POJ:http://poj.org/problem?id=2528
这两天在学习线段树算法,参考了网上许多线段树的资料,用Google搜一下,就能搜到很多,这里就不详细解释什么事线段树了。
线段树在解决区间重合问题,比如求一段区间,最大值,最小值,求和等问题非常有效,一次查询的时间复杂度是log(n),时间复杂度非常理想。
题目大意:在墙壁上贴广告,广告的版面有大有小,并且贴广告有先后之分,后面贴的广告会覆盖前面的广告,求解最后能看到的广告面,如下图所示:
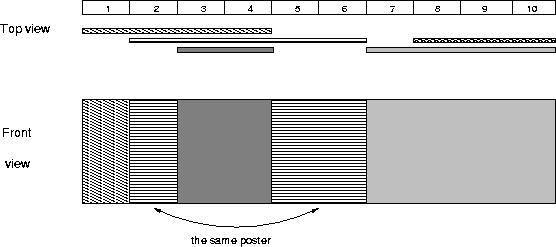
两种视图,最后从From View能看见的广告数目是4。
题目分析:这里面不仅用到了线段树,还用到了离散化方法,意思是将区间范围很大的数据集映射到较小的数据集,这样构造线段树更加高效,具体方法就是把所有线段的端点排序,从左至右,一次编号(两条线段相同的端点,用同一个编号),并且将新的编号替代原来的端点值,这样既不改变各个线段的性质,同时能够缩小数据范围。
具体代码如下:
/*
* my_poj2528.cpp
*
* Created on: 2012-6-15
* Author: ict
*/
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
#define MAX 20010
#define LC(x) ((x) << 1) //计算左孩子位置
#define RC(x) (((x) << 1) + 1) //计算右孩子位置
struct Node
{
int l; //线段左端点值
int r; //线段右端点
int c; //线段的颜色
}nodes[MAX * 5];
int map[MAX][2]; //记录输入线段的左右两个端点
int record[MAX]; //记录颜色是否已经出现
int total;
//用于离散化
struct Line
{
int point; //记录端点的坐标
int num; //记录原来的编号
}line[MAX * 2];
int mycmp(const Line &a, const Line &b)
{
return a.point < b.point;
}
void buildTree(int l, int r, int position)
{
nodes[position].l = l;
nodes[position].r = r;
nodes[position].c = 0; //初始化颜色都为0
if(l == r)
return ;
int mid = (l + r) >> 1;
buildTree(l, mid, LC(position)); //构造左子树
buildTree(mid + 1, r, RC(position)); //构造右子树
return ;
}
/*
* @para l, r: 线段的左、右端点
* @para position: 插入树的位置
* @para color: 线段的颜色
*/
void insert(int l, int r, int position, int color)
{
if(nodes[position].l == l && nodes[position].r == r) //刚好覆盖,修改颜色,直接返回
{
nodes[position].c = color;
return ;
}
if(nodes[position].c > 0) //如果当前线段已经有颜色,先将颜色复制给左右两个子树,非常重要
{
nodes[LC(position)].c = nodes[position].c;
nodes[RC(position)].c = nodes[position].c;
nodes[position].c = 0; //标记线段没有颜色
}
if(l >= nodes[RC(position)].l) //完全在右子树
insert(l, r, RC(position), color);
else
if(r <= nodes[LC(position)].r) //完全在左子树
insert(l, r, LC(position), color);
else //两个子树都有
{
insert(l, nodes[LC(position)].r, LC(position), color);
insert(nodes[RC(position)].l, r, RC(position), color);
}
}
/*
* @para position: 查询指定线段的颜色
*/
void update(int position)
{
if(nodes[position].c != 0) //如果当前线段有颜色,记录,并且直接返回
{
if(!record[nodes[position].c])
{
total++;
record[nodes[position].c] = 1;
}
return ;
}
//如果当前线段没有颜色,递归调用左右子树,查询颜色
update(LC(position));
update(RC(position));
return ;
}
int main()
{
int number;
int n;
int i;
scanf("%d", &number);
while(number--)
{
scanf("%d", &n);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
scanf("%d%d", &map[i][0], &map[i][1]);
line[2*i].point = map[i][0]; //记录数据,用于离散化
line[2*i + 1].point = map[i][1];
line[2*i].num = -(i + 1); //线段第一个端点用负数记录
line[2*i + 1].num = i + 1; //线段第二个端点用正数记录
}
//首先将所有端点排序
sort(line, line + 2*n, mycmp);
int temp = line[0].point;
int count = 1; //重新开始编号,从1开始
for(i = 0; i < 2*n; i++)
{
if(temp != line[i].point) //如果当前端点和前面的端点不一样,编号值+1
{
count++;
temp = line[i].point;
}
if(line[i].num < 0)
map[-line[i].num - 1][0] = count;
else
map[line[i].num - 1][1] = count;
}
buildTree(1, count, 1);
for(i = 0; i < n; i++)
insert(map[i][0], map[i][1], 1, i + 1);
memset(record, 0, sizeof(record));
total = 0;
update(1);
printf("%d\n", total);
}
return 0;
}





 本文介绍了如何运用线段树和离散化方法解决广告贴图问题,通过实例展示了算法的实现过程及优化策略。
本文介绍了如何运用线段树和离散化方法解决广告贴图问题,通过实例展示了算法的实现过程及优化策略。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








