实验三内容展示:

图一 实验三内容展示
实验任务1.(数据结构之链表)
1. 编写程序link.h,实现教材例9-6的链表类,在测试程序中声明两个整型链表A和B,分别插入5个元素,并把B中元素加入A的尾部。
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
// 定义链表节点的结构
template <typename T>
class SListNode {
public:
T data; // 存储的数据
SListNode* next; // 指向下一个节点的地址
SListNode(T val) : data(val), next(nullptr) {}
};
// 链表的类模板
template <typename T>
class SinglyLinkedList {
private:
SListNode<T>* head; // 链表的头指针
public:
// 构造函数
SinglyLinkedList() : head(nullptr) {}
// 析构函数
~SinglyLinkedList() {
clear();
}
// 清空链表
void clear() {
SListNode<T>* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
SListNode<T>* next = current->next;
delete current;
current = next;
}
head = nullptr;
}
// 尾插法
void pushBack(T x) {
SListNode<T>* newNode = new SListNode<T>(x);
if (head == nullptr) {
head = newNode;
}
else {
SListNode<T>* current = head;
while (current->next != nullptr) {
current = current->next;
}
current->next = newNode;
}
}
// 头插法
void pushFront(T x) {
SListNode<T>* newNode = new SListNode<T>(x);
newNode->next = head;
head = newNode;
}
// 尾删除
void popBack() {
assert(head != nullptr && "Cannot pop from an empty list");
if (head->next == nullptr) {
delete head;
head = nullptr;
}
else {
SListNode<T>* current = head;
while (current->next->next != nullptr) {
current = current->next;
}
delete current->next;
current->next = nullptr;
}
}
// 头删除
void popFront() {
assert(head != nullptr && "Cannot pop from an empty list");
SListNode<T>* nextNode = head->next;
delete head;
head = nextNode;
}
// 打印链表
void print() const {
SListNode<T>* current = head;
while (current != nullptr) {
cout << current->data << " ";
current = current->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
};这个测试比较简单,就不单独拿出来了。
实验任务2.(数据结构之栈,队列)
2. 下面任务二选一,也可双选:
(1)编写程序queue.h,用链表实现队列类。在测试程序中声明一个整型队列对象,插入5个整数,压入队列,再依据顺序取出并显示出来。
(2)编写程序stack.h,用链表实现栈类。在测试程序中声明一个整型栈对象,插入5个整数,压入栈,再依据相应顺序取出并显示出来。
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
template <typename T>
struct QueueNode {
T val;
QueueNode* next;
QueueNode(T v) : val(v), next(nullptr) {}
};
template <typename T>
class Queue {
private:
QueueNode<T>* phead;
QueueNode<T>* ptail;
int size;
public:
Queue() : phead(nullptr), ptail(nullptr), size(0) {}
~Queue() {
QueueDestroy();
}
void QueueInit() {
phead = ptail = nullptr;
size = 0;
}
void QueueDestroy() {
while (phead != nullptr) {
QueueNode<T>* next = phead->next;
delete phead;
phead = next;
}
ptail = nullptr;
size = 0;
}
void QueuePush(T x) {
QueueNode<T>* newNode = new QueueNode<T>(x);
if (ptail == nullptr) {
phead = ptail = newNode;
}
else {
ptail->next = newNode;
ptail = newNode;
}
size++;
}
void QueuePop() {
assert(phead != nullptr && "Cannot pop from an empty queue");
QueueNode<T>* temp = phead;
phead = phead->next;
if (phead == nullptr) {
ptail = nullptr;
}
delete temp;
size--;
}
T QueueFront() const {
assert(phead != nullptr && "Front called on empty queue");
return phead->val;
}
T QueueBack() const {
assert(ptail != nullptr && "Back called on empty queue");
return ptail->val;
}
bool QueueEmpty() const {
return phead == nullptr;
}
int QueueSize() const {
return size;
}
};分别写到queue.h和stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
template <typename T>
class Stack {
private:
T* a; // 存储栈内元素的数组
int top; // 栈顶索引
int capacity; // 栈的最大容量
public:
// 构造函数
Stack(int size = 10) : capacity(size), top(-1) {
a = new T[capacity];
}
// 析构函数
~Stack() {
destroy();
}
// 初始化栈
void init() {
top = -1;
}
// 销毁栈,释放内存
void destroy() {
delete[] a;
a = nullptr;
top = -1;
capacity = 0;
}
// 压栈操作
void push(T x) {
if (top == capacity) {
int newcapacity = capacity * 2;
T* tmp = (T*)realloc(a, newcapacity * sizeof(T));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
a = tmp;
}
a[++top] = x;
}
// 出栈操作
void pop() {
assert(top > -1 && "Stack underflow");
top--;
}
// 获取栈顶元素
T topValue() const {
assert(top > -1 && "Stack is empty");
return a[top];
}
// 获取栈的大小
int size() const {
return top + 1;
}
// 检查栈是否为空
bool empty() const {
return top == -1;
}
};实验任务3.(排序算法)
3. 将直接插入排序、直接选择排序、冒泡排序与顺序查找函数封装到数组类中,作为成员函数,实现并设计这个类。
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <utility> // For std::swap
template <typename T>
class Array {
private:
T* data;
size_t capacity;
size_t length;
public:
// 构造函数
Array(size_t size) : capacity(size), length(0), data(new T[size]) {}
// 析构函数
~Array() {
delete[] data;
}
// 禁止拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符
Array(const Array&) = delete;
Array& operator=(const Array&) = delete;
// 插入元素
void insert(const T& value) {
if (length >= capacity) {
capacity *= 2;
T* tmp = (T*)realloc(data, sizeof(T) * capacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
data = tmp;
}
data[length++] = value;
}
// 直接插入排序
void insertionSort() {
for (size_t i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
T key = data[i];
//j一定从后往前来,避免覆盖掉已有元素
size_t j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && data[j] > key) {
data[j + 1] = data[j];
--j;
}
data[j + 1] = key;
}
}
/*
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
// [0, end] end+1
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + 1];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (tmp < a[end])
{
a[end + 1] = a[end];
--end;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + 1] = tmp;
}
}
*/
// 直接选择排序
void selectionSort() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length - 1; ++i) {
size_t minIndex = i;
for (size_t j = i + 1; j < length; ++j) {
if (data[j] < data[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
std::swap(data[minIndex], data[i]);
}
}
// 冒泡排序
void bubbleSort() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length - 1; ++i) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < length - i - 1; ++j) {
if (data[j] > data[j + 1]) {
std::swap(data[j], data[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
// 顺序查找
size_t linearSearch(const T& value) const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
if (data[i] == value) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // Not found
}
// 打印数组
void print() const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
std::cout << data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void print_pointer() const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
std::cout << *(T*)data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 获取数组长度
size_t size() const {
return length;
}
};这里试图写通过cout遍历打印的函数,数据是指针类型的没有成功。
实验任务4.(综合系统实现)
4. 声明一个对people类对象数组按编号排序的函数,一个按编号查找people对象的函数。在测试程序中使用前面实验得到的结果声明教师数组和学生数组,分别对你教师数组和学生数组进行排序和查找。
原有的函数不够用,新写一点东西,让他适应更强大的功能
#pragma once
#include <iostream>
#include <utility> // For std::swap
template <typename T>
class Array {
private:
T* data;
size_t capacity;
size_t length;
public:
// 构造函数
Array(size_t size) : capacity(size), length(0), data(new T[size]) {}
// 析构函数
~Array() {
delete[] data;
}
// 禁止拷贝构造函数和赋值运算符
Array(const Array&) = delete;
Array& operator=(const Array&) = delete;
// 插入元素
void insert(const T& value) {
if (length >= capacity) {
capacity *= 2;
T* tmp = (T*)realloc(data, sizeof(T) * capacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail");
return;
}
data = tmp;
}
data[length++] = value;
}
// 直接插入排序
void insertionSort() {
for (size_t i = 1; i < length; ++i) {
T key = data[i];
//j一定从后往前来,避免覆盖掉已有元素
size_t j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && data[j] > key) {
data[j + 1] = data[j];
--j;
}
data[j + 1] = key;
}
}
/*
void InsertSort(int* a, int n)
{
for (int i = 0; i < n-1; i++)
{
// [0, end] end+1
int end = i;
int tmp = a[end + 1];
while (end >= 0)
{
if (tmp < a[end])
{
a[end + 1] = a[end];
--end;
}
else
{
break;
}
}
a[end + 1] = tmp;
}
}
*/
// 直接选择排序
void selectionSort() {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length - 1; ++i) {
size_t minIndex = i;
for (size_t j = i + 1; j < length; ++j) {
if (data[j] < data[minIndex]) {
minIndex = j;
}
}
std::swap(data[minIndex], data[i]);
}
}
// 冒泡排序
void bubbleSort(int (*cmp)(const void* p1, const void* p2)) {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length - 1; ++i) {
for (size_t j = 0; j < length - i - 1; ++j) {
if (cmp(data[j], data[j + 1]) > 0) {
std::swap(data[j], data[j + 1]);
}
}
}
}
// 顺序查找
size_t linearSearch(void* value,int(*cmp)(const void* p1, const void* p2)) const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
if (cmp(data[i], value)) {
return i;
}
}
return -1; // Not found
}
// 打印数组
void print() const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
std::cout << data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
void print_pointer() const {
for (size_t i = 0; i < length; ++i) {
std::cout << *(T*)data[i] << " ";
}
std::cout << std::endl;
}
// 获取数组长度
size_t size() const {
return length;
}
T* getpointer() {
return data;
}
};这下,比较就可以写各种比较方式了,按什么查找也可以写相应的方法函数
#include "link.h"
#include "queue.h"
#include "stack.h"
#include "array_sort.h"
#include "test_people.h"
int cmp_num(const void* p1, const void* p2)
{
civil* pp1 = (civil*)p1;
civil* pp2 = (civil*)p2;
return pp1->num-pp2->num;
}
int cmp_search(const void* p1, const void* p2) {
civil* pp1 = (civil*)p1;
string* pp2 = (string*)p2;
return pp1->identified() == (*pp2);
}
int test2() {
civil* cp = nullptr;
Student* s1 = new Student("张三", 1, "211103000012030000", MAN);
Student* s2 = new Student("张三三", 5, "211103000012030004", MAN);
Teacher* t1 = new Teacher("李四", 2, "211003000012030001", MAN);
DoctorHelpTeacher* Dht1 = new DoctorHelpTeacher("王五", 3, "211003000012030002", MAN);
Doctor* D1 = new Doctor("赵六", 4, "211003000012030003", MAN);
Array<civil*> arr_stu(1);
arr_stu.insert(s1);
arr_stu.insert(D1);
arr_stu.insert(Dht1);
arr_stu.insert(s2);
//插入数量超额自动扩容为二倍
// arr_stu.print_pointer();
for (int i = 0; i < arr_stu.size();i++) {
arr_stu.getpointer()[i]->printinfo(cout);
}
cout << "排序后" << endl;
arr_stu.bubbleSort(cmp_num);
for (int i = 0; i < arr_stu.size(); i++) {
arr_stu.getpointer()[i]->printinfo(cout);
}
string tmp = "211103000012030004";
cout << arr_stu.linearSearch(&tmp,cmp_search);
Array<civil*> arr_teacher(1);
arr_teacher.insert(Dht1);
arr_teacher.insert(t1);
// arr_teacher.print_pointer();
return 0;
}这里学生和老师类一样就没再测试,我们看看这段测试代码的输出结果吧
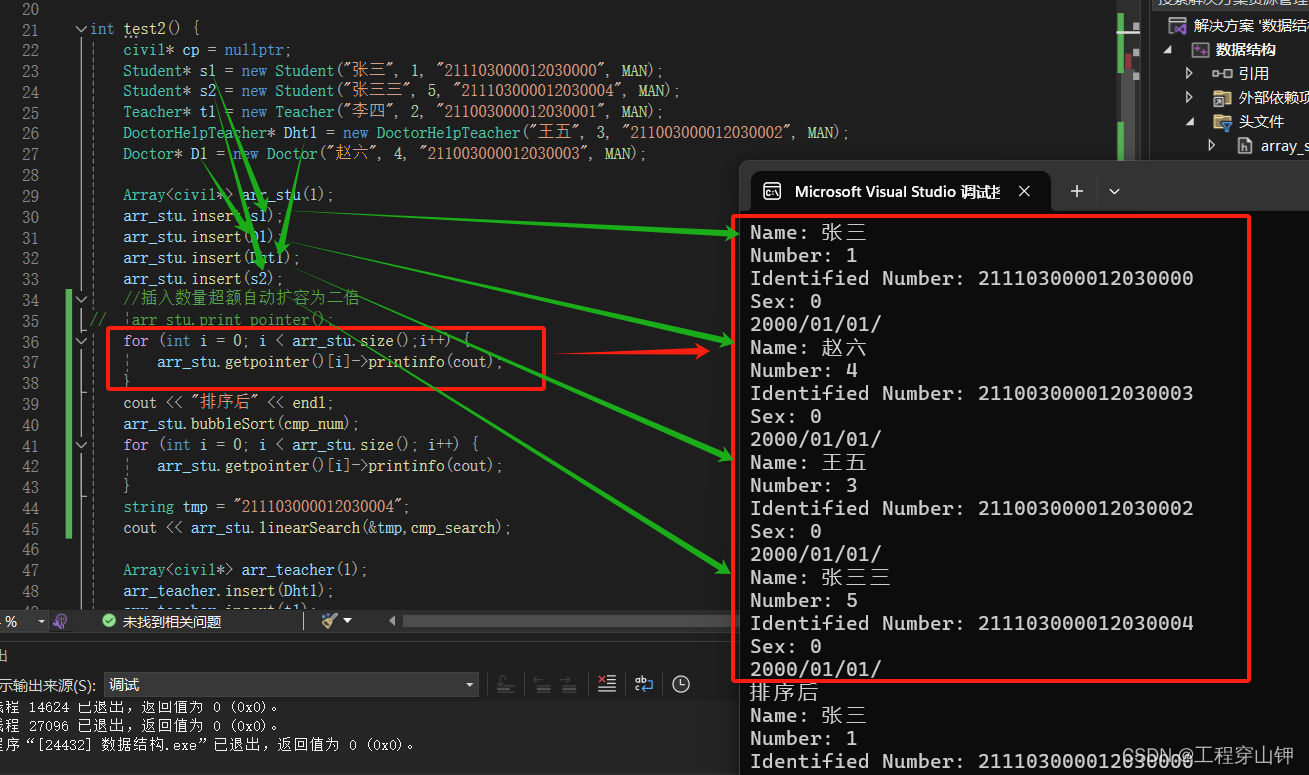 先看排序前,数据与插入时一一对应,证明正确。
先看排序前,数据与插入时一一对应,证明正确。
接下来看排序后
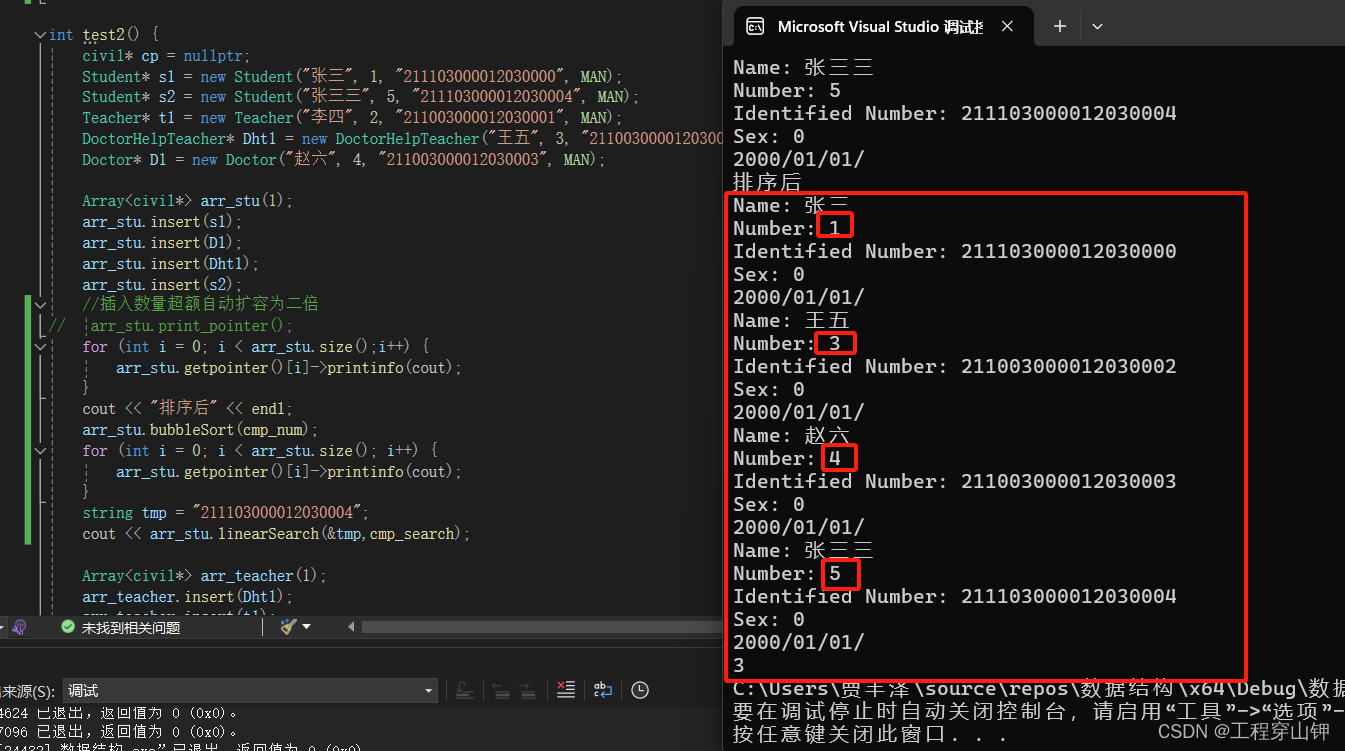 是按序号顺序,说明排序没问题。
是按序号顺序,说明排序没问题。
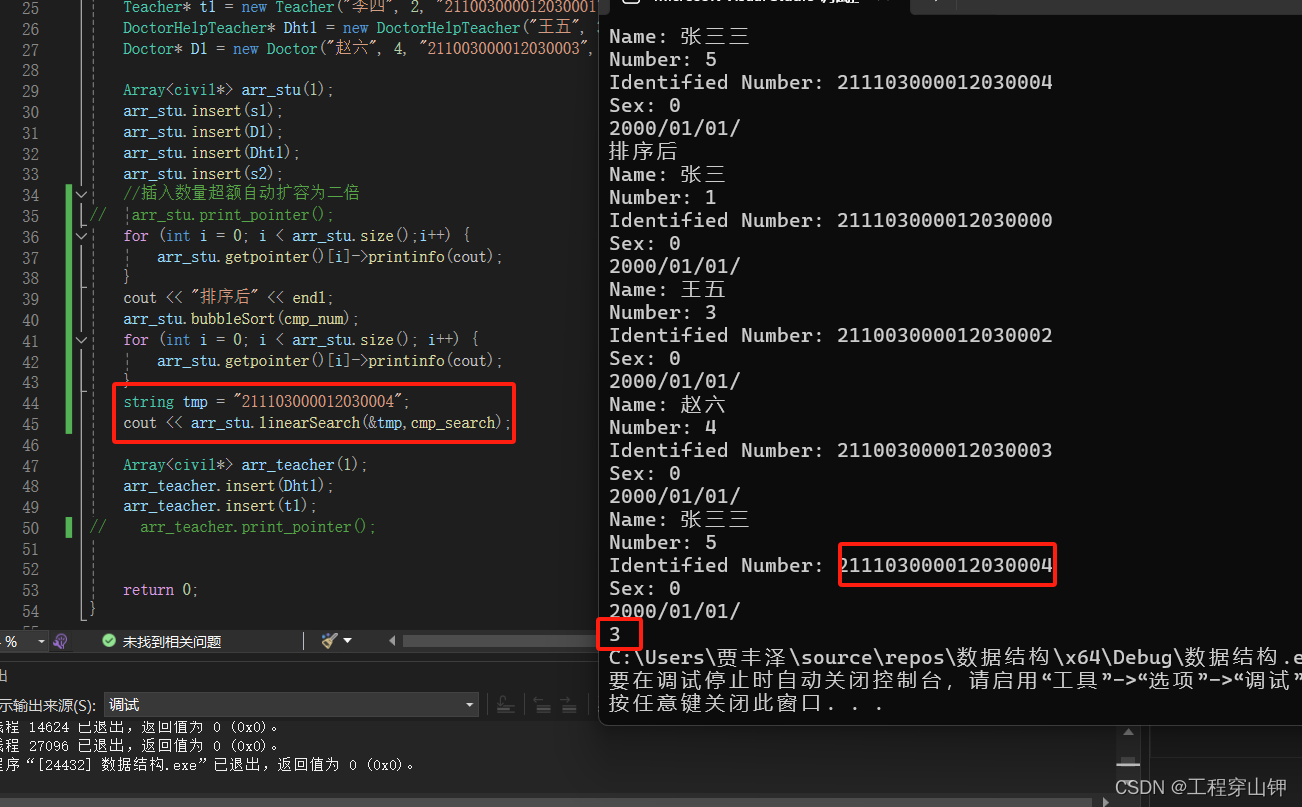 打印出了查找到的学生的下标,说明查找没错
打印出了查找到的学生的下标,说明查找没错
这种回调函数使用方法可以查找相关博客




















 3012
3012

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








