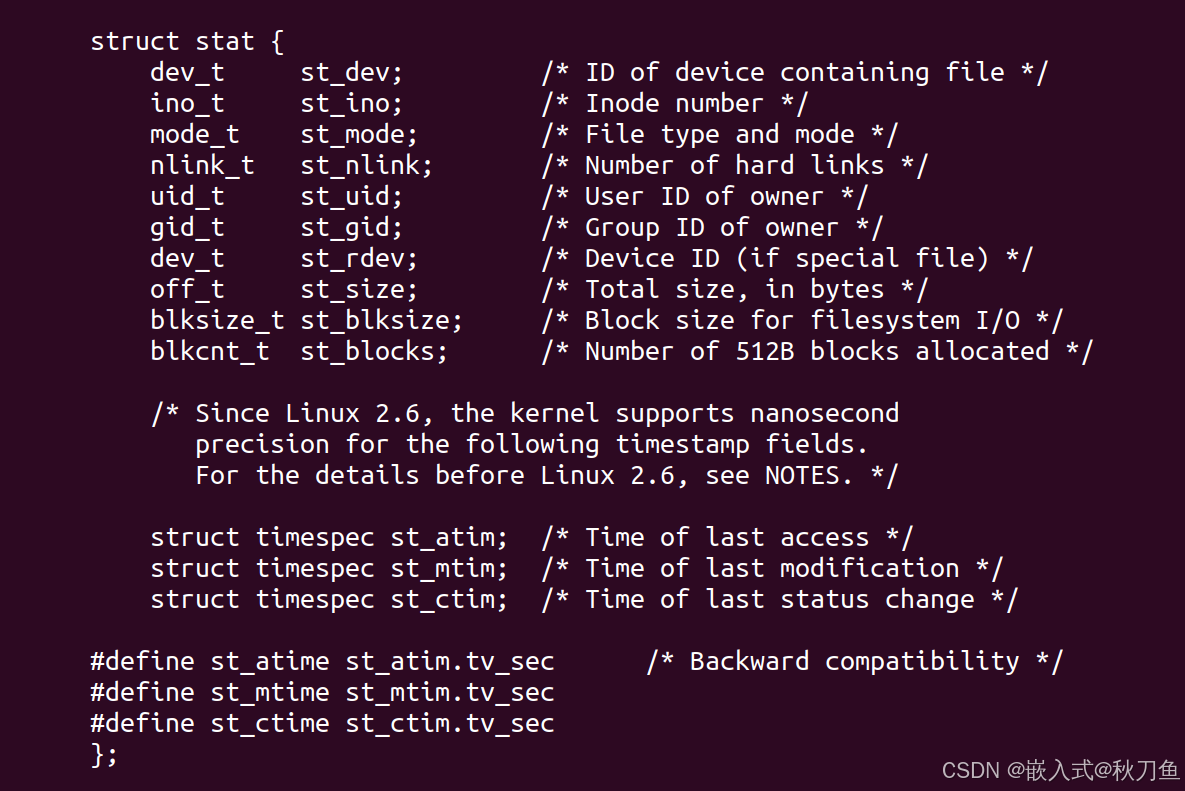
stat函数模型以及所需的头文件有:
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
int stat(const char *pathname, struct stat *buf);
-
pathname:用于指定一个需要查看属性的文件路径。
-
buf: struct stat 类型指针,用于指向一个 struct stat 结构体变量。调用 stat 函数的时候需要传入一个 struct stat 变量的指针,获取到的文件属性信息就记录在 struct stat 结构体中
-
返回值:成功返回 0;失败返回-1,并设置 error
struct stat 是内核定义的一个结构体,在<sys/stat.h>头文件中申明,所以可以在应用层使用,这个结构体中的所有元素加起来构成了文件的属性信息。
通过 stat(), fstat(), 或 lstat() 系统调用获取。它记录了文件的类型、权限、大小、时间戳等信息。
1. 文件类型与权限
| 字段名 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
st_mode | mode_t | 文件类型和权限掩码(如 S_IFMT 提取类型,S_IFREG 表示普通文件)。 |
st_uid | uid_t | 文件所有者的用户 ID。 |
st_gid | gid_t | 文件所属组的组 ID。 |
struct stat file_stat;
stat("test.txt", &file_stat);
if (S_ISREG(file_stat.st_mode)) {
printf("普通文件\n");
} else if (S_ISDIR(file_stat.st_mode)) {
printf("目录\n");
}
2. 文件大小与存储信息
| 字段名 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
st_size | off_t | 文件大小(字节)。对符号链接,表示链接指向的路径长度。 |
st_blksize | blksize_t | 文件系统 I/O 操作的最佳块大小(如 4096)。 |
st_blocks | blkcnt_t | 文件占用的磁盘块数量(每块通常为 512 字节)。 |
文件大小:1024 字节
占用块数:8 块(实际占用 8×512=4096 字节,因块分配对齐)
3. 时间戳
| 字段名 | 类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
st_atime | time_t | 最后访问时间(Access Time)。 |
st_mtime | time_t | 最后修改时间(Modify Time,内容变更)。 |
st_ctime | time_t | 最后状态变更时间(Change Time,如权限或元数据修改)。 |
#include <time.h>
printf("最后修改时间: %s", ctime(&file_stat.st_mtime));
可以通过终端命令:man 2 stat 查看 具体详情
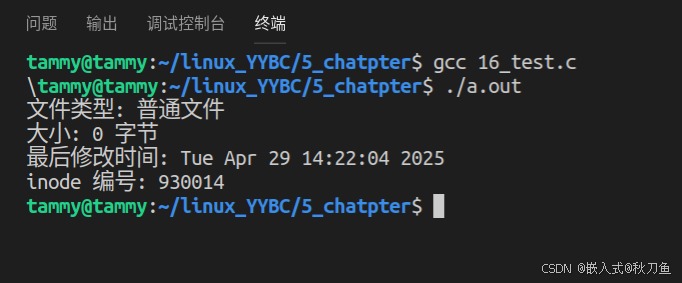
代码演示1:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
int main() {
struct stat file_stat;
if (stat("test.txt", &file_stat) == -1) {
perror("stat() 失败");
return 1;
}
printf("文件类型: ");
if (S_ISREG(file_stat.st_mode)) printf("普通文件\n");
else if (S_ISDIR(file_stat.st_mode)) printf("目录\n");
else if (S_ISLNK(file_stat.st_mode)) printf("符号链接\n");
printf("大小: %ld 字节\n", (long)file_stat.st_size);
printf("最后修改时间: %s", ctime(&file_stat.st_mtime));
printf("inode 编号: %lu\n", (unsigned long)file_stat.st_ino);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
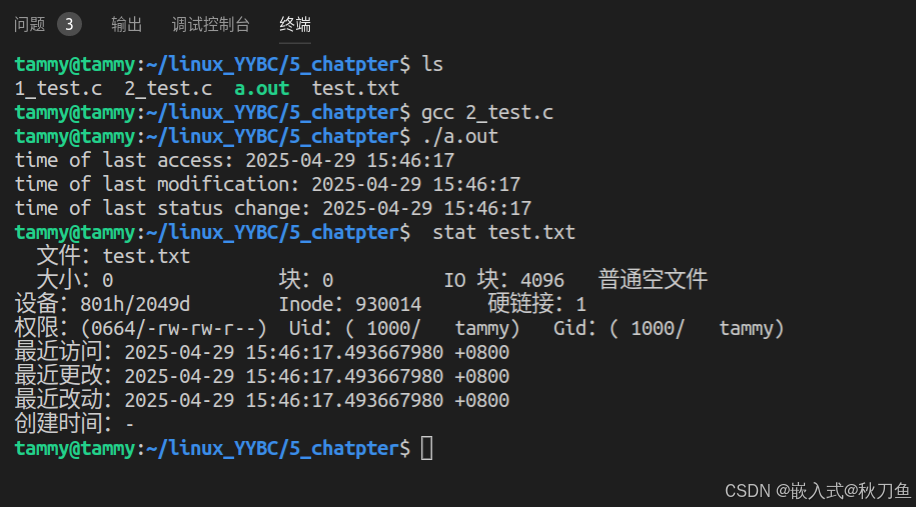
代码演示2:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <time.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int main() {
struct stat file_stat;
struct tm file_tm;
char time_str[100];
int ret;
//获取文件的属性
ret = stat("./test.txt",&file_stat);
if (-1 == ret)
{
perror("stat error");
return 1;
}
//打印文件内容的最后的被访问时间
localtime_r(&file_stat.st_atim.tv_sec, &file_tm);
strftime(time_str, sizeof(time_str),"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &file_tm);
printf("time of last access: %s\n", time_str);
/* 打印文件内容最后被修改的时间 */
localtime_r(&file_stat.st_mtim.tv_sec, &file_tm);
strftime(time_str, sizeof(time_str),"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &file_tm);
printf("time of last modification: %s\n", time_str);
/* 打印文件状态最后改变的时间 */
localtime_r(&file_stat.st_ctim.tv_sec, &file_tm);
strftime(time_str, sizeof(time_str),"%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S", &file_tm);
printf("time of last status change: %s\n", time_str);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
常见问题与建议
-
符号链接处理:
-
使用
lstat()获取链接自身信息,stat()会跟随链接到目标文件。
-
-
错误处理:
-
始终检查
stat()的返回值,避免未初始化结构体。
-
-
时间精度:
-
如需纳秒级时间戳,使用
st_atim(Linux 下为struct timespec类型,包含tv_sec和tv_nsec)。
-
























 2108
2108

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








