由于单向链表只能从某个节点开始单向访问其后继节点,并没有存储其前驱节点信息,访问前面的节点是不容易办到的。
为了能从某个节点开始,既可以访问前驱节点也可以访问后继节点,我们可以改造一下单向链表的节点结构,在结构中多参加一个指向前驱节点的指针。
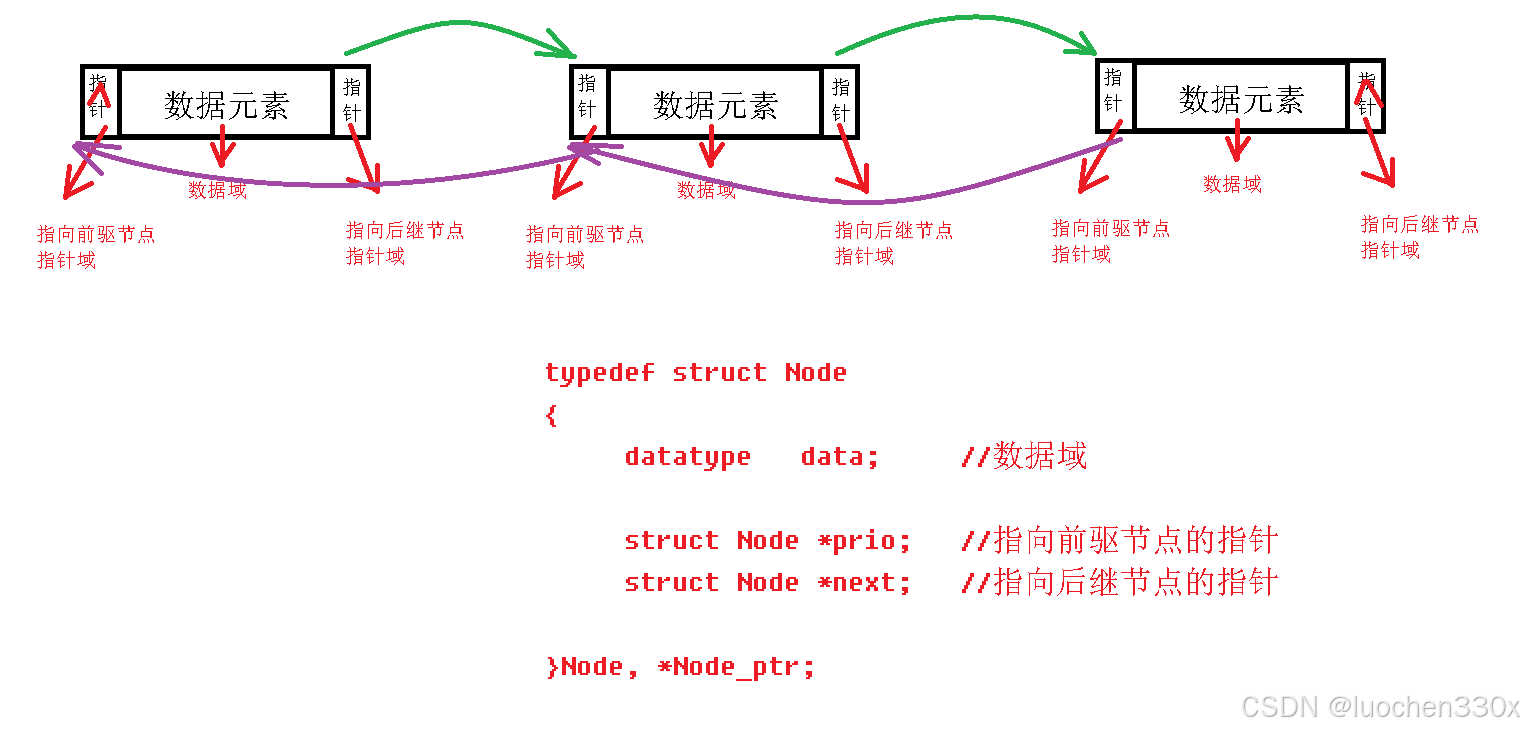
节点结构体类型
1.相比于单向链表的节点类型,多了一个指向前驱节点的指针
2.通过任意一个节点,既可以访问前驱节点也可以访问后继节点
typedef char datatype; //数据元素类型
//定义双向链表结点类型
typedef struct Node
{
union
{
datatype data; //普通结点数据域
int len; //头结点数据域
};
struct Node *prio; //指向前驱节点的指针
struct Node *next; //指向后继节点的指针
}Node, *Node_ptr;
创建双向链表
1.只需要创建一个头节点即可
2.初始化时,需要两个指针域都置空
3.返回值为头节点的指针
//创建双向链表
Node_ptr list_create()
{
//堆区申请一个头结点的大小
Node_ptr L = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("链表创建失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//初始化头结点
L->len = 0; //链表长度
L->prio = NULL; //前驱指针为空
L->next = NULL; //后继指针为空
printf("链表创建成功\n");
return L;
}
双向链表判空
//判空:1表示空,0表示非空
int list_empty(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("链表不合法\n");
return -1;
}
return L->next==NULL;
}
申请节点封装数据
static Node_ptr list_node_apply(datatype e)
{
//堆区申请一个结点
Node_ptr p = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==p)
{
printf("结点申请失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//将数据封装进数据域
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
p->prio = NULL;
return p;
}
双向链表头插
//头插
int list_insert_head(Node_ptr L, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL == L)
{
printf("所给链表不合法\n");
return -1;
}
//申请结点封装数据
Node_ptr p = list_node_apply(e);
if(NULL==p)
{
return -1;
}
//头插逻辑
if(list_empty(L))
{
//链表为空
p->prio = L;
L->next = p;
}else
{
//链表不为空
p->next = L->next;
p->prio = L;
L->next->prio = p; //p->next->prio = p;
L->next = p;
}
//表长变化
L->len++;
printf("插入成功\n");
return 0;
}
双向链表的遍历
//遍历
void list_show(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return ;
}
//遍历逻辑
printf("当前链表中的元素分别是:");
Node_ptr q = L->next; //定义遍历指针从第一个结点出发
while(q!=NULL)
{
printf("%c\t", q->data);
q = q->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
按位置查找返回节点
//按位置查找返回结点
Node_ptr list_search_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L) ||pos<0 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("查找失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//定义遍历指针从头结点出发
Node_ptr q = L;
for(int i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
//将找到的结点返回
return q;
}
双向链表任意位置插入
1.插入时。可以找到要插入的位置进行插入,也可以找到其前驱节点进行插入
2.使用双向链表完成尾插时要额外注意
//任意位置插入
int list_insert_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || pos<1 || pos>L->len+1)
{
printf("插入失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到其前驱结点
Node_ptr q = list_search_pos(L, pos-1);
//申请结点封装数据
Node_ptr p = list_node_apply(e);
if(NULL==p)
{
return -1;
}
//插入逻辑
if(q->next ==NULL)
{
//说明要进行尾插
p->prio = q;
q->next = p;
}else
{
//中间任意位置
p->next = q->next;
p->prio = q;
q->next->prio = p;
q->next = p;
}
//表长变化
L->len++;
printf("插入成功\n");
return 0;
}
双向链表的头删
//头删
int list_delete_head(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("删除失败\n");
return -1;
}
//删除逻辑
Node_ptr p = L->next; //标记
//判断要删除的结点后面是否还有结点
if(NULL == p->next)
{
//说明p是链表中最后一个结点
L->next = NULL;
}else
{
//说明p不是最后一个结点
L->next = p->next;
p->next->prio = L;
}
free(p); //释放结点
p = NULL;
//表长变化
L->len--;
printf("删除成功\n");
return 0;
}
双向链表任意位置删除
//任意位置删除
int list_delete_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L ||list_empty(L) ||pos<1 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("删除失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到要删除的结点
Node_ptr q = list_search_pos(L, pos);
//删除逻辑
if(q->next == NULL)
{
//说明要删除的是最后一个结点
q->prio->next = NULL; //将前面的结点后继指针置空
}else
{
//交接工作
q->prio->next = q->next;
q->next->prio = q->prio;
}
free(q); //释放结点
q = NULL;
//表长变化
L->len--;
printf("删除成功\n");
return 0;
}
双向链表按位置修改
//按位置进行修改
int list_update_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L) ||pos<1 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("修改失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到要修改的结点
Node_ptr p = list_search_pos(L, pos);
p->data = e; //将当前数据域进行修改
printf("修改成功\n");
return 0;
}
双向链表的释放
//销毁双向链表
void list_destroy(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断链表是否合法
if(NULL == L)
{
return ;
}
//开始将所有结点释放
while(!list_empty(L))
{
//不断进行头删
list_delete_head(L);
}
//释放头结点
free(L);
L = NULL;
printf("销毁成功\n");
}
全部代码
doublelinklist.h
#ifndef DOUBLKELINKLIST_H
#define DOUBLKELINKLIST_H
typedef char datatype; //数据元素类型
//定义双向链表结点类型
typedef struct Node
{
union
{
datatype data; //普通结点数据域
int len; //头结点数据域
};
struct Node *prio; //指向前驱节点的指针
struct Node *next; //指向后继节点的指针
}Node, *Node_ptr;
//创建双向链表
Node_ptr list_create();
//判空
int list_empty(Node_ptr L);
//头插
int list_insert_head(Node_ptr L, datatype e);
//遍历
void list_show(Node_ptr L);
//按位置查找返回结点
Node_ptr list_search_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos);
//任意位置插入
int list_insert_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e);
//头删
int list_delete_head(Node_ptr L);
//任意位置删除
int list_delete_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos);
//按位置进行修改
int list_update_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e);
//销毁双向链表
void list_destroy(Node_ptr L);
#endif
doublelinklist.c
#include<myhead.h>
#include"doublelinklist.h"
//创建双向链表
Node_ptr list_create()
{
//堆区申请一个头结点的大小
Node_ptr L = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("链表创建失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//初始化头结点
L->len = 0; //链表长度
L->prio = NULL; //前驱指针为空
L->next = NULL; //后继指针为空
printf("链表创建成功\n");
return L;
}
//判空:1表示空,0表示非空
int list_empty(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("链表不合法\n");
return -1;
}
return L->next==NULL;
}
//定义申请结点封装数据函数
static Node_ptr list_node_apply(datatype e)
{
//堆区申请一个结点
Node_ptr p = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==p)
{
printf("结点申请失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//将数据封装进数据域
p->data = e;
p->next = NULL;
p->prio = NULL;
return p;
}
//头插
int list_insert_head(Node_ptr L, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL == L)
{
printf("所给链表不合法\n");
return -1;
}
//申请结点封装数据
Node_ptr p = list_node_apply(e);
if(NULL==p)
{
return -1;
}
//头插逻辑
if(list_empty(L))
{
//链表为空
p->prio = L;
L->next = p;
}else
{
//链表不为空
p->next = L->next;
p->prio = L;
L->next->prio = p; //p->next->prio = p;
L->next = p;
}
//表长变化
L->len++;
printf("插入成功\n");
return 0;
}
//遍历
void list_show(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return ;
}
//遍历逻辑
printf("当前链表中的元素分别是:");
Node_ptr q = L->next; //定义遍历指针从第一个结点出发
while(q!=NULL)
{
printf("%c\t", q->data);
q = q->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//按位置查找返回结点
Node_ptr list_search_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L) ||pos<0 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("查找失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//定义遍历指针从头结点出发
Node_ptr q = L;
for(int i=0; i<pos; i++)
{
q = q->next;
}
//将找到的结点返回
return q;
}
//任意位置插入
int list_insert_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || pos<1 || pos>L->len+1)
{
printf("插入失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到其前驱结点
Node_ptr q = list_search_pos(L, pos-1);
//申请结点封装数据
Node_ptr p = list_node_apply(e);
if(NULL==p)
{
return -1;
}
//插入逻辑
if(q->next ==NULL)
{
//说明要进行尾插
p->prio = q;
q->next = p;
}else
{
//中间任意位置
p->next = q->next;
p->prio = q;
q->next->prio = p;
q->next = p;
}
//表长变化
L->len++;
printf("插入成功\n");
return 0;
}
//头删
int list_delete_head(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("删除失败\n");
return -1;
}
//删除逻辑
Node_ptr p = L->next; //标记
//判断要删除的结点后面是否还有结点
if(NULL == p->next)
{
//说明p是链表中最后一个结点
L->next = NULL;
}else
{
//说明p不是最后一个结点
L->next = p->next;
p->next->prio = L;
}
free(p); //释放结点
p = NULL;
//表长变化
L->len--;
printf("删除成功\n");
return 0;
}
//任意位置删除
int list_delete_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L ||list_empty(L) ||pos<1 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("删除失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到要删除的结点
Node_ptr q = list_search_pos(L, pos);
//删除逻辑
if(q->next == NULL)
{
//说明要删除的是最后一个结点
q->prio->next = NULL; //将前面的结点后继指针置空
}else
{
//交接工作
q->prio->next = q->next;
q->next->prio = q->prio;
}
free(q); //释放结点
q = NULL;
//表长变化
L->len--;
printf("删除成功\n");
return 0;
}
//按位置进行修改
int list_update_pos(Node_ptr L, int pos, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L) ||pos<1 || pos>L->len)
{
printf("修改失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到要修改的结点
Node_ptr p = list_search_pos(L, pos);
p->data = e; //将当前数据域进行修改
printf("修改成功\n");
return 0;
}
//销毁双向链表
void list_destroy(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断链表是否合法
if(NULL == L)
{
return ;
}
//开始将所有结点释放
while(!list_empty(L))
{
//不断进行头删
list_delete_head(L);
}
//释放头结点
free(L);
L = NULL;
printf("销毁成功\n");
}
main.c
#include"doublelinklist.h"
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//调用创建链表函数
Node_ptr L = list_create();
if(NULL==L)
{
return -1;
}
//调用头插函数
list_insert_head(L,'Q');
list_insert_head(L,'W');
list_insert_head(L,'E');
list_insert_head(L, 'R');
//调用遍历函数
list_show(L);
//调用任意位置插入函数
list_insert_pos(L, 1, 'D');
list_insert_pos(L, L->len+1, 'F');
list_insert_pos(L, 3, 'K');
list_show(L);
//调用头删函数
list_delete_head(L);
list_delete_head(L);
list_show(L);
//调用任意位置删除函数
list_delete_pos(L, 1);
list_delete_pos(L, 3);
list_show(L);
//调用按位置修改函数
list_update_pos(L, 1, 'M');
list_show(L);
//销毁双向链表
list_destroy(L);
L = NULL;
list_show(L);
return 0;
}
循环链表
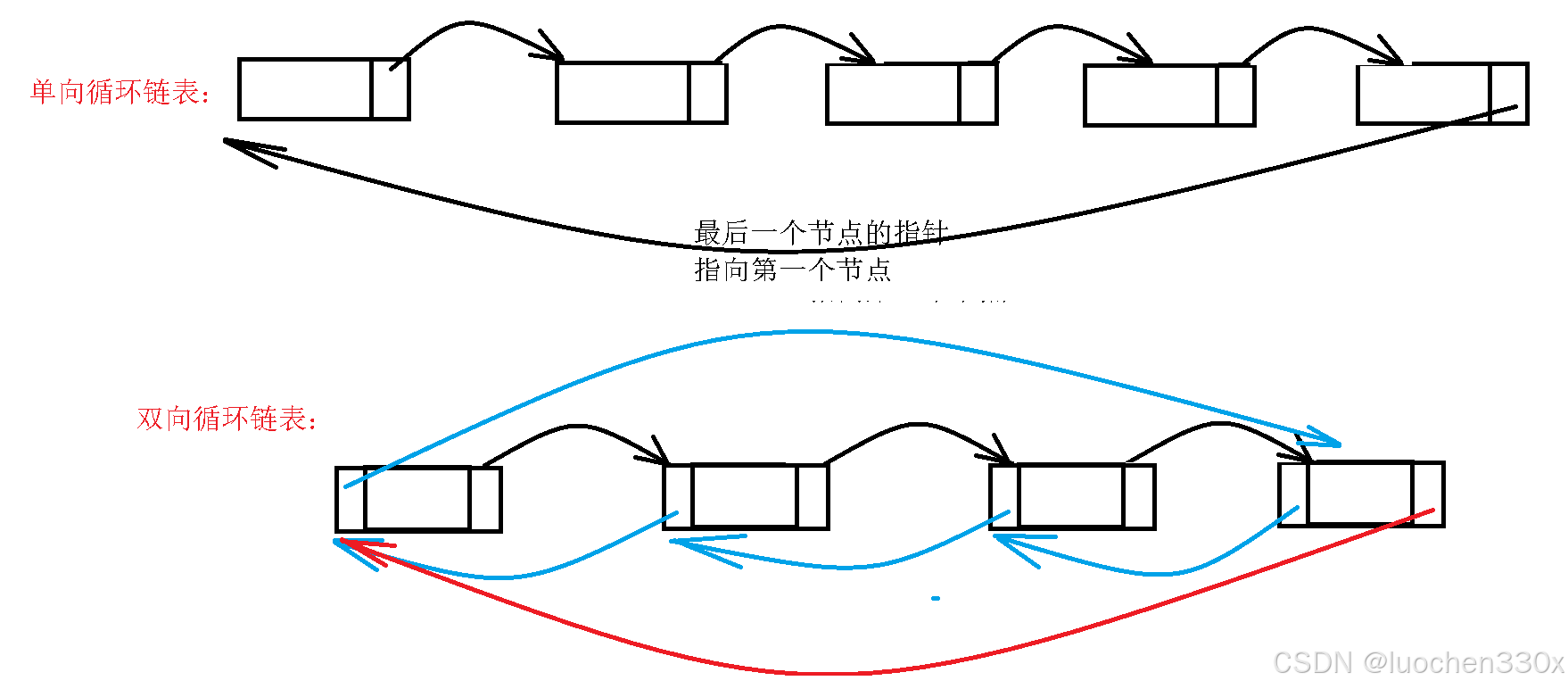
1.循环链表:首尾相接的链表称为循环链表
特点:在循环链表中,没有一个节点的指针域为空
分类:
单向循环链表:将单链表最后一个节点的指针域指向第一个节点即可(或者指向头节点)
双向循环链表:将头节点的前驱指针指向最后一个节点,最后一个节点的后继指针指向头节点
单向循环链表节点结构体
typedef struct Node
{
union
{
int len; //头节点数据域
datatype data; //普通结点数据域
};
//指针域
struct Node * next;
}Node, *Node_ptr;
循环链表的创建
注意:创建链表时,头节点指针域指向自己
//创建循环链表
Node_ptr list_create()
{
//在堆区申请一个头结点的空间
Node_ptr L = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("创建链表失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//初始化
L->len = 0;
L->next = L; //指针域指向自己
printf("循环链表创建成功\n");
return L;
}
全部代码
looplinklist.h
#ifndef LOOPLINKLIST_H
#define LOOPLINKLIST_H
typedef char datatype; //数据元素类型
//定义节点类型
typedef struct Node
{
union
{
int len; //头节点数据域
datatype data; //普通结点数据域
};
//指针域
struct Node * next;
}Node, *Node_ptr;
//创建循环链表
Node_ptr list_create();
//判空
int list_empty(Node_ptr L);
//尾插
int list_insert_tail(Node_ptr L, datatype e);
//遍历
void list_show(Node_ptr L);
//尾删
int list_delete_tail(Node_ptr L);
//删除头结点
Node_ptr list_head_delete(Node_ptr L);
//销毁
void list_destroy(Node_ptr L);
//删除头结点的循环链表的遍历
void list_desplay(Node_ptr H);
#endif
looplinklist.c
#include"looplinklist.h"
#include<myhead.h>
//创建循环链表
Node_ptr list_create()
{
//在堆区申请一个头结点的空间
Node_ptr L = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("创建链表失败\n");
return NULL;
}
//初始化
L->len = 0;
L->next = L; //指针域指向自己
printf("循环链表创建成功\n");
return L;
}
//判空 : 1表示空,0表示非空
int list_empty(Node_ptr L)
{
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("链表不合法\n");
return -1;
}
return L->next == L; //判断是否为空格
}
//尾插
int list_insert_tail(Node_ptr L, datatype e)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("插入失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到最后一个结点
Node_ptr q = L; //定义遍历指针从头结点出发
while(q->next != L)
{
q = q->next; //不断将遍历指针后移,直到移到最后一个结点位置
}
//申请结点将数据封装
Node_ptr p = (Node_ptr)malloc(sizeof(Node));
if(NULL==p)
{
printf("结点申请失败\n");
return -1;
}p->data = e; //将数据封装进结点
p->next = NULL; //防止野指针
//插入逻辑
p->next = L; //将新节点指针域指向头结点
q->next = p; //将最后一个结点的指针域指向自己
//表长变化
L->len++;
printf("插入成功\n");
}
//遍历
void list_show(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return ;
}
//遍历逻辑
printf("链表中的元素分别是:");
Node_ptr q = L->next; //定义遍历指针从第一个结点开始
while(q != L)
{
printf("%c\t", q->data);
q = q->next;
}
printf("\n");
}
//尾删
int list_delete_tail(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L || list_empty(L))
{
printf("删除失败\n");
return -1;
}
//找到倒数第二个结点
Node_ptr q = L;
while(q->next->next != L)
{
q = q->next;
}
//删除逻辑
free(q->next); //释放最后一个结点
q->next = L; //将新的最后一个结点指针域指向头结点
//表长变化
L->len--;
printf("删除成功\n");
return 0;
}
//删除头结点
Node_ptr list_head_delete(Node_ptr L)
{
//判断逻辑
if(NULL==L)
{
printf("去头失败\n");
return NULL;
}
if(list_empty(L)) //如果为空,直接释放
{
free(L); //释放头结点
return NULL;
}
//遍历整个链表找到最后一个结点
Node_ptr q = L->next; //从第一个结点出发
while(q->next != L)
{
q = q->next;
}
//将最后一个结点的指针域指向第一个结点
q->next = L->next;
free(L); //将头结点释放
L = NULL;
printf("去头成功\n");
return q->next;
}
//删除头结点的循环链表的遍历
void list_desplay(Node_ptr H)
{
//判断链表释放为空
if(NULL==H)
{
printf("遍历失败\n");
return ;
}
//定义遍历指针从当前结点出发
printf("链表总的结点元素分别是:");
Node_ptr q = H;
do
{
printf("%c\t", q->data);
q = q->next;
}while(q!=H);
printf("\n");
}
//销毁
void list_destroy(Node_ptr H)
{
if(NULL==H) //说明已经销毁了
{
return;
}
//先将其他结点释放
while(H->next != H)
{
Node_ptr p = H->next; //标记下一个结点
H->next = p->next; //孤立
free(p); //释放
p = NULL;
}
//将第一个结点释放
free(H);
H = NULL;
printf("销毁成功\n");
return ;
}
main.c
#include"looplinklist.h"
#include<myhead.h>
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
//调用创建链表函数
Node_ptr L = list_create();
if(NULL==L)
{
return -1;
}
//调用尾插函数
list_insert_tail(L, 'Q');
list_insert_tail(L, 'W');
list_insert_tail(L, 'E');
list_insert_tail(L, 'R');
//调用遍历函数
list_show(L);
//调用尾删函数
list_delete_tail(L);
list_delete_tail(L);
list_show(L);
//调用循环链表去头操作
Node_ptr H = list_head_delete(L);
L = NULL;
//此时的H就是指向链表的头指针
//调用遍历函数,遍历去头后的链表
list_desplay(H);
//调用销毁函数
list_destroy(H);
H = NULL;
list_desplay(H);
return 0;
}




















 906
906

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








