目录
一、kNN的原理详解
k-近邻算法(kNN)是根据测量不同特征值之间的距离来进行分类的一种算法。具体来说,当存在一个样本数据集合或者训练样本集,该样本集的每个数据都存在一个分类标签。当输入没有标签的新数据之后,即测试数据集合,将新数据的每个特征与样本集合中的数据对应的特征进行比较,然后提取样本集中特征最相似数据(即最近邻)的分类标签。k的值对应的是选择训练集合中前k个最相似的数据,通常k是不大于20的整数,最后,选择k个最相似数据中出现次数最多的分类,作为测试集合的分类预测结果。
二、k-近邻算法的流程
第一、收集数据:使用任何方法收集数据作为训练集和测试结合。
第二、准备数据:准备距离计算所需要的数值,最好是结构化的数据格式。
第三、分析数据:可以使用任何方法。
第四、训练算法:次步骤不使用于k-近邻算法(kNN算法不需要训练数据)
得到处理好的数据之后,就需要考虑使用python计算特殊集合每个点到训练集合中每个点的距离,然后按照距离递增排序,选取与当前点距离最小的k个点,最后确定前k个点所在类别出现的频率,返回前k个点出现频率最高的类别作为当前点的预测分类。
在计算距离时,一般使用欧式距离

代码如下:
#计算距离
def classigy0(inX, dataSet, labels, k):
'''
计算欧拉距离
:param inX:
:param dataSet:
:param labels:
:param k:
:return:
'''
dataSetSize = dataSet.shape[0]
#距离
diffMat = tile(inX, (dataSetSize, 1)) - dataSet
sqDiffMat = diffMat ** 2
sqDistances = sqDiffMat.sum(axis=1)
distance = sqDistances**0.5
#选择k个距离最小的值
sortedDistIndicies = distance.argsort() #索引
# print(sortedDistIndicies)
classCount = {}
for i in range(k):
voteIlable = labels[sortedDistIndicies[i]]
classCount[voteIlable] = classCount.get(voteIlable, 0) + 1
# print(classCount)
#按照value值升序
sortedClassCount = sorted(classCount.items(), key=operator.itemgetter(1),reverse=True)
# print(sortedClassCount)
return sortedClassCount[0][0]三、使用kNN算法对约会网站的建模实例
在该数据集中样本数据有三种,
1、每年获得的飞行常客里程数。
2、玩视频游戏所耗时间百分比。
3、每周消费的冰淇淋公升数
最后一列是标签:
40920 8.326976 0.953952 3
14488 7.153469 1.673904 2
26052 1.441871 0.805124 1
75136 13.147394 0.428964 1
38344 1.669788 0.134296 1
72993 10.141740 1.032955 1
35948 6.830792 1.213192 3
42666 13.276369 0.543880 3
67497 8.631577 0.749278 1
35483 12.273169 1.508053 3
50242 3.723498 0.831917 1
63275 8.385879 1.669485 1
.......在进行分析时,首先要从文件中读取样本数据和标签,然后转化为Numpy矩阵格式:这里提供一个将文本记录转化为numpy数组的解析函数:
#将文本记录到转化为numpy的解析程序
def file2matrix(filename):
'''
解析txt文本数据
:param filename:
:return:
'''
fr = open(filename)
arrayOLines = fr.readlines()
numbersOflines = len(arrayOLines)
returnMat = np.zeros((numbersOflines,3))
classLabelVector = []
classMarker = []
marker = ['.',',', 'o','v','^','<','>','8','s','p','*','+','D','d','x','|','_']
index = 0
for line in arrayOLines:
line = line.strip()
listFromLine = line.split('\t')
returnMat[index,:] = listFromLine[0:3]
classLabelVector.append(int(listFromLine[-1]))
classMarker.append(marker[int(listFromLine[-1])])
index += 1
#返回数据和label
return returnMat, classLabelVector, classMarker取数之后,进行一个归一化处理,归一化处理的好处是方便计算,减少数字差值最大的属性对计算结果的影响,因为考虑到不同特征值的值域不同,但是对预测结果的重要性是等同的,即样本集的特征是等权重特征,进行归一化处理可减少不同特征数值对预测结果的影响。
归一化处理的原理也很简单:
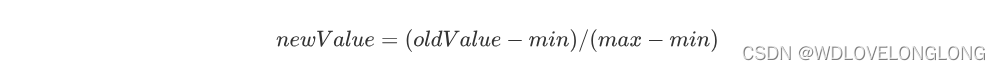
这就要求我们把同意特征集合中的最大值和最小值求出来,具体实现如下:
#归一化处理
def autoNorm(dataset):
'''
归一化处理
:param dataset:
:return:
'''
minVals = dataset.min(0)
maxVals = dataset.max(0)
ranges = maxVals - minVals
normDataSet = np.zeros(shape=dataset.shape)
m = dataset.shape[0]
normDataSet = dataset - tile(minVals, (m, 1))
normDataSet = normDataSet / tile(ranges, (m,1))
return normDataSet, ranges, minVals然后建立测试代码,完成取数,特征归一化,进行kNN算法,验证错误率,代码如下:
#分类器测试
def datingClassTest(datingDataMat, datingLables):
hoRatio = 0.1
# 归一化
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
m = normMat.shape[0]
numTestVecs = int(m * hoRatio)
errorCount = 0
for i in range(numTestVecs):
classifierResult = classigy0(normMat[i,:], normMat[numTestVecs:m,:],
datingLables[numTestVecs:m], 5)
print("the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer is: %d"%(
classifierResult, datingLables[i]))
if (classifierResult != datingLables[i]) : errorCount += 1
print("the total error rate is: %f"%(errorCount/float(numTestVecs)))在测试代码文件上运行下列代码,KNN是上述所有代码的文件名。
dataMat, labels, _ = KNN.file2matrix(FILENAME)
KNN.datingClassTest(dataMat, labels)结果如下:
the classifier came back with: 2, the real answer is: 1 the classifier came back with: 1, the real answer is: 1 the total error rate is: 0.050000
可以看到使用kNN算法处理约会数据集的错误率为5%,也可以改变k的值,观察错误率的变化。
最后构建kNN系统,即集成所有的方法:
def classifyPerson(filename):
resultList = ['not at all', 'in small doses', 'in large doses']
percentTats = float(raw_input("percentage of time spent playing video games?"))
ffMiles = float(raw_input("frequent flier miles earned per year?"))
iceCream = float(raw_input("liters of ice cream consumed per year?"))
datingDataMat, datingLabels, datingMaker = file2matrix(filename)
normMat, ranges, minVals = autoNorm(datingDataMat)
inArr = np.array([ffMiles, percentTats, iceCream])
classifierResult = classigy0((inArr-minVals) / ranges, normMat, datingLabels,3)
print('You wil probly like this person: ', resultList[classifierResult-1])即可输入新数据,得到预测结果:
percentage of time spent playing video games?11.865402 frequent flier miles earned per year?36661 liters of ice cream consumed per year?0.882810 You wil probly like this person: in large doses
四、数字识别
这里有一个使用kNN进行数字识别的建模过程,原来是一样的,只是标签和要把矩形的txt数据转变为向量模式,全部代码如下:
#将矩阵数据转化为一维向量
def img2vector(filename):
'''
将图像转化为一维向量
:param filename:
:return:
'''
returnVect = np.zeros((1,1024))
with open(filename) as fr:
for i in range(32):
lineStr = fr.readline()
for j in range(32):
returnVect[0,i * j] = int(lineStr[j])
return returnVect
def handwriteingClassTest(fileNameTrain,fileNameTest):
'''
传入训练文件和测试文件名,进行分类
:param fileNameTrain:
:param fileNameTest:
:return:
'''
hwLables = [] #数字
trainingFileList = getFilename(fileNameTrain)
m = len(trainingFileList)
trainingMat = np.zeros((m, 1024))
for i in range(m):
fileStr = trainingFileList[i].split('.')[0]
classNumstr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])
hwLables.append(classNumstr)
trainingMat[i, :] = img2vector(os.path.join(fileNameTrain,trainingFileList[i]))
testFileList = getFilename(fileNameTest)
errorCount = 0
mTest = len(testFileList)
for i in range(mTest):
fileNameStr = testFileList[i]
fileStr = fileNameStr.split('.')[0]
classNumStr = int(fileStr.split('_')[0])
vectorUnderTest = img2vector(os.path.join(fileNameTest,fileNameStr))
classifierResult = classigy0(vectorUnderTest,trainingMat,hwLables,3)
print("the classifier came back with: %d, the real answer"
"is: %d" % (classifierResult, classNumStr))
if (classifierResult != classNumStr):errorCount += 0
print("the total number or errors is: %d" %(errorCount))
print("the total error rate is: %f" %(errorCount / float(mTest)))五、总结
kNN算法是机器学习中一个比较简单的算法,原理以及实现过程都比较简单,并且不涉及训练数据,只有对数据的预处理,具有精度高,对异常值不敏感,无数据输入假定的有点;但是其中设计欧式距离等的计算,并且对于n个样本数据数据集,m个测试数据就要进行n * m次距离计算,其计算复杂度和空间复杂度较高,但可以进行多分类任务,该算法适用于数值型和标称型的分类任务。
约会网站数据集:
【免费】knn实现中约会网站的数据集_约会特征数据集下载资源-优快云文库
手写识别系统数据集:







 本文详细介绍了k-近邻算法的工作原理,流程,包括如何使用kNN对约会网站进行建模和手写识别系统的应用。尽管kNN算法简单直观,但因其计算复杂度高,主要适用于数值型和标称型分类任务。
本文详细介绍了k-近邻算法的工作原理,流程,包括如何使用kNN对约会网站进行建模和手写识别系统的应用。尽管kNN算法简单直观,但因其计算复杂度高,主要适用于数值型和标称型分类任务。


















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








