基础语法
目录
Java基础知识
1.注释,标识符,关键字
2.数据类型
3.类型转换
4.变量,常量
5.运算符
6.包机制,JavaDoc
1.注释,标识符,关键字
1.注释:
//单行注释
/* 多行注释*/
/** 文档注释/
//单行注释 /* 多行注释 */ /*** 文档注释 * ii. ;9ABH, * SA391, .r9GG35&G * &#ii13Gh; i3X31i;:,rB1 * iMs,:,i5895, .5G91:,:;:s1:8A * 33::::,,;5G5, ,58Si,,:::,sHX;iH1 * Sr.,:;rs13BBX35hh11511h5Shhh5S3GAXS:.,,::,,1AG3i,GG * .G51S511sr;;iiiishS8G89Shsrrsh59S;.,,,,,..5A85Si,h8 * :SB9s:,............................,,,.,,,SASh53h,1G. * .r18S;..,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,....,,.1H315199,rX, * ;S89s,..,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,....,,.......,,,;r1ShS8,;Xi * i55s:.........,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,.,,,......,.....,,....r9&5.:X1 * 59;.....,. .,,,,,,,,,,,... .............,..:1;.:&s * s8,..;53S5S3s. .,,,,,,,.,.. i15S5h1:.........,,,..,,:99 * 93.:39s:rSGB@A; ..,,,,..... .SG3hhh9G&BGi..,,,,,,,,,,,,.,83 * G5.G8 9#@@@@@X. .,,,,,,..... iA9,.S&B###@@Mr...,,,,,,,,..,.;Xh * Gs.X8 S@@@@@@@B:..,,,,,,,,,,. rA1 ,A@@@@@@@@@H:........,,,,,,.iX: * ;9. ,8A#@@@@@@#5,.,,,,,,,,,... 9A. 8@@@@@@@@@@M; ....,,,,,,,,S8 * X3 iS8XAHH8s.,,,,,,,,,,...,..58hH@@@@@@@@@Hs ...,,,,,,,:Gs * r8, ,,,...,,,,,,,,,,..... ,h8XABMMHX3r. .,,,,,,,.rX: * :9, . .:,..,:;;;::,.,,,,,.. .,,. ..,,,,,,.59 * .Si ,:.i8HBMMMMMB&5,.... . .,,,,,.sMr * SS :: h@@@@@@@@@@#; . ... . ..,,,,iM5 * 91 . ;:.,1&@@@@@@MXs. . .,,:,:&S * hS .... .:;,,,i3MMS1;..,..... . . ... ..,:,.99 * ,8; ..... .,:,..,8Ms:;,,,... .,::.83 * s&: .... .sS553B@@HX3s;,. .,;13h. .:::&1 * SXr . ...;s3G99XA&X88Shss11155hi. ,;:h&, * iH8: . .. ,;iiii;,::,,,,,. .;irHA * ,8X5; . ....... ,;iihS8Gi * 1831, .,;irrrrrs&@ * ;5A8r. .:;iiiiirrss1H * :X@H3s....... .,:;iii;iiiiirsrh * r#h:;,...,,.. .,,:;;;;;:::,... .:;;;;;;iiiirrss1 * ,M8 ..,....,.....,,::::::,,... . .,;;;iiiiiirss11h * 8B;.,,,,,,,.,..... . .. .:;;;;iirrsss111h * i@5,:::,,,,,,,,.... . . .:::;;;;;irrrss111111 * 9Bi,:,,,,...... ..r91;;;;;iirrsss1ss1111 */2.标识符
命名规范(以mouthSalary为例): -类名,MouthSalary -大驼峰:首字母大写和驼峰原则。其它命名采用小驼峰,需要见名知其意。 -常量,static final double MONTH_SALARY = 10000; -final 变量名 = 值; 注意:变量名大写加_ -类成员变量,static double mouthSalary = 10000; -从属于类,跟上static修饰符 -实例变量,double mouthSalary; -可以在类中进行调用 -局部变量,double mouthSalary = 10000; -只能在当前方法中使用//类,方法,变量都是标识符,取名要规范 开头用大小写字母或$或_,不使用关键字。最好不使用中文3.关键字
常用的关键字,也就只有这些,不多。
关键字 abstract assert boolean break byte case catch char class const countinue default do double else enum extends final finally float for goto if implements import instanceof int interface long native new package private protected public return strictfp short static super switch synchronized this throw throws transient try void volatile while
2.数据类型
1.java是强类型语言,变量名严格区分大小写,数据类型与值需要严格一致。
2.数据类型分为8大数据类型和引用数据类型
3.八大数据类型:整数型byte,short,int(常用),long,浮点型有float,double(常用),char类型,boolean类型。
引用数据类型:String字符串,类,接口,数组
代码演示
public static void main(String[] args){ //java是强类型语言,严格区分大小写,数据类型与值需要严格一致 JavaScript是弱类型语言 //8大基本数据类型 //整数类型 byte,short,int,long byte num1 = 10; short num2 = 20; int num3 = 30; //最常用 long num4 = 40l; //在long后面加l区分 //浮点类型 double num5 = 3.14; //最常用 float num6 = 3.141f; //在float后加f区分 //char 字符类型 char name = '兵'; String name1 = "冯总"; //String 不是基本数据类型 //boolean 布尔类型 boolean demo = true; boolean demo1 = false; /*浮点数拓展 *银行业务拓展时候,使用BigDecimal类 * 避免使用浮点数进行比较 * * */ float num7 = 1233333333333f; float num8 = num7 + 1; System.out.print("--浮点数拓展--\n"); System.out.print(num7 == num8); //当num7小的时候,结果不等。当num7很大的时候,结果相等。因为浮点数有舍入误差 //char字符类型拓展 char c1 = 'a'; char c2 = '兵'; System.out.print("\n--字符类型拓展--\n"); System.out.println(c1); System.out.println((int)c1); //强制转换 转换为数字 System.out.println(c2); System.out.println((int)c2); //强制转换 //所有的字符本质 还是数字 //转义字符 // \t 制表符tab \n 换行 System.out.print("\n--转义字符--\n"); System.out.println("Hello\tWorld"); //对象 从内存分析 System.out.println("----"); String sa =new String("hello world"); String sb =new String("hello world"); System.out.println(sa == sb); String sc = "hello world"; String sd = "hello world"; System.out.println(sc == sd); //boolean 拓展 boolean bool = true; if (bool==true){} //新手 if(bool){} //老手 }
3.类型转换
1.根据存储大小排序 byte,short,char,int,long,float,double
运算中,不同类型需要转化为同意类型,再进行计算
2.类型转换分为,自动转换和强制转换
3.自动转换是 由低--高的存储空间。强制转换由高--低的存储空间。
-强制转换格式:(类型)变量名,byte b = (byte)i ,将 i 转换为byte类型
代码演示
/*java是强类型语言,运算时,需要用到类型转换。byte,short,char,int,long,float,double 运算中,不同类型需要转化为同一类型,再进行计算 转换分为 强制类型和自动类型转换 */ int i =127; byte b = (byte)i; //强制转换 格式:(类型)变量名 由高--低 System.out.println(b); float f = i; System.out.println(f);//自动转换 由低--高 /* 注意点: 1.高容量转为低容量,强制转换 2.转换的时候注意容量溢出,或者精度问题 */ System.out.println("--转换精度问题--"); System.out.println((int)34.1); //34 System.out.println((int)-24.2); //24 System.out.println("--字符转换编码--"); char c = 'a'; int in = c + 1; //自动转换 System.out.println(in); //98 System.out.println((char)in);// b //如果我查 冯,的编码 char char1 = '冯'; System.out.println((int)char1); //20911 //操作数比较大的时候,注意数据溢出 System.out.println("--思考溢出问题--"); int money =10_0000_0000; int years = 20; int total = money * years; System.out.println(total); //计算值已经溢出了 long total1 = money * years; System.out.println(total1);//long值可以装下 但是计算值还是溢出了。可能是计算了int类型 long total2 = money * (long)years; System.out.println(total2);//计算成功了,将变量years转换为long类型 }
4.变量,常量
1.变量:局部变量,放在某一方法中,且只能本方法内使用。
实例变量,从属于对象,放在类里方法外
类成员变量,从属于类,放在类里方法外,用static修饰符修饰。
2.常量:常量的值不能修改。放在类里方法外,格式: final 常量名(大写)=值
变量_代码演示
static double salary = 1000; //类成员变量,从属于类在方法外。用static声明 int int1; //实例变量,从属于对象在方法外。 float float1;//0.0 如果不设置初始值,默认值0,0.0,布尔型false,char是个符号,引用类型null char char1; //打不出来 boolean boolean1;//false String String1; //null public static void main(String[] args) { int i1=9,i2=8,i3=7; //局部变量(在方法内,在其它方法不能用),必须声明和初始化值。可以声明多个同类型变量,但代码可读性较差,不建议写在一行 变量 bl = new 变量(); System.out.println(bl.char1); System.out.println(bl.String1);//调用实例变量 System.out.println(salary); }常量_代码演示
//常量值不可修改,常量用final来定义,常量名需要大写。 //声明的浮点型变量double前的都称为修饰符,修饰符部分前后顺序 static final double PI = 3.14;//static类变量 格式: final 常量名(大写)=值; public static void main(String[] args) { }
5.基本运算符
1.基本运算符; -算术运算符:+,-,*,/,%,++,--,其中a++是先赋值给变量名,再自增;++a是先自增,再赋值。 -赋值运算符:= -关系运算符:>,<,>=,<=,==,!=,instanceof -逻辑运算符:&&,||,! -位运算符:&,|,^,~,>>,<<,>>> 了解 -条件运算符:? : -拓展赋值运算符:+=,-=,*=,/=算术运算符
public static void main(String[] args) { //算术运算符 int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 30; int d = 40; System.out.println("加法"+(a+b)); System.out.println("减法"+(a-b)); System.out.println("乘法"+a*b); System.out.println("除法"+a/(double)b); //0.5,需要转换一下数据类型 System.out.println("取余"+a%b); }public static void main(String[] args) { //算数运算符 long a = 123123123123L; int b = 123; short c = 10; byte d = 8; double e = 1.1; System.out.println(a+b+c+d);//long类型 计算中有long类型,结果为long类型。否则就是int类型 System.out.println(b+c+d);//int类型 System.out.println((double) c+d);//int类型 System.out.println(a+e);//double类型 //调用Math类 double pow = Math.pow(3,2); System.out.println(pow); }public static void main(String[] args) { //++ -- 自增,自减 int a = 3; int b = a++; //先赋值,后自增 System.out.println(a);//4 System.out.println(b);//3 int a1 = 3; int b1 = ++a1;//先自增,后赋值 System.out.println(a1);//4 System.out.println(b1);//4 int c = ++a; System.out.println(a); System.out.println(b); System.out.println(c); }关系运算符
public static void main(String[] args) { //关系运算符返回结果: ture false int a = 10; int b = 20; int c = 33; System.out.println(a>b); System.out.println(a<b); System.out.println(a==b); System.out.println(a!=b); }逻辑运算符
public static void main(String[] args) { //&&与 ||或 !非 boolean a = true; boolean b = false; System.out.println("a&&b:"+(a&&b));//&&与运算,有假则为假 System.out.println("a||b:"+(a||b));// || 或运算,有真则为真 System.out.println("!(a||b)"+(!a||b));// !非运算 //短路运算 int c = 5; // false boolean d = (c<4)&&(c++<4);//在与运算中,若前面为false则跳过。 System.out.println(d); System.out.println(c); }位运算符
public static void main(String[] args) { /* A=0011 1100 B=0000 1101 ------------------ A&B =0000 1100 有0则0 A|B =0011 1101 有1则1 A^B =0011 0001 同0异1 ~B=1111 0010 */ // <<表示2^ >>表示/2 //若求 24,24=6*4=6*(2^2) or 24=3*8=3*(2^3) System.out.println(6<<2); System.out.println(3<<3); }条件运算符
public static void main(String[] args) { //条件 x?y : z //如果 x==true,则返回y,否则为z int score = 50; String type = score<60?"不及格":"及格"; System.out.println(type); //赋值运算 int a = 10; int b = 20; System.out.println(a+=b);//a=a+b 30=10+20 System.out.println(a-=b);//a=a-b 10=30-20 //字符串连接符 + System.out.println(""+a+b);//拼接 System.out.println(a+b+""); }
6.包机制,JavaDoc
1.包机制,命名java包,一般采用公司域名倒置命名。例如com.baidu.www.
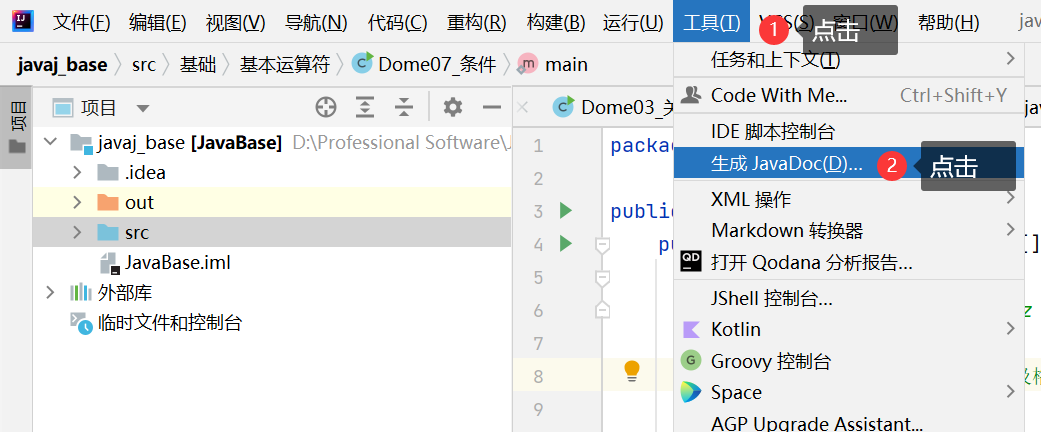
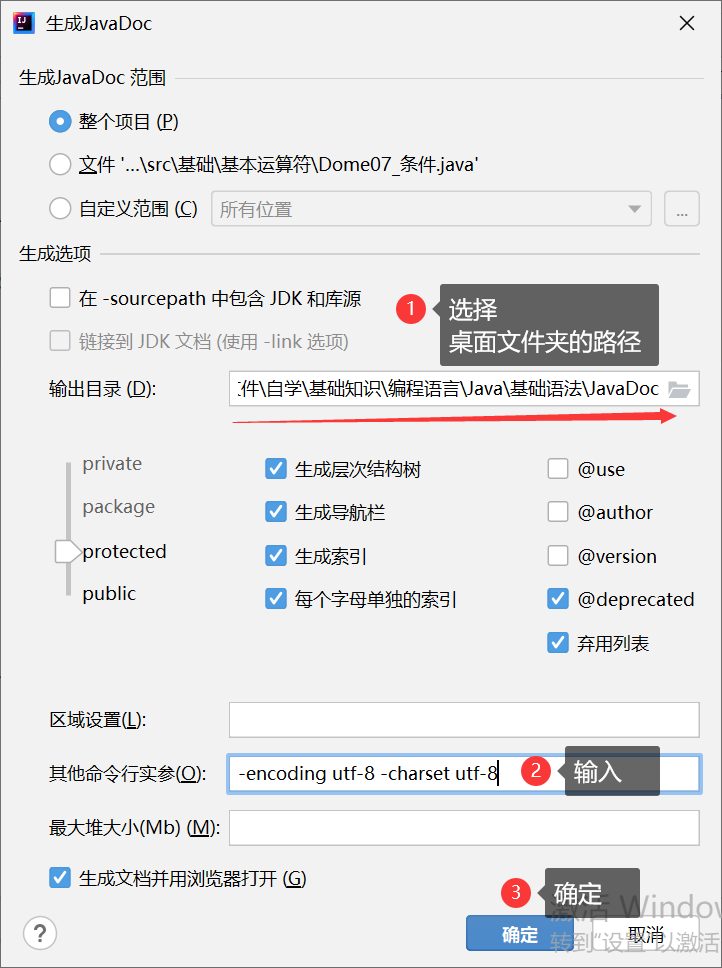
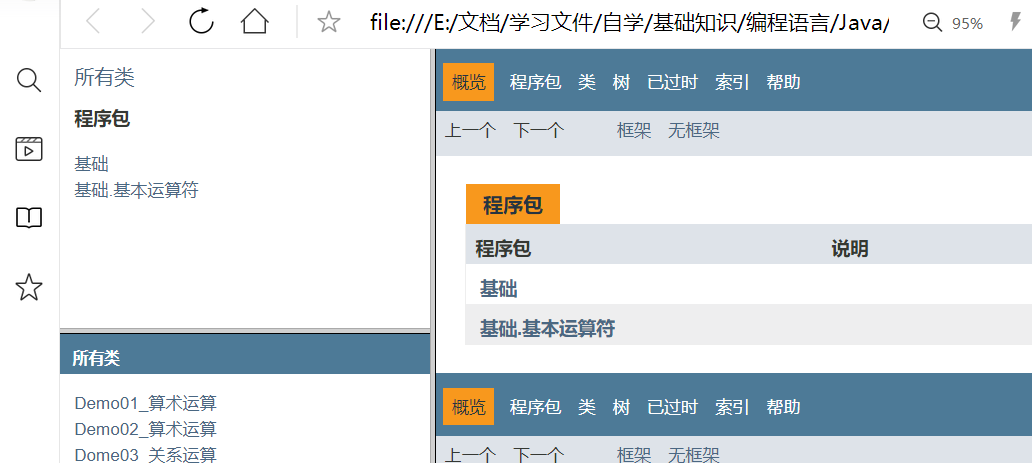
2.使用IDEA生成JavaDoc文档
手把手步骤:





 这篇博客详细介绍了Java的基础语法,包括注释、标识符、关键字、数据类型、类型转换、变量与常量、运算符以及包机制和JavaDoc的使用。内容覆盖了Java初学者所需掌握的关键知识点。
这篇博客详细介绍了Java的基础语法,包括注释、标识符、关键字、数据类型、类型转换、变量与常量、运算符以及包机制和JavaDoc的使用。内容覆盖了Java初学者所需掌握的关键知识点。



















 2084
2084












