断言
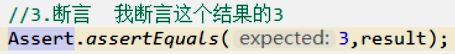 前面是期望的值,后面是真正的值 Assert.assertEquals(期望的结果,运算的结果)
前面是期望的值,后面是真正的值 Assert.assertEquals(期望的结果,运算的结果)
反射
类名.class() 对象.getClass() Class.forName(包名.类名)
返回的是Class
获取构造方法(没有Declared获取的都是公共的)
c.getConstructors() 获取class文件对象中的所有公共的构造方法 返回的是Constructor [ ]
c.getConstructor() 获取指定的构造方法 如:空参构造方法 返回的是Constructor
运行无参数构造方法 newInstance()
有参构造方法c.get Constructor(int.class,String.class) 传递要获取的构造方法的参数列表 返回的是Constructor 有参数构造方c.newInstance(15,”张三”); 返回的是Object
c.getDeclaredConstructors() 获取所有的构造方法 包括私有的 返回的是Constructor [ ]
c.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,String.class) 获取指定的私有的构造方法
c.setAccessible(true)
获取成员变量(没有Declared获取的都是公共的)
c.getFields() 获取公共的成员变量 返回的是Field [ ]
c.getField(传递字符串类型的变量名) 返回的是Field field
设置值:field.set(Object obj, Object value)
Object obj 必须有对象的支持, Object value 修改后的值
c.getMethods() 获取的是class文件中所有公共成员方法,包括继承 返回的是 Method[]
c.getMethod(String methodName,Class .. c) 获取的是指定的方法
methodName获取的是方法名 c 获取的是参数列表
运行获取到的方法method.invoke(obj,Object…o)
网络编程
网络编程三要素:IP地址 端口 协议
返回本地主机: 静态方法 InetAddress.getLocalHost() 返回值是InetAddress对象
非静态方法: getHostAddress() 获取主机IP地址 getHostName() 获取主机名
传递主机名,获取IP对象(拿到别人的):InetAddress.getByName(String hostName);
UDP:无连接通信协议
TCP:面向连接的通信协议,每次连接都需要经过“三次握手”
第一次握手,客户端向服务器端发出连接请求,等待服务器确认
第二次握手:服务器端向客户端回送一个响应,通知客户端收到了请求
第三次握手:客户端再次向服务器端发送确认信息,确认连接
DatagramePacket:封装的(类似“集装箱”)
DatagramSocket:运输的
实现UDP协议的发送端:
- 创建DatagramPacket对象,封装数据,长度,接收的地址和端口
- 创建DatagramSocket
- 调用DatagramSocket类方法send,发送数据包
- 关闭资源
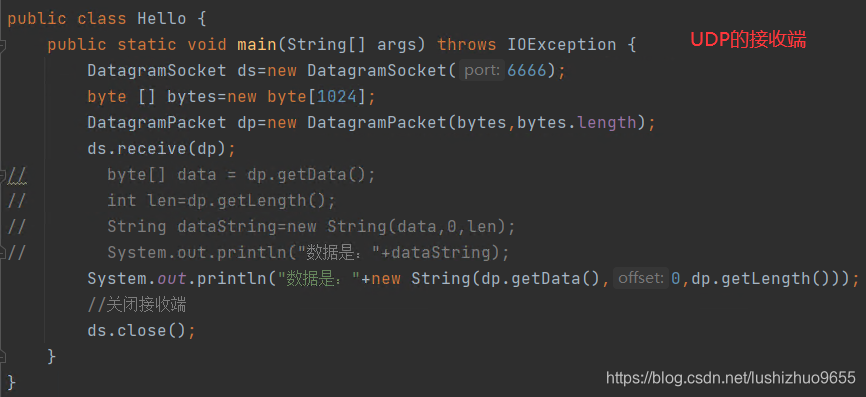
实现UDP协议的接收端:
1. 创建DatagramSocket对象,绑定端口号 要和发送端端口号一致
2. 创建字节数组,接收发来的数据
3. 创建数据包对象DatagramPacket
4. 调用DatagramSocket对象方法 receive(DatagramPacket dp)接收数据,数据放在数据包中
5. 拆包
发送的IP地址
数据包对象DatagramPacket方法getAddress()获取的是发送端的IP地址对象
返回值是InetAddress对象
接收到的字节个数 数据包对象DatagramPacket方法 getLength()
发送方的端口号 数据包对象DatagramPacket方法 getPort()
关闭资源
UDP通信只有发送端和接收端,不区分客户端与服务器端
TCP通信严格区分客户端和服务器端
ServerSocket类,用于表示服务器端,Socket类表示客户端
客户端:
Socket(String host ,int port):传递服务器IP和端口号
socket.getOutputStream() socket.getInputStream()
服务器端
ServerSocket(int port) 传递端口号 serverSocket.accept()
必须获得客户端的套接字对象Socket
服务器读取客户端的字节数组,永远也不会读到-1,因此一直等待
需要在客户端里面写socket.shutdownOutput ()
问题:
新增:UDP通信程序练习
按照下面的要求实现程序
UPD发送数据:数据来自键盘录入,知道输入的数据是886,发送数据结束
UDP接收数据:因为接收端不知道发送端什么时候停止发送,故采用死循环接收
public class UDPSend {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
if("886".equals(line)){
break;
}
byte [] bytes=line.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length,InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"),6666);
ds.send(dp);
}
ds.close();
}
}
public class UDPReceive {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(6666);
while (true){
byte [] bytes=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length);
ds.receive(dp);
System.out.println("数据是:"+new String(dp.getData(),0,dp.getLength()));
}
}
}
新增:TCP通信程序练习
客户端:数据来自于键盘录入,知道输入的数据是886,发送数据结束
服务端:接收到的数据在控制台输出
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null){
if("886".equals(line)){
break;
}
/* OutputStream os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write(line.getBytes());*/
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
socket.close();
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String line;
while ((line=br.readLine())!=null) {
System.out.println(line);
}
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
新增:TCP通信程序练习
客户端:数据来自于键盘录入,直到输入的数据是886,发送数据结束
服务端:接收到的数据写入文本文件
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
if("886".equals(line)){
break;
}
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
socket.close();
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("untitled\\demo.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
新增:TCP通信程序练习
客户端:数据来自文本文件
服务端:接收到的数据写入文本文件
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\项目实战\\1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
br.close();
socket.close();
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("untitled\\demo.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
bw.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
新增:TCP通信程序练习
客户端:数据来自文本文件,接收服务器反馈
服务端:接收到的数据写入文本文件,给出反馈
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\项目实战\\1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
socket.shutdownOutput();
//给出反馈
BufferedReader brClient=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String data = brClient.readLine();
System.out.println("服务器的反馈是: "+data);
br.close();
socket.close();
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
Socket socket = ss.accept();
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("untitled\\demo.txt"));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//给出反馈
BufferedWriter bwServer=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
bwServer.write("文件上次成功");
bwServer.newLine();
bwServer.flush();
bw.close();
socket.close();
ss.close();
}
}
新增:TCP通信程序练习
客户端:数据来自文本文件,接收服务器反馈
服务端:接收到的数据写入文本文件,给出反馈,代码用线程进行封装,为每一个客户端开启一个线程
public class ClientDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",6666);
BufferedReader br=new BufferedReader(new FileReader("F:\\项目实战\\1.txt"));
BufferedWriter bw=new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(socket.getOutputStream()));
String line;
while((line=br.readLine())!=null){
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
socket.shutdownOutput();
//给出反馈
BufferedReader brClient=new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(socket.getInputStream()));
String data = brClient.readLine();
System.out.println("服务器的反馈是: "+data);
br.close();
socket.close();
}
}
public class ServerThread implements Runnable {
private Socket s;
public ServerThread(Socket s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
//接收数据写到文本文件
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(s.getInputStream()));
// BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("myNet\\Copy.java"));
//解决名称冲突问题
int count = 0;
File file = new File("untitled\\Copy[" + count + "].java");
while (file.exists()) {
count++;
file = new File("untitled\\Copy[" + count + "].java");
}
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter(file));
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
bw.write(line);
bw.newLine();
bw.flush();
}
//给出反馈
BufferedWriter bwServer = new BufferedWriter(new OutputStreamWriter(s.getOutputStream()));
bwServer.write("文件上传成功");
bwServer.newLine();
bwServer.flush();
//释放资源
s.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ServerDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket ss=new ServerSocket(6666);
while (true){
Socket socket = ss.accept();
new Thread(new ServerThread(socket)).start();
}
// ss.close(); 一般服务器不关闭
}
}
新增:通过配置文件运行类中的方法
public class Student {
private void study() {
System.out.println("哈哈学习,天天向上");
}
}
public class Teacher {
public void teach(){
System.out.println("好好上课");
}
}
public class ClassDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException, NoSuchMethodException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException {
//加载数据
Properties prop = new Properties();
FileReader fr = new FileReader("untitled\\class.txt");
prop.load(fr);
fr.close();
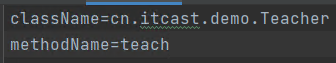
String className = prop.getProperty("className");
String methodName = prop.getProperty("methodName");
//通过反射来使用
Class<?> c = Class.forName(className);
Constructor<?> con = c.getConstructor();
Object obj = con.newInstance();
Method m = c.getMethod(methodName);
m.invoke(obj);
}
}
1.获取class文件对象三种方式
2.获取所有的公共的构造方法 获取指定的构造方法,如空参数的构造方法 并运行 获取指定的构造方法,如(String,int)参数的构造方法 并运行
3.反射获取构造方法的快捷键
4.获取所有的构造方法 包括私有 获取指定的构造方法,如(int,String)参数的构造方法 并运行 包括私有
5.获取所有的公共的成员变量 获取所有的公共的成员变量 (包括私有) 获取指定的成员变量 并修改成员变量的值
6.获取所有的公共的方法 获取指定的空参数方法 eat 获取指定的有参数方法sleep(String,int,double)
7.反射的泛型擦除 定义集合类,泛型String,要求向集合中添加Integer类型
8.通过静态方法获取本地主机 通过非静态方法获取IP地址和主机名 获取别人的ip地址
9.写UDP的发送端
10.写UDP的接收端
11.实现UDP发送,键盘输入的形式 输入完毕,发送给接收端 11和12是一起的
12.实现UDP接收端 永不停歇的接收端
13.实现TCP客户端,连接到服务器 然后实现客户端发送消息到服务端 服务端收到消息然后发回到客户端
14.实现TCP服务器
15.图片上传案列,从客户端将一张图片上传到服务器中,服务器将图片保存在一个文件夹中 客户端收到 上传成功
16.服务器端
17.多线程实现客户端上传 客户端不需要修改 服务器端写在upload里面
//使用这个作为对象
public class Person {
public String name;
private int age;
public Person(){
}
public Person(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
private Person(int age,String name){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void eat(){
System.out.println("人吃饭");
}
public void sleep(String s, int a,double d){
System.out.println("人在睡觉"+s+"....."+a+"....."+d);
}
private void playGame(){
System.out.println("人在打游戏");
}
public String toString() {
return "Person [name=" + name + ", age=" + age + "]";
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
}
public class Answer1 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ClassNotFoundException {
Person p=new Person();
Class c1=p.getClass();
Class c2=Person.class;
Class c3=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
System.out.println(c1);
System.out.println(c2);
System.out.println(c3);
}
}
public class Answer2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
function();
function_1();
function_2();
}
//获取所有的公共的构造方法
public static void function() throws ClassNotFoundException{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Constructor[] cons=c.getConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons){
System.out.println(con);
}
}
// 获取指定的构造方法,空参数的构造方法
public static void function_1() throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Constructor con=c.getConstructor();
Object obj=con.newInstance();
Person p=(Person)obj;
p.eat();
}
// 获取指定的构造方法,(String,int)参数的构造方法
public static void function_2()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Constructor con=c.getConstructor(String.class,int.class);
Object obj=con.newInstance("张三",18);
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public class Answer3 {
/*
* 反射获取构造方法并运行,有快捷点的方式
* 有前提:
* 被反射的类,必须具有空参数构造方法
* 构造方法权限必须public
*/
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Object obj=c.newInstance();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public class Answer4 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
function();
function_1();
}
//获取所有的构造方法 包括私有
public static void function() throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Constructor[] cons=c.getDeclaredConstructors();
for(Constructor con:cons){
System.out.println(con);
}
}
// 获取私有的(int,String)有参数的构造方法
public static void function_1()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Constructor con=c.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class,String.class);
con.setAccessible(true);
Object obj=con.newInstance(14,"李四");
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public class Answer5 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
function();
function_1();
function_2();
function_3();
}
//获取所有的成员变量 公共的
public static void function()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Field[] fields=c.getFields();
for(Field f:fields){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
//获取所有的成员变量 包括私有的
public static void function_1()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Field[] fields=c.getDeclaredFields();
for(Field f:fields){
System.out.println(f);
}
}
//获取指定的成员变量
public static void function_2()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Field field=c.getField("name");
System.out.println(field);
}
//获取指定的成员变量 并修改值
public static void function_3()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Object obj=c.newInstance();
Field field=c.getField("name");
field.set(obj, "张三");
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
public class Answer6 {
public static void main(String[] args)throws Exception {
function();
function_1();
function_2();
}
//获取所有的公共的方法
public static void function()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Method[] methods=c.getMethods();
for(Method met:methods){
System.out.println(met);
}
}
//获取指定的空参数方法 eat
public static void function_1()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Object obj=c.newInstance();
Method met=c.getMethod("eat");
met.invoke(obj);
}
// 获取指定的有参数方法sleep(String,int,double)
public static void function_2()throws Exception{
Class c=Class.forName("cn.itcast.answer10.Person");
Object obj=c.newInstance();
Method met=c.getMethod("sleep", String.class,int.class,double.class);
met.invoke(obj, "张三",100,2000.0);
}
}
/*
* 定义集合类,泛型String
* 要求向集合中添加Integer类型
*
* 反射方式,获取出集合ArrayList类的class文件对象
* 通过class文件对象,调用add方法
*
* 对反射调用方法是否理解
*/
public class Answer7 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
ArrayList<String> array=new ArrayList<>();
array.add("张三");
//反射方式,获取出集合ArrayList类的class文件对象
Class c=array.getClass();
//获取ArrayList.class文件中的方法add
Method met=c.getMethod("add", Object.class);
//使用invoke运行ArrayList方法add
met.invoke(array, 10);
met.invoke(array, 12);
met.invoke(array, 13);
System.out.println(array);
}
}
public class Answer8 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnknownHostException{
function();
function_1();
function_2();
}
public static void function() throws UnknownHostException{
InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
//输出的是主机名和ip地址
System.out.println(inet);
}
public static void function_1()throws UnknownHostException{
InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getLocalHost();
String hostname=inet.getHostName();
String ip=inet.getHostAddress();
System.out.println(hostname+"\t"+ip);
}
public static void function_2()throws UnknownHostException{
InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("LAPTOP-B32LHBOI");
System.out.println(inet);
}
}
public class Answer9 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
byte [] bytes="你好UDP".getBytes();
InetAddress inet=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
DatagramPacket data=new DatagramPacket(bytes, bytes.length, inet,6000);
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket();
ds.send(data);
ds.close();
}
}
public class Answer10 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(6000);
byte [] bytes=new byte[1024];
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length);
ds.receive(dp);
//拆包
String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
int length = dp.getLength();
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,length)+"..."+ip+":"+port);
ds.close();
}
}
public class Answer11 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket();
InetAddress ip=InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
while(true){
String message=sc.nextLine();
byte[] bytes=message.getBytes();
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length,ip,6001);
ds.send(dp);
}
}
}
public class Answer12 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
DatagramSocket ds=new DatagramSocket(6001);
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
while(true){
DatagramPacket dp=new DatagramPacket(bytes,bytes.length);
ds.receive(dp);
//拆包 dp.getAddress() 返回的是InetAddress
String ip=dp.getAddress().getHostAddress();
int port = dp.getPort();
int length = dp.getLength();
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,length)+"..."+ip+":"+port);
}
// ds.close();
}
}
public class Answer13 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//创建Socket对象,连接服务器
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8888);
//通过客户端的套接字对象Socket方法,获取字节输出流,将数据写向服务器
OutputStream os=socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好TCP服务器".getBytes());
//给服务器写终止序列
socket.shutdownOutput();
//读取服务器发回的数据,使用socket套接字对象中的字节输入流
InputStream in=socket.getInputStream();
byte [] bytes=new byte[1024];
int len=0;
while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
}
socket.close();
}
}
public class Answer14 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(8888);
//调用服务器套接字对象中的方法accept() 获取客户端套接字对象
Socket socket = server.accept();
//通过客户端套接字对象,socket获取字节输入流,读取的是客户端发送来的数据
InputStream in=socket.getInputStream();
byte[] data = new byte[1024];
int len = 0;
while((len=in.read(data))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(data,0,len));
}
//服务器向客户端回数据,字节输出流,通过客户端套接字对象获取字节输出流
OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream();
out.write("我已经收到了,谢谢".getBytes());
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
public class Answer15 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
Socket socket=new Socket("127.0.0.1",8889);
//获取字节输出流,图片写到服务器
OutputStream out=socket.getOutputStream();
//创建字节输入流,读取本机上的数据源图片
InputStream fis=new FileInputStream("E:\\images\\1.png");
//开始读写字节数组
int len=0;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
while((len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
out.write(bytes,0,len);
}
socket.shutdownOutput();
//获取字节输入流,读取服务器的上传成功
InputStream in=socket.getInputStream();
len=in.read(bytes);
System.out.println(new String(bytes,0,len));
fis.close();
socket.close();
}
}
public class Answer16 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException{
ServerSocket server=new ServerSocket(8889);
Socket socket=server.accept();
//通过客户端连接对象,获取字节输入流,读取客户端图片
InputStream in=socket.getInputStream();
//将目的文件夹封装到File对象
File upload = new File("e:\\upload");
if(!upload.exists())
upload.mkdirs();
//防止文件同名被覆盖,从新定义文件名字
//规则: 域名+毫秒值+6位随机数
String filename="itcast"+System.currentTimeMillis()+new Random().nextInt(999999)+".jpg";
//创建字节输出流,将图片写入到目的文件夹中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(upload+"\\"+filename);
// FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(upload+File.separator+filename);
int len=0;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
//服务器读客户端的字节数组,永远读不到-1
while((len=in.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes,0,len);
}
//通过客户端连接对象获取字节输出流
//上传成功写回客户端
socket.getOutputStream().write("上传成功".getBytes());
fos.close();
socket.close();
server.close();
}
}
public class Upload implements Runnable{
private Socket socket;
public Upload(Socket socket){this.socket=socket;}
public void run() {
try{
//通过客户端连接对象,获取字节输入流,读取客户端图片
InputStream in = socket.getInputStream();
//将目的文件夹封装到File对象
File upload = new File("e:\\upload");
if(!upload.exists())
upload.mkdirs();
//防止文件同名被覆盖,从新定义文件名字
//规则: 域名+毫秒值+6位随机数
String filename="itcast"+System.currentTimeMillis()+new Random().nextInt(999999)+".jpg";
//创建字节输出流,将图片写入到目的文件夹中
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(upload+File.separator+filename);
//读写字节数组
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
int len = 0 ;
while((len = in.read(bytes))!=-1){
fos.write(bytes, 0, len);
}
//通过客户端连接对象获取字节输出流
//上传成功写回客户端
socket.getOutputStream().write("上传成功".getBytes());
fos.close();
socket.close();
}catch(Exception ex){
}
}
}
public class Answer17 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8889);
while(true){
//获取到一个客户端,必须开启新线程
Socket socket = server.accept();
new Thread( new Upload(socket) ).start();
}
}
}








 博客介绍了Java中断言和反射的使用,如断言的比较方法、反射获取类的构造方法、成员变量和方法等。还阐述了网络编程三要素,详细讲解了UDP和TCP协议的通信原理、实现步骤,并给出多个网络编程练习,包括不同数据来源和处理方式的UDP、TCP通信程序。
博客介绍了Java中断言和反射的使用,如断言的比较方法、反射获取类的构造方法、成员变量和方法等。还阐述了网络编程三要素,详细讲解了UDP和TCP协议的通信原理、实现步骤,并给出多个网络编程练习,包括不同数据来源和处理方式的UDP、TCP通信程序。

















 650
650

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










