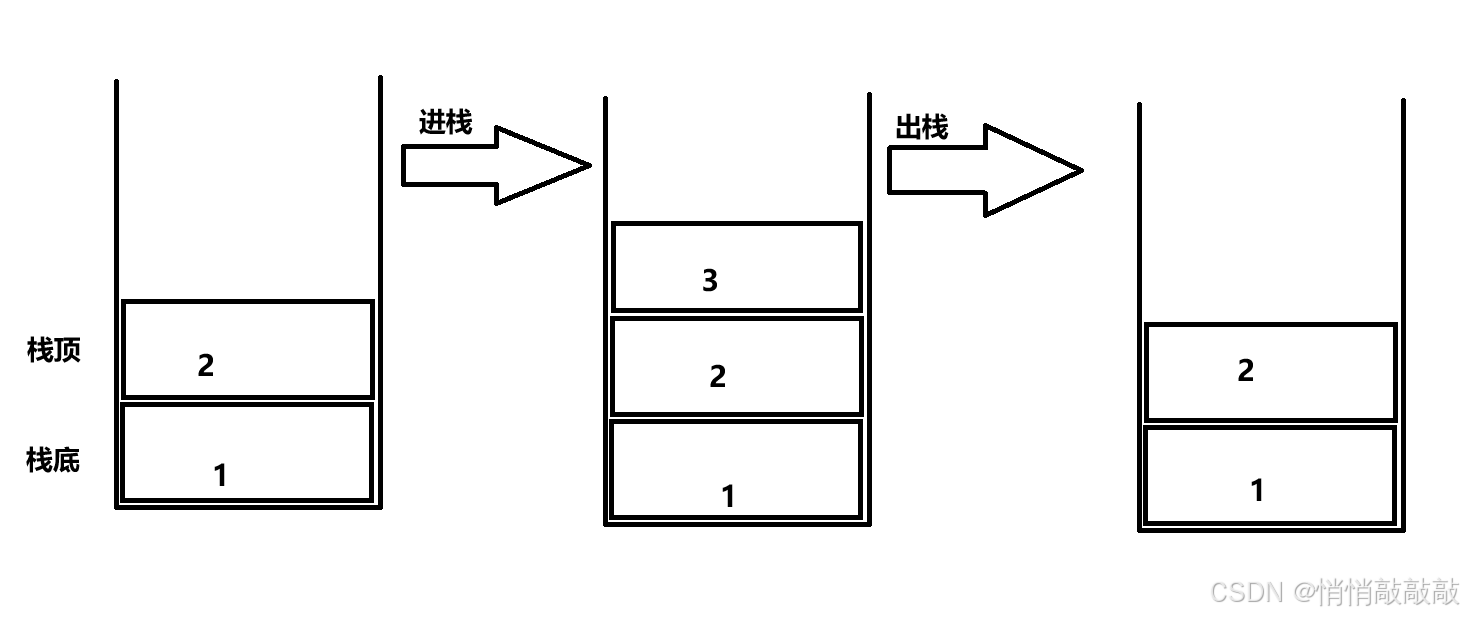
栈是一种特殊的线性表,只允许在固定的一端进行插入和删除元素。进入数据插入和删除操作的一端成为栈顶另一端称为栈底,栈中元素遵守后进先出或先进后出原则
压栈:栈的插入操作叫做(进栈/压栈/入栈)(入数据在栈顶)
出栈:栈的删除操作叫出栈。(出数据在栈顶)
二. 栈的实现方式
栈可以用链表实现也可以用数组实现
1.链表实现栈
如果用尾做栈顶,尾插尾删要设计成双向链表否则插入效率极低
如果用头做栈顶可以设计成单链表的方式
虽然不用扩容但是cpu命中率低
2. 数组实现栈
可以静态实现也可以动态实现
需要扩容,但是cpu命中率高
两种方式各有优劣,这里我们选择使用数组实现
三. 栈各个功能实现
1. 结构体的定义
typedef int StackType;
typedef struct Stack
{
StackType* a;//StackType是存储元素的类型
int Top;
int capacity;
}ST,*pS;三个参数的含义:
a:指针,用来存储数据
Top:栈顶元素在a中的位置
capacity:a能容纳的元素个数
2. 栈的初始化
void StackInit(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->Top = 0;
}
此处pst->Top可以初始化为0也可以初始化为-1,代表栈顶元素在a中的位置或者代表栈顶元素在a中位置的下一个(两种写法对后面代码会产生影响)
3. 入栈操作
void BuyNode(pS pst)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackType* tmp = (StackType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StackType) * newcapacity );
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("relloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
void StackPush(pS pst, StackType data)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->Top == pst->capacity)
{
BuyNode(pst);
}
pst->a[pst->Top] = data;
pst->Top++;
}扩容时要看是容量(capacity)是0还是非0,非0就扩充2倍,0就赋值为4来开辟动态内存
如果上文Top初始化为-1,此处的pst->Top++要在赋值前
4. 出栈操作
void StackPop(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->Top--;//数组里的值不用改,再添加数据会覆盖掉
}5. 返回栈顶的值
StackType StackTop(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->a[pst->Top-1];
}因为Top指向的是栈顶元素的下一个位置,所以要-1
6. 销毁栈
void StackDestroy(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->Top = 0;
}7. 判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->Top == 0;
}
8. 返回栈有多少元素
int StackSize(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->Top;
}数组存储是有0这个下标的,所以直接返回Top,如果Top是指向栈顶元素那返回Top+1
四. 完整代码
1. stack.h
#include<stdio.h>
#include<assert.h>
#include<stdbool.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
typedef int StackType;
typedef struct Stack
{
StackType* a;
int Top;
int capacity;
}ST,*pS;
//初始化
void StackInit(pS pst);
//入栈
void StackPush(pS pst,StackType data);
//出栈
void StackPop(pS pst);
//取栈顶数据
StackType StackTop(pS pst);
//判空
bool StackEmpty(pS pst);
//获取数据个数
int StackSize(pS pst);
void StackDestroy(pS pst);2. stack.c
#include"stack.h"
//初始化
void StackInit(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->Top = 0;
}
void BuyNode(pS pst)
{
int newcapacity = pst->capacity == 0 ? 4 : pst->capacity * 2;
StackType* tmp = (StackType*)realloc(pst->a, sizeof(StackType) * newcapacity );
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("relloc fail");
return;
}
pst->a = tmp;
pst->capacity = newcapacity;
}
void StackPush(pS pst, StackType data)
{
assert(pst);
if (pst->Top == pst->capacity)
{
BuyNode(pst);
}
pst->a[pst->Top] = data;
pst->Top++;
}
void StackPop(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
pst->Top--;//数组里的值不用改,再添加数据会覆盖掉
}
StackType StackTop(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->a[pst->Top-1];
}
void StackDestroy(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
free(pst->a);
pst->a = NULL;
pst->capacity = 0;
pst->Top = 0;
}
bool StackEmpty(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->Top == 0;
}
int StackSize(pS pst)
{
assert(pst);
return pst->Top;
}3. test.c
#include"stack.h"
int main()
{
ST s = { 0 };
StackInit(&s);
StackPush(&s, 2);
StackPush(&s, 2);
StackPush(&s, 3);
StackPush(&s, 3);
printf("%d\n", StackSize(&s));
while(!StackEmpty(&s))
{
printf("%d\n", StackTop(&s));
StackPop(&s);
}
StackDestroy(&s);
return 0;
}本篇文章到此结束希望可以帮到您(๑′ᴗ‵๑)I Lᵒᵛᵉᵧₒᵤ❤
(づ ̄3 ̄)づ╭❤~ 再见啦~
























 2628
2628

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








