- C++ 支持三种 member function:static、nonstatic 和 virtual
Member Function 的调用方式
nonstatic member function
- C++ 保证 nonstatic member function 至少和普通 non-member function 有相同的效率,member function 会被内部转化为 non-member function 的形式
double magnitude(const Point3d* p3d)
{ return sqrt(p3d->x * p3d->x + p3d->y * p3d->y + p3d->z * p3d->z); }
double Point3d::magnitude const ()
{ return sqrt(x*x + y*y + z*z); }
Point3d point, *p3d;
point.magnitude();
p3d->magnitude();
// 程序转化,包括名字编码
double magnitude__7Point3dFv(const Point3d *const this)
{ return sqrt(this->x * this->x + this->y * this->y + this->z * this->z); }
magnitude_7Point3dFv(&point);
magnitude_7Point3dFv(p3d);
Point3d Point3d::normalize() const
{
register double mag = magnitude();
Point3d normal;
normal.x = x / mag;
normal.y = y / mag;
normal.z = z / mag;
return normal;
}
// 程序转化
void normalize_7Point3dFv(register const Point3d *const this, Point3d& __result)
{
register double mag = this->magnitude();
__result.Point3d::Point3d();
__result.x = this->x / mag;
__result.y = this->y / mag;
__result.z = this->z / mag;
return;
}
Point3d Point3d::normalize() const
{
register double mag = magnitude();
return Point3d(x/mag, y/mag, z/mag);
}
// 程序转化
void normalize_7Point3dFv(register const Point3d *const this, Point3d& __result)
{
register double mag = this->magnitude();
__result.Point3d::Point3d(this->x/mag, this->y/mag, this->z/mag);
return;
}
virtual member function
// 若 normalize() 是 virtual member function,那么
p3d->normalize();
point.normalize();
// 会转化为
(*p3d->vptr[1])(p3d);
(point.vptr[1])(&point);
static member function
// 若 normalize() 是 static member function,那么
p3d->normalize();
point.normalize();
// 会转化为
normalize_7Point3SFv();
normalize_7Point3SFv();
- static member function 的特性
- 没有
this指针 - 不能直接存取 class 的 nonstatic member
- 不能被声明为 const、volatile 或 virtual
- 不需要经由 class object 调用
- 没有
Virtual Member Function
- C++ 中,多态表示以一个 public base class 的指针或引用寻址出一个 derived class object
- 经由 public base class pointer or reference,可以在程序的任何地方采用一组 public derived class
Point* pp;
pp = new Point2d;
pp = new Point3d;
- 一个 class 只有一个 virtual table,每个 table 包含所有的 active virtual function 实体的地址,包括
- class 所定义的函数实体,会改写可能存在的 base class virtual function 实体
- 继承自 base class 的函数实体,此时 class 没有改写 base class 的 virtual function
pure_virtual_called()
- 每个 virtual function 配有一个固定的索引值
单一继承
class Point
{
public:
Point() : _x(0) {}
Point(double x) : _x(x) {}
virtual ~Point();
virtual Point& mult(double) = 0; // pure virtual function
double x() const { return _x; }
virtual double y() { return 0.0; }
virtual double z() { return 0.0; }
protected:
Point(double x = 0.0);
double _x;
};
// virtual ~Point() 在 vtbl 中的索引为 1
// mult() 为 pure virtual function,没有函数定义,因此 pure_virtual_called() 的索引为 2
// y() 和 z() 的索引分别为 3 和 4
// vtbl 中索引为 0 的位置存放 Point 的 type_info
class Point2d : public Point
{
public:
Point2d() : Point(), _y(0) {}
Point2d(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0) : Point(x), _y(y) {}
~Point2d();
Point2d& mult(double); // rewrite base class virtual function
double y() { return _y; } // rewrite base class virtual function
protected:
double _y;
};
class Point3d : public Point2d
{
public:
Point3d() : Point2d(), _z(0) {}
Point3d(double x = 0.0, double y = 0.0, double z = 0.0) : Point2d(x, y), _z(z) {}
Point3d& mult(double); // rewrite base class virtual function
double z() { return _z; } // rewrite base class virtual function
protected:
double _z;
};
// 当出现以下调用时
ptr->z();
// 1. 编译时期并不知道 ptr 所指对象的真正类型,但经由 ptr 可以访问到该对象的 vtbl
// 2. 每一个 z() 的地址都放在 vtbl[4] 中
// 因此以上调用可转换为
(*ptr->vptr[4])(ptr);
// 到运行期便可根据 ptr 所指的对象调用 z() 的正确实体
多重继承
class Base1
{
public:
Base1() {}
virtual ~Base1();
virtual void speak();
virtual Base1* clone() const;
protected:
double _datab1;
};
class Base2
{
public:
Base2() {}
virtual ~Base1();
virtual void mumble();
virtual Base2* clone() const;
protected:
double _datab2;
};
class Derived : public Base1, public Base2
{
public:
Derived() {}
virtual ~Derived();
virtual Derived* clone() const;
private:
double _datad;
};
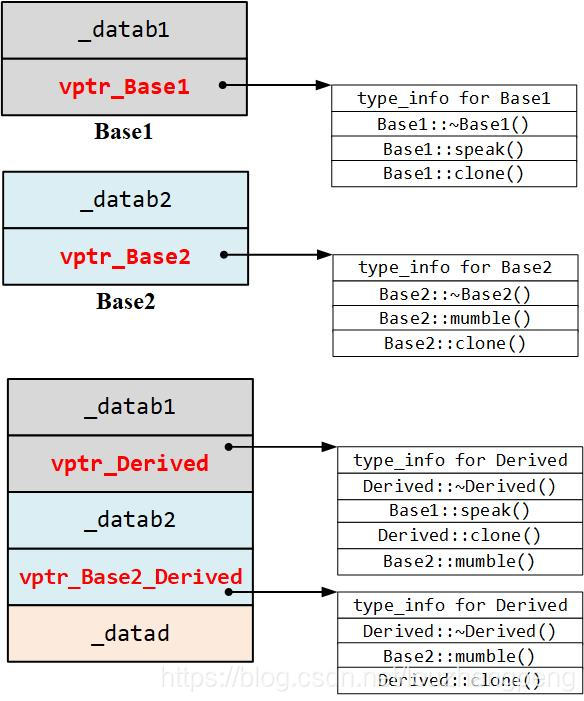
- 在多重继承下,一个 derived class 内含的 vtbl 与它的直接父类个数相同
- 针对每一个 vtbl,derived class 对象中都有一个
vptr与之对应- 当把 Derived 对象地址赋给 Base1 指针或 Derived 指针时,访问 vtbl_Derived
- 当把 Derived 对象地址赋给 Base2 指针时,访问 vtbl_Base2_Derived
虚拟继承
不要在 virtual base class 中声明 nonstatic data member!





 本文深入探讨了C++中三种成员函数(静态、非静态和虚函数)的特性及调用方式,解释了它们如何在编译器层面进行转换,并详细分析了虚函数表的工作原理及其在多态实现中的关键作用。
本文深入探讨了C++中三种成员函数(静态、非静态和虚函数)的特性及调用方式,解释了它们如何在编译器层面进行转换,并详细分析了虚函数表的工作原理及其在多态实现中的关键作用。
















 483
483

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








