本文聚焦ekf_localization_node节点,只关注主要函数。
目录
1、RobotLocalization::RosFilter ekf(nh, nh_priv);
1.1.10 enqueueMeasurement函数和Measurement结构体
1.1.12 integrateMeasurements函数
1.2.4 computeDynamicProcessNoiseCovariance函数
1、RobotLocalization::RosFilter<Ekf> ekf(nh, nh_priv);
1.1 RosFilter<T>类
1.1.1 Initialize()函数初始化
主要是loadParams()函数和periodicUpateTimer循环函数,以及初始化发布odom,设置速度频率等。不是本文重点,所以就大部分都省略了。主要是学习代码:
1、对差分differential的处理
//以odom为例
//其中poseUpdateVec和twistUpdateVec分别为odom_config更新位姿和速度向量,0表示不更新,1表示更新
if (poseUpdateSum > 0)
{
if (differential)
{
//twistVarCounts是速度数据来源个数,初始值为0
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVx] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberX];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVy] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberY];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVz] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberZ];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVroll] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberRoll];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVpitch] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberPitch];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVyaw] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberYaw];
}
else
{
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberX] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberX];
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberY] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberY];
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberZ] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberZ];
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberRoll] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberRoll];
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberPitch] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberPitch];
absPoseVarCounts[StateMemberYaw] += poseUpdateVec[StateMemberYaw];
}
}
if (twistUpdateSum > 0)
{
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVx] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVx];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVy] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVx];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVz] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVz];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVroll] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVroll];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVpitch] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVpitch];
twistVarCounts[StateMemberVyaw] += twistUpdateVec[StateMemberVyaw];
}
2、回调函数数据对象(结构体)
odom创建了pose和twist两个
pose只创建了一个callbackData
twist我们没有使用到,跳过。
imu创建了pose、twist和accel三个
const CallbackData poseCallbackData(odomTopicName + "_pose", poseUpdateVec, poseUpdateSum, differential,
relative, poseMahalanobisThresh);
const CallbackData twistCallbackData(odomTopicName + "_twist", twistUpdateVec, twistUpdateSum, false, false,
twistMahalanobisThresh);
nh_.subscribe<nav_msgs::Odometry>(odomTopic, odomQueueSize,
boost::bind(&RosFilter::odometryCallback, this, _1, odomTopicName, poseCallbackData, twistCallbackData),
ros::VoidPtr(), ros::TransportHints().tcpNoDelay(nodelayOdom));
//回调函数声明
template<typename T>
void RosFilter<T>::odometryCallback(const nav_msgs::Odometry::ConstPtr &msg, const std::string &topicName,
const CallbackData &poseCallbackData, const CallbackData &twistCallbackData);3、读取yaml文件,允许混用double和科学计数法
Eigen::MatrixXd processNoiseCovariance(STATE_SIZE, STATE_SIZE);
processNoiseCovariance.setZero();
XmlRpc::XmlRpcValue processNoiseCovarConfig;
if (nhLocal_.hasParam("process_noise_covariance"))
{
try
{
nhLocal_.getParam("process_noise_covariance", processNoiseCovarConfig);
ROS_ASSERT(processNoiseCovarConfig.getType() == XmlRpc::XmlRpcValue::TypeArray);
int matSize = processNoiseCovariance.rows();
for (int i = 0; i < matSize; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < matSize; j++)
{
try
{
// These matrices can cause problems if all the types
// aren't specified with decimal points. Handle that
// using string streams.
std::ostringstream ostr;
ostr << processNoiseCovarConfig[matSize * i + j];
std::istringstream istr(ostr.str());
istr >> processNoiseCovariance(i, j);
}
catch(XmlRpc::XmlRpcException &e)
{
throw e;
}
catch(...)
{
throw;
}
}
}
}
catch (XmlRpc::XmlRpcException &e)
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("ERROR reading sensor config: " <<
e.getMessage() <<
" for process_noise_covariance (type: " <<
processNoiseCovarConfig.getType() << ")");
}
filter_.setProcessNoiseCovariance(processNoiseCovariance);
} 4、创建了一个ROS定时器,在重复执行RosFilter<T>::periodicUpdate函数。其中,frequency_是更新频率,this是指向当前对象的指针。periodicUpdate函数用于更新滤波器的状态。
periodicUpdateTimer_ = nh_.createTimer(ros::Duration(1./frequency_), &RosFilter<T>::periodicUpdate, this);1.1.2 odometryCallback回调函数
1、忽略早于reset时间戳的消息
2、分别存下odom的pose和twist(包括协方差矩阵),分别调用poseCallback和twistCallback
//如果odom_config中pose部分有true
if (poseCallbackData.updateSum_ > 0)
{
// Grab the pose portion of the message and pass it to the poseCallback
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped *posPtr = new geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped();
posPtr->header = msg->header;
posPtr->pose = msg->pose; // Entire pose object, also copies covariance
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr pptr(posPtr);
poseCallback(pptr, poseCallbackData, worldFrameId_, false);
//最后一个false表示数据不是来自IMU。
}
//如果odom_config中twist部分有true
if (twistCallbackData.updateSum_ > 0)
{
// Grab the twist portion of the message and pass it to the twistCallback
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped *twistPtr = new geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped();
twistPtr->header = msg->header;
twistPtr->header.frame_id = msg->child_frame_id;
twistPtr->twist = msg->twist; // Entire twist object, also copies covariance
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr tptr(twistPtr);
twistCallback(tptr, twistCallbackData, baseLinkFrameId_);
}
1.1.3 poseCallback回调函数
1、忽略早于reset时间戳的消息
2、如果最新消息时间戳为空,则lastMessageTimes_(是一个map容器)中插入当前时间戳。
如果某个主题正在快速接收消息,则可能会收到一个比上一个更旧的消息,使用这个变量可以避免这种情况。在处理消息时,该变量被用来比较当前消息的时间戳和上次接收消息的时间戳,以确定是否需要更新缓存中的数据。此外,当监听位姿(Pose)消息时,它还被用来判断是否应该使用来自该主题的消息。
3、准备数据,最重要的两个函数preparePose和enqueueMeasurement。细节看下面。
// 保证数据是最新的
if (msg->header.stamp >= lastMessageTimes_[topicName])
{
Eigen::VectorXd measurement(STATE_SIZE);
Eigen::MatrixXd measurementCovariance(STATE_SIZE, STATE_SIZE);
measurement.setZero();
measurementCovariance.setZero();
// Make sure we're actually updating at least one of these variables
std::vector<int> updateVectorCorrected = callbackData.updateVector_;
// 准备pose数据,imudata是个bool型,表示位姿是否从IMU来的。
if (preparePose(msg,
topicName,
targetFrame,
callbackData.differential_,
callbackData.relative_,
imuData,
updateVectorCorrected,
measurement,
measurementCovariance))
{
// Store the measurement. Add a "pose" suffix so we know what kind of measurement
// we're dealing with when we debug the core filter logic.
//存储测量值进入待更新队列。
enqueueMeasurement(topicName,
measurement,
measurementCovariance,
updateVectorCorrected,
callbackData.rejectionThreshold_,
msg->header.stamp);
RF_DEBUG("Enqueued new measurement for " << topicName << "\n");
}
else
{
RF_DEBUG("Did *not* enqueue measurement for " << topicName << "\n");
}
lastMessageTimes_[topicName] = msg->header.stamp;
RF_DEBUG("Last message time for " << topicName << " is now " <<
lastMessageTimes_[topicName] << "\n");
}
else if (resetOnTimeJump_ && ros::Time::isSimTime())
{
reset();
}
else
{
std::stringstream stream;
stream << "The " << topicName << " message has a timestamp before that of the previous message received," <<
" this message will be ignored. This may indicate a bad timestamp. (message time: " <<
msg->header.stamp.toSec() << ")";
addDiagnostic(diagnostic_msgs::DiagnosticStatus::WARN,
topicName + "_timestamp",
stream.str(),
false);
RF_DEBUG("Message is too old. Last message time for " << topicName << " is "
<< lastMessageTimes_[topicName] << ", current message time is "
<< msg->header.stamp << ".\n");
}
1.1.4 twistCallback回调函数
与上面几乎一致,最重要的两个函数prepareTwist和enqueueMeasurement
1.1.5 imuCallback
主要是分别对pose、twist和acceleration处理。分别调用poseCallback、twistCallback和accelerationCallback函数。
//如果imu_config中pose有true
if (poseCallbackData.updateSum_ > 0)
{
// Per the IMU message specification, if the IMU does not provide orientation,
// then its first covariance value should be set to -1, and we should ignore
// that portion of the message. robot_localization allows users to explicitly
// ignore data using its parameters, but we should also be compliant with
// message specs.
// 如果IMU的旋转协方差矩阵的第一个值为-1,则忽略该部分消息
if (::fabs(msg->orientation_covariance[0] + 1) < 1e-9)
{
RF_DEBUG("Received IMU message with -1 as its first covariance value for orientation. "
"Ignoring orientation...");
}
else
{
// Extract the pose (orientation) data, pass it to its filter
// 提取旋转的数据
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped *posPtr = new geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStamped();
posPtr->header = msg->header;
posPtr->pose.pose.orientation = msg->orientation;
// Copy the covariance for roll, pitch, and yaw
//复制欧拉角的协方差矩阵3*3
for (size_t i = 0; i < ORIENTATION_SIZE; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < ORIENTATION_SIZE; j++)
{
posPtr->pose.covariance[POSE_SIZE * (i + ORIENTATION_SIZE) + (j + ORIENTATION_SIZE)] =
msg->orientation_covariance[ORIENTATION_SIZE * i + j];
}
}
// IMU data gets handled a bit differently, since the message is ambiguous and has only a single frame_id,
// even though the data in it is reported in two different frames. As we assume users will specify a base_link
// to imu transform, we make the target frame baseLinkFrameId_ and tell the poseCallback that it is working
// with IMU data. This will cause it to apply different logic to the data.
//然后再次调用poseCallback函数
geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr pptr(posPtr);
poseCallback(pptr, poseCallbackData, baseLinkFrameId_, true);
}
}
//速度也同理,调用twistCallback函数
if (twistCallbackData.updateSum_ > 0)
{
// Ignore rotational velocity if the first covariance value is -1
if (::fabs(msg->angular_velocity_covariance[0] + 1) < 1e-9)
{
RF_DEBUG("Received IMU message with -1 as its first covariance value for angular "
"velocity. Ignoring angular velocity...");
}
else
{
// Repeat for velocity
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped *twistPtr = new geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped();
twistPtr->header = msg->header;
twistPtr->twist.twist.angular = msg->angular_velocity;
// Copy the covariance
for (size_t i = 0; i < ORIENTATION_SIZE; i++)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < ORIENTATION_SIZE; j++)
{
twistPtr->twist.covariance[TWIST_SIZE * (i + ORIENTATION_SIZE) + (j + ORIENTATION_SIZE)] =
msg->angular_velocity_covariance[ORIENTATION_SIZE * i + j];
}
}
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr tptr(twistPtr);
twistCallback(tptr, twistCallbackData, baseLinkFrameId_);
}
}
//重点是accelerationCallback函数
if (accelCallbackData.updateSum_ > 0)
{
// Ignore linear acceleration if the first covariance value is -1
if (::fabs(msg->linear_acceleration_covariance[0] + 1) < 1e-9)
{
RF_DEBUG("Received IMU message with -1 as its first covariance value for linear "
"acceleration. Ignoring linear acceleration...");
}
else
{
// Pass the message on
accelerationCallback(msg, accelCallbackData, baseLinkFrameId_);
}
}1.1.6 accelerationCallback函数
同样判断时间戳是否最新,是否晚于reset时间。然后调用prepareAcceleration和enqueueMeasurement函数
接下来看一下三个prepare函数
1.1.7 preparePose函数
template<class T>
bool RobotLocalization::RosFilter<...>::preparePose
(const geometry_msgs::PoseWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr &msg,
const std::__cxx11::string &topicName,
const std::__cxx11::string &targetFrame,
bool differential, bool relative,
bool imuData,
std::vector<...> &updateVector,
Eigen::VectorXd &measurement,
Eigen::MatrixXd &measurementCovariance)
Prepares a pose message for integration into the filter
//准备位姿数据,以便加入到filter中
参数:
msg – - The pose message to prepare
topicName – - The name of the topic over which this message was received
targetFrame – - The target tf frame
differential – - Whether we're carrying out differential integration
relative – - Whether this measurement is processed relative to the first
imuData – - Whether this measurement is from an IMU
updateVector – - The update vector for the data source
measurement – - The pose data converted to a measurement转换为测量值的位姿数据;
measurementCovariance – - The covariance of the converted measurement测量值的协方差矩阵。
返回:
true indicates that the measurement was successfully prepared, false otherwise1、如果是来源odom,pose的targetframe就是worldFrameId_,正常使用的是odom,这里用了差分,所以是用的worldFrameId_
2、如果是来源slam,也就是pose,在订阅时候用boost::bind设置为了worldFrameId_
3、如果是imu,pose、twist和accel都是baseLinkFrameId_
if (targetFrame == "" && msg->header.frame_id == "")
{
// Blank target and message frames mean we can just
// use our world_frame
//如果目标帧和消息帧的坐标系都是空的,那么就用世界坐标系
finalTargetFrame = worldFrameId_;
poseTmp.frame_id_ = finalTargetFrame;
}
else if (targetFrame == "")
{
// A blank target frame means we shouldn't bother
// transforming the data
finalTargetFrame = msg->header.frame_id;
poseTmp.frame_id_ = finalTargetFrame;
}
else
{
// Otherwise, we should use our target frame
finalTargetFrame = targetFrame;
poseTmp.frame_id_ = (differential && !imuData ? finalTargetFrame : msg->header.frame_id);
//如果differential为true且imuData为false,则使用targetframe;否则,使用msg->header.frame_id。
//这里我们的odom使用了差分,所以用的是targetframe,也就是worldFrameId_
}然后处理消息,这里省略了检查四元数是否为空的步骤
poseTmp.stamp_ = msg->header.stamp;
//位置
poseTmp.setOrigin(tf2::Vector3(msg->pose.pose.position.x,
msg->pose.pose.position.y,
msg->pose.pose.position.z));
//。。。省略
//旋转
tf2::fromMsg(msg->pose.pose.orientation, orientation);
if (fabs(orientation.length() - 1.0) > 0.01)
{
ROS_WARN_ONCE("An input was not normalized, this should NOT happen, but will normalize.");
orientation.normalize();
}
poseTmp.setRotation(orientation);然后查找poseTmp.frame_id_到finalTargetFrame的tf是否存在
然后如果有变换,就开始处理,其中IMU单独处理
先创建两个mask用于选取我们在config中预先设置为true的数据,是个对角阵。
tf2::Matrix3x3 maskPosition(updateVector[StateMemberX], 0, 0,
0, updateVector[StateMemberY], 0,
0, 0, updateVector[StateMemberZ]);
tf2::Matrix3x3 maskOrientation(updateVector[StateMemberRoll], 0, 0,
0, updateVector[StateMemberPitch], 0,
0, 0, updateVector[StateMemberYaw]);由于IMU可能有安装角度不一样,导致IMU的俯仰,变成了车辆的滚转,所以用安装yaw角旋转一下,其他的直接旋转mask
if (imuData)
{
/* We have to treat IMU orientation data differently. Even though we are dealing with pose
* data when we work with orientations, for IMUs, the frame_id is the frame in which the
* sensor is mounted, and not the coordinate frame of the IMU. Imagine an IMU that is mounted
* facing sideways. The pitch in the IMU frame becomes roll for the vehicle. This means that
* we need to rotate roll and pitch angles by the IMU's mounting yaw offset, and we must apply
* similar treatment to its update mask and covariance. */
double dummy, yaw;
targetFrameTrans.getBasis().getRPY(dummy, dummy, yaw);
tf2::Matrix3x3 transTmp;
transTmp.setRPY(0.0, 0.0, yaw);
maskPosition = transTmp * maskPosition;
maskOrientation = transTmp * maskOrientation;
}
else
{
maskPosition = targetFrameTrans.getBasis() * maskPosition;
maskOrientation = targetFrameTrans.getBasis() * maskOrientation;
}然后根据mask的列中至少有一个为true,则updateVector对应为true,以复制协方差矩阵对应的值
Eigen::MatrixXd covariance(POSE_SIZE, POSE_SIZE);
covariance.setZero();
copyCovariance(&(msg->pose.covariance[0]), covariance, topicName, updateVector, POSITION_OFFSET, POSE_SIZE);然后旋转协方差矩阵,这里略了。我的IMU这里没有旋转。
对于IMU数据,我们得到的转换是从base_link到IMU安装框架的变换。它不是IMU方向数据报告的坐标系。如果IMU以non-neutral方向安装,我们需要删除这些偏移量,然后可能需要“交换”滚转和俯仰。请注意,此转换不处理NED->ENU转换。当数据接收时,假设数据位于ENU帧中。(也就是z轴向上)
进行一个纠正
if (imuData)
{
//把旋转和测量转换成RPY
// @todo: There must be a way to handle this with quaternions. Need to look into it.
double rollOffset = 0;
double pitchOffset = 0;
double yawOffset = 0;
double roll = 0;
double pitch = 0;
double yaw = 0;
RosFilterUtilities::quatToRPY(targetFrameTrans.getRotation(), rollOffset, pitchOffset, yawOffset);
RosFilterUtilities::quatToRPY(poseTmp.getRotation(), roll, pitch, yaw);
//应用偏移量(确保它们绑定),并将它们放入向量中
tf2::Vector3 rpyAngles(FilterUtilities::clampRotation(roll - rollOffset),
FilterUtilities::clampRotation(pitch - pitchOffset),
FilterUtilities::clampRotation(yaw - yawOffset));
//现在,我们需要通过偏航偏移值旋转横滚和俯仰。想象一个IMU朝向侧面的情况。
// 在这种情况下IMU的世界框架的俯仰是机器人的横滚。
tf2::Matrix3x3 mat;
mat.setRPY(0.0, 0.0, yawOffset);
rpyAngles = mat * rpyAngles;
poseTmp.getBasis().setRPY(rpyAngles.getX(), rpyAngles.getY(), rpyAngles.getZ());
//我们将在稍后使用此目标转换,但是我们已经转换了IMU数据,就好像IMU
//在机器人上中立安装,所以我们可以使变换成单位矩阵。
//就是说现在旋转是正确的了。变换为单位矩阵。
targetFrameTrans.setIdentity();
}接下来分两种情况,一个是差分模式,需要生成twist消息,否则直接将其转换为目标坐标系下。
我们的odom使用了差分
if (differential)
{
bool success = false;
//我们将使用poseTmp,因此存储它,
//因为我们需要保存其当前值以供下一个测量使用。
curMeasurement = poseTmp;
//确保我们有以前的测量结果
if (previousMeasurements_.count(topicName) > 0 && previousMeasurementCovariances_.count(topicName) > 0)
{
//如果我们正在进行差分积分并且有这个传感器的先前测量,那就相减,获得deta
//即使我们不使用来自该传感器的所有变量,我们需要使用整个测量来确定到新测量的deta
tf2::Transform prevMeasurement = previousMeasurements_[topicName];
poseTmp.setData(prevMeasurement.inverseTimes(poseTmp));
//现在,我们在frame_id中有一个测量的delta,但我们希望该delta在目标框架中,因此
//我们需要应用目标框架变换的旋转
//这里其实没有动。
targetFrameTrans.setOrigin(tf2::Vector3(0.0, 0.0, 0.0));
poseTmp.mult(targetFrameTrans, poseTmp);
//现在使用与上一条消息的时间差来计算平移和旋转速度
double dt = msg->header.stamp.toSec() - lastMessageTimes_[topicName].toSec();
double xVel = poseTmp.getOrigin().getX() / dt;
double yVel = poseTmp.getOrigin().getY() / dt;
double zVel = poseTmp.getOrigin().getZ() / dt;
double rollVel = 0;
double pitchVel = 0;
double yawVel = 0;
RosFilterUtilities::quatToRPY(poseTmp.getRotation(), rollVel, pitchVel, yawVel);
rollVel /= dt;
pitchVel /= dt;
yawVel /= dt;
//填写消息中的速度数据
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped *twistPtr = new geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped();
twistPtr->header = msg->header;
twistPtr->header.frame_id = baseLinkFrameId_;
twistPtr->twist.twist.linear.x = xVel;
twistPtr->twist.twist.linear.y = yVel;
twistPtr->twist.twist.linear.z = zVel;
twistPtr->twist.twist.angular.x = rollVel;
twistPtr->twist.twist.angular.y = pitchVel;
twistPtr->twist.twist.angular.z = yawVel;
std::vector<int> twistUpdateVec(STATE_SIZE, false);
std::copy(updateVector.begin() + POSITION_OFFSET,
updateVector.begin() + POSE_SIZE,
twistUpdateVec.begin() + POSITION_V_OFFSET);
std::copy(twistUpdateVec.begin(), twistUpdateVec.end(), updateVector.begin());
geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStampedConstPtr ptr(twistPtr);
//现在旋转此测量的旧的协方差
//并当前测量的旋转协方差 + 先前测量的旋转协方差,并乘以时间差。
//作为速度的协方差
Eigen::MatrixXd prevCovarRotated = rot6d * previousMeasurementCovariances_[topicName] * rot6d.transpose();
covarianceRotated = (covarianceRotated.eval() + prevCovarRotated) * dt;
copyCovariance(covarianceRotated, &(twistPtr->twist.covariance[0]), POSE_SIZE);
//再调用prepareTwist
success = prepareTwist(ptr,
topicName + "_twist",
twistPtr->header.frame_id,
updateVector,
measurement,
measurementCovariance);
}
// 7f. Update the previous measurement and measurement covariance
//更新上一次的测量和测量协方差
previousMeasurements_[topicName] = curMeasurement;
previousMeasurementCovariances_[topicName] = covariance;
retVal = success;
}没有使用差分的消息。
//如果我们处于relative模式,则删除初始测量
if (relative)
{
//初始化测量
if (initialMeasurements_.count(topicName) == 0)
{
initialMeasurements_.insert(std::pair<std::string, tf2::Transform>(topicName, poseTmp));
}
tf2::Transform initialMeasurement = initialMeasurements_[topicName];
poseTmp.setData(initialMeasurement.inverseTimes(poseTmp));
}
//将目标帧转换应用于姿态对象。
poseTmp.mult(targetFrameTrans, poseTmp);
poseTmp.frame_id_ = finalTargetFrame;
//最后,将所有内容复制到我们的测量和协方差对象中
measurement(StateMemberX) = poseTmp.getOrigin().x();
measurement(StateMemberY) = poseTmp.getOrigin().y();
measurement(StateMemberZ) = poseTmp.getOrigin().z();
// 滤波器需要rpy而不是四元数
double roll, pitch, yaw;
RosFilterUtilities::quatToRPY(poseTmp.getRotation(), roll, pitch, yaw);
measurement(StateMemberRoll) = roll;
measurement(StateMemberPitch) = pitch;
measurement(StateMemberYaw) = yaw;
measurementCovariance.block(0, 0, POSE_SIZE, POSE_SIZE) = covarianceRotated.block(0, 0, POSE_SIZE, POSE_SIZE);
// 2D mode
if (twoDMode_)
{
forceTwoD(measurement, measurementCovariance, updateVector);
}
retVal = true;1.1.8 prepareTwist函数
template<typename T>
bool RosFilter<T>::prepareTwist
(const geometry_msgs::TwistWithCovarianceStamped::ConstPtr &msg,
const std::string &topicName,
const std::string &targetFrame,
std::vector<int> &updateVector,
Eigen::VectorXd &measurement,
Eigen::MatrixXd &measurementCovariance)
Prepares a twist message for integration into the filter
参数:
msg – - The twist message to prepare
topicName – - The name of the topic over which this message was received
targetFrame – - The target tf frame
updateVector – - The update vector for the data source
measurement – - The twist data converted to a measurement
measurementCovariance – - The covariance of the converted measurement1、 如果是来源odom,twist的targetframe就是baseLinkFrameId_
2、 如果是imu,pose、twist和accel都是baseLinkFrameId_
3、我这里还有可能是odom的差分来源,同样也是baseLinkFrameId_
大概内容也是旋转mask,然后mask来更新updateVector,然后获得线速度和角速度的6*6旋转矩阵,对线速度和角速度进行变换,然后同样旋转斜方差矩阵,最后获得measurement和measuremCovariance。
注意这里:传感器可能不测量旋转速度。但是如果它测量线性速度,那么我们需要删除由于角速度和传感器相对于车辆原点的位置偏移而产生的“虚假”线性速度。
//先获得当前状态
const Eigen::VectorXd &state = filter_.getState();
tf2::Vector3 stateTwistRot(state(StateMemberVroll),
state(StateMemberVpitch),
state(StateMemberVyaw));
//旋转速度测量
measTwistRot = targetFrameTrans.getBasis() * measTwistRot;
twistLin = targetFrameTrans.getBasis() * twistLin + targetFrameTrans.getOrigin().cross(stateTwistRot);
//getOrigin()返回一个3D向量,表示目标帧相对于本地帧的原点坐标。cross是用来计算两个向量的叉积1.1.9 prepareAcceleration函数
template<typename T>
bool RosFilter<T>::prepareAcceleration(
const sensor_msgs::Imu::ConstPtr &msg,
const std::string &topicName,
const std::string &targetFrame,
std::vector<int> &updateVector,
Eigen::VectorXd &measurement,
Eigen::MatrixXd &measurementCovariance)
Prepares an IMU message's linear acceleration for integration into the filter
参数:
msg – - The IMU message to prepare
topicName – - The name of the topic over which this message was received
targetFrame – - The target tf frame
updateVector – - The update vector for the data source
measurement – - The twist data converted to a measurement
measurementCovariance – - The covariance of the converted measurementimu,pose、twist和accel都是baseLinkFrameId_,加速度只有IMU有。
与前面也基本一致,旋转测量值、协方差矩阵和Mask到目标坐标系。但是多一个步骤,就是加速度需要去掉重力加速度分量。
// 处理加速度中的重力分量
if (removeGravitationalAcc_[topicName])
{
tf2::Vector3 normAcc(0, 0, gravitationalAcc_);
tf2::Transform trans;
//如果消息的方向协方差矩阵的第一个元素为-1,说明消息中没有方向信息,需要使用滤波器状态的方向信息来转换和移除加速度
if (::fabs(msg->orientation_covariance[0] + 1) < 1e-9)
{
const Eigen::VectorXd &state = filter_.getState();
tf2::Matrix3x3 stateTmp;
stateTmp.setRPY(state(StateMemberRoll),
state(StateMemberPitch),
state(StateMemberYaw));
tf2::Transform imuFrameTrans;
RosFilterUtilities::lookupTransformSafe(tfBuffer_,
targetFrame,
msgFrame,
msg->header.stamp,
tfTimeout_,
imuFrameTrans);
trans.setBasis(stateTmp * imuFrameTrans.getBasis());
}
else
{
tf2::Quaternion curAttitude;
tf2::fromMsg(msg->orientation, curAttitude);
if (fabs(curAttitude.length() - 1.0) > 0.01)
{
ROS_WARN_ONCE("An input was not normalized, this should NOT happen, but will normalize.");
curAttitude.normalize();
//四元数归一化
}
trans.setRotation(curAttitude);
}
//去掉重力分量
tf2::Vector3 rotNorm = trans.getBasis().inverse() * normAcc;
accTmp.setX(accTmp.getX() - rotNorm.getX());
accTmp.setY(accTmp.getY() - rotNorm.getY());
accTmp.setZ(accTmp.getZ() - rotNorm.getZ());
}
以及准备好后插入队列函数
1.1.10 enqueueMeasurement函数和Measurement结构体
内容很简单,就是加入queue中
目录
本文聚焦ekf_localization_node节点,只关注主要函数。
1、RobotLocalization::RosFilter ekf(nh, nh_priv);
1.1.10 enqueueMeasurement函数和Measurement结构体
1.1.12 integrateMeasurements函数
// typedef boost::shared_ptr<Measurement> MeasurementPtr;
// struct Measurement
MeasurementPtr meas = MeasurementPtr(new Measurement());
meas->topicName_ = topicName;
meas->measurement_ = measurement;
meas->covariance_ = measurementCovariance;
meas->updateVector_ = updateVector;
meas->time_ = time.toSec();
meas->mahalanobisThresh_ = mahalanobisThresh;
meas->latestControl_ = latestControl_;
meas->latestControlTime_ = latestControlTime_.toSec();
measurementQueue_.push(meas);measurement结构体有点类似message,必然包括测量值和协方差,还有马氏距离阈值、时间戳、话题名、更新向量等。这里用的是boost的智能指针,也可以使用<memory>中的std::shared_ptr。
struct Measurement
{
// The time stamp of the most recent control term (needed for lagged data)
double latestControlTime_;
// The Mahalanobis distance threshold in number of sigmas
double mahalanobisThresh_;
// The real-valued time, in seconds, since some epoch
// (presumably the start of execution, but any will do)
double time_;
// The topic name for this measurement. Needed
// for capturing previous state values for new
// measurements.
std::string topicName_;
// This defines which variables within this measurement
// actually get passed into the filter. std::vector<bool>
// is generally frowned upon, so we use ints.
std::vector<int> updateVector_;
// The most recent control vector (needed for lagged data)
Eigen::VectorXd latestControl_;
// The measurement and its associated covariance
Eigen::VectorXd measurement_;
Eigen::MatrixXd covariance_;
// We want earlier times to have greater priority
//这里是给priority_queue进行按照时间排序的仿函数,越早的时间优先级越高,越先被处理
//就是他typedef std::priority_queue<MeasurementPtr, std::vector<MeasurementPtr>, Measurement> MeasurementQueue;
//他在ros_filter.h文件中
bool operator()(const boost::shared_ptr<Measurement> &a, const boost::shared_ptr<Measurement> &b)
{
return (*this)(*(a.get()), *(b.get()));
}
bool operator()(const Measurement &a, const Measurement &b)
{
return a.time_ > b.time_;
}
Measurement() :
latestControlTime_(0.0),
mahalanobisThresh_(std::numeric_limits<double>::max()),
time_(0.0),
topicName_("")
{
}
};
typedef boost::shared_ptr<Measurement> MeasurementPtr;1.1.11 periodicUpdate循环更新函数
主要是发布数据和integrateMeasurements(curTime)
template<typename T>
void RosFilter<T>::periodicUpdate(const ros::TimerEvent& event)
{
// 警告用户如果更新时间太长(> 2个周期)
const double loop_elapsed = (event.current_real - event.last_expected).toSec();
if (loop_elapsed > 2./frequency_)
{ROS_WARN_STREAM("Failed to meet update rate! Took " << std::setprecision(20) << loop_elapsed);}
// 等待过滤器被启用
if (!enabled_)
{
ROS_INFO_STREAM_ONCE("Filter is disabled. To enable it call the " << enableFilterSrv_.getService() <<
" service");
return;
}
ros::Time curTime = ros::Time::now();
if (toggledOn_)
{
// Now we'll integrate any measurements we've received if requested
// 现在,如果需要,我们将集成我们收到的任何测量
integrateMeasurements(curTime);
}
else
{
// 清除测量,因为我们目前没有处理新输入
clearMeasurementQueue();
// Reset last measurement time so we don't get a large time delta on toggle on
// 重置最后的测量时间,这样我们就不会在切换时得到一个大的时间差
if (filter_.getInitializedStatus())
{
filter_.setLastMeasurementTime(ros::Time::now().toSec());
}
}
// 获取最新的状态并发布它
nav_msgs::Odometry filteredPosition;
if (getFilteredOdometryMessage(filteredPosition))
{
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform = tf2::toMsg(tf2::Transform::getIdentity());
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.header.stamp = filteredPosition.header.stamp + tfTimeOffset_;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.header.frame_id = filteredPosition.header.frame_id;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.child_frame_id = filteredPosition.child_frame_id;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform.translation.x = filteredPosition.pose.pose.position.x;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform.translation.y = filteredPosition.pose.pose.position.y;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform.translation.z = filteredPosition.pose.pose.position.z;
worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform.rotation = filteredPosition.pose.pose.orientation;
// filteredPosition是包含状态和协方差的消息:nav_msgs::Odometry
//状态变量出错
if (!validateFilterOutput(filteredPosition))
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Critical Error, NaNs were detected in the output state of the filter." <<
" This was likely due to poorly conditioned process, noise, or sensor covariances.");
}
// 如果worldFrameId_是odomFrameId_帧,那么我们可以直接发送变换。
// 如果worldFrameId_是mapFrameId_帧,我们将有一些工作要做。
if (publishTransform_)
{
if (filteredPosition.header.frame_id == odomFrameId_)
{
worldTransformBroadcaster_.sendTransform(worldBaseLinkTransMsg_);
//发布从odom到base_link的变换
}
else if (filteredPosition.header.frame_id == mapFrameId_)
{
try
{
tf2::Transform worldBaseLinkTrans;
tf2::fromMsg(worldBaseLinkTransMsg_.transform, worldBaseLinkTrans);
//这是map下的当前位姿,也就是map到base_link的变换
tf2::Transform baseLinkOdomTrans;
tf2::fromMsg(tfBuffer_.lookupTransform(baseLinkFrameId_, odomFrameId_, ros::Time(0)).transform,
baseLinkOdomTrans);
//这个函数是 要把odom下的数据变到base_link下
//也就是获得base_link到odom的变换
tf2::Transform mapOdomTrans;
mapOdomTrans.mult(worldBaseLinkTrans, baseLinkOdomTrans);
//把map到baselink变换 乘以 baselink到odom变换,得到map到odom的变换
geometry_msgs::TransformStamped mapOdomTransMsg;
mapOdomTransMsg.transform = tf2::toMsg(mapOdomTrans);
mapOdomTransMsg.header.stamp = filteredPosition.header.stamp + tfTimeOffset_;
mapOdomTransMsg.header.frame_id = mapFrameId_;
mapOdomTransMsg.child_frame_id = odomFrameId_;
worldTransformBroadcaster_.sendTransform(mapOdomTransMsg);
}
catch(...)
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM_DELAYED_THROTTLE(5.0, "Could not obtain transform from "
<< odomFrameId_ << "->" << baseLinkFrameId_);
}
}
else
{
ROS_ERROR_STREAM("Odometry message frame_id was " << filteredPosition.header.frame_id <<
", expected " << mapFrameId_ << " or " << odomFrameId_);
}
}
// 发布位置和变换
positionPub_.publish(filteredPosition);
if (printDiagnostics_)
{
freqDiag_->tick();
}
}
// 如果需要加速度并且过滤器已初始化,则发布加速度
geometry_msgs::AccelWithCovarianceStamped filteredAcceleration;
if (publishAcceleration_ && getFilteredAccelMessage(filteredAcceleration))
{
accelPub_.publish(filteredAcceleration);
}
/* Diagnostics can behave strangely when playing back from bag
* files and using simulated time, so we have to check for
* time suddenly moving backwards as well as the standard
* timeout criterion before publishing. */
double diagDuration = (curTime - lastDiagTime_).toSec();
if (printDiagnostics_ && (diagDuration >= diagnosticUpdater_.getPeriod() || diagDuration < 0.0))
{
diagnosticUpdater_.force_update();
lastDiagTime_ = curTime;
}
// Clear out expired history data
if (smoothLaggedData_)
{
clearExpiredHistory(filter_.getLastMeasurementTime() - historyLength_);
}
}1.1.12 integrateMeasurements函数
纠正测量的时间戳,增加过去的测量值,进行预测更新,如果长时间没有接收到传感器数据就只进行预测。重点是revertTo(firstMeasurementTime - 1e-9)纠正滤波器最新状态以及插入旧的测量。还有就是核心filter_.processMeasurement(*(measurement.get()));调用滤波器处理测量值。
template<typename T>
void RosFilter<T>::integrateMeasurements(const ros::Time ¤tTime)
{
const double currentTimeSec = currentTime.toSec();
RF_DEBUG("------ RosFilter::integrateMeasurements ------\n\n"
"Integration time is " << std::setprecision(20) << currentTimeSec << "\n"
<< measurementQueue_.size() << " measurements in queue.\n");
bool predictToCurrentTime = predictToCurrentTime_;
//这个参数是最新测量到当前时间比较长的标志位,如果为true,则需要先预测到当前时间,再进行更新。
// 如果队列中有任何测量值,则要开始恢复时间戳,然后遍历所有测量,进行预测更新。
if (!measurementQueue_.empty())
{
// 检查我们要处理的第一个测量值是否比滤波器的最后一个测量值旧。
// 这意味着我们收到了一个序列外的消息(一个旧的时间戳),我们需要恢复滤波器状态和测量队列到第一个状态,该状态是我们第一个测量值的时间的状态。
const MeasurementPtr& firstMeasurement = measurementQueue_.top();
int restoredMeasurementCount = 0;
if (smoothLaggedData_ && firstMeasurement->time_ < filter_.getLastMeasurementTime())
{
RF_DEBUG("Received a measurement that was " << filter_.getLastMeasurementTime() - firstMeasurement->time_ <<
" seconds in the past. Reverting filter state and measurement queue...");
int originalCount = static_cast<int>(measurementQueue_.size());
const double firstMeasurementTime = firstMeasurement->time_;
const std::string firstMeasurementTopic = firstMeasurement->topicName_;
//找到在第一个测量值之前的最新过滤器状态,并将其再次设置为当前状态。相当于之前算的不要了,重新计算。
//把历史测量中 晚于给定时间戳,且 晚于滤波器最新状态时间(这是早于给定时间的) 的测量,重新放入测量队列
if (!revertTo(firstMeasurementTime - 1e-9)) // revertTo may invalidate firstMeasurement
{
RF_DEBUG("ERROR: history interval is too small to revert to time " << firstMeasurementTime << "\n");
ROS_WARN_STREAM_DELAYED_THROTTLE(historyLength_, "Received old measurement for topic " <<
firstMeasurementTopic << ", but history interval is insufficiently sized. Measurement time is " <<
std::setprecision(20) << firstMeasurementTime << ", current time is " << currentTime.toSec() <<
", history length is " << historyLength_ << ".");
restoredMeasurementCount = 0;
}
restoredMeasurementCount = static_cast<int>(measurementQueue_.size()) - originalCount;
}
//遍历所有的测量值。
while (!measurementQueue_.empty() && ros::ok())
{
MeasurementPtr measurement = measurementQueue_.top();
// 如果我们已经到达一个时间比现在时刻晚的测量值,它应该等 将来的迭代。
// 由于测量值存储在优先级队列中,所有剩余的测量值都将在未来。
if (measurement->time_ > currentTime.toSec())
{
break;
}
measurementQueue_.pop();
if (useControl_ && restoredMeasurementCount > 0)
{
filter_.setControl(measurement->latestControl_, measurement->latestControlTime_);
restoredMeasurementCount--;
}
// 这将调用预测,如果必要,进行更新步骤
filter_.processMeasurement(*(measurement.get()));
// Store old states and measurements if we're smoothing
if (smoothLaggedData_)
{
// 保持 历史测量的时间 小于 当前测量队列第一个测量值的时间
measurementHistory_.push_back(measurement);
// 测量处理完了,或者,测量值的时间大致不等于滤波器最新的测量值时间,就保存一次滤波器。
if (measurementQueue_.empty() ||
::fabs(measurementQueue_.top()->time_ - filter_.getLastMeasurementTime()) > 1e-9)
{
saveFilterState(filter_);
}
}
}
}
else if (filter_.getInitializedStatus())
{
// 如果我们很长时间没有得到任何测量值,我们仍然需要继续估计我们的状态。因此,我们应该在这里向前预测状态。
double lastUpdateDelta = currentTimeSec - filter_.getLastMeasurementTime();
// If we get a large delta, then continuously predict until
if (lastUpdateDelta >= filter_.getSensorTimeout())
{
predictToCurrentTime = true;
RF_DEBUG("Sensor timeout! Last measurement time was " << filter_.getLastMeasurementTime() <<
", current time is " << currentTimeSec <<
", delta is " << lastUpdateDelta << "\n");
}
}
else
{
RF_DEBUG("Filter not yet initialized.\n");
}
if (filter_.getInitializedStatus() && predictToCurrentTime)
{
double lastUpdateDelta = currentTimeSec - filter_.getLastMeasurementTime();
filter_.validateDelta(lastUpdateDelta);
filter_.predict(currentTimeSec, lastUpdateDelta);
// Update the last measurement time and last update time
filter_.setLastMeasurementTime(filter_.getLastMeasurementTime() + lastUpdateDelta);
}
RF_DEBUG("\n----- /RosFilter::integrateMeasurements ------\n");
}1.1.13 revertTo函数
总结一下就是把最新测量的第一个测量值时间戳作为基准,晚于这个基准的滤波器状态都删掉,然后把删除后的历史滤波器状态中最新的那个,设置为当前滤波器状态(相当于把滤波器状态退回到第一个测量值时间戳前面)。
然后把历史测量中 晚于给定时间戳,且 晚于滤波器最新状态时间(这是早于给定时间的) 的测量,重新放入测量队列。
我们发现这里插入测量队列中是直接push,这里用了一个priority_queue的容器,可以自动排序,有点类似set和map,可以自动排序,但是这里是先进先出的原则,所以用queue。
template<typename T>
bool RosFilter<T>::revertTo(const double time)
{
RF_DEBUG("\n----- RosFilter::revertTo -----\n");
RF_DEBUG("\nRequested time was(firstMeasurementTime - 1e-9) " << std::setprecision(20) << time << "\n")
size_t history_size = filterStateHistory_.size();
// 从后往前遍历历史队列,直到找到一个时间戳小于等于请求时间的滤波器状态。
// 因为在那个时间之后的所有保存的状态都将被覆盖/修正,所以我们可以从队列中弹出。
// 如果历史记录不够短,我们只需要取最旧的状态。
FilterStatePtr lastHistoryState;
while (!filterStateHistory_.empty() && filterStateHistory_.back()->lastMeasurementTime_ > time)
{
lastHistoryState = filterStateHistory_.back();
filterStateHistory_.pop_back();
}
// 如果状态历史记录此时不为空,这意味着我们的历史记录足够大,我们应该恢复到历史队列的最后一个状态。
bool retVal = false;
if (!filterStateHistory_.empty())
{
retVal = true;
lastHistoryState = filterStateHistory_.back();
}
else
{
RF_DEBUG("Insufficient history to revert to time " << time << "\n");
if (lastHistoryState)
{
RF_DEBUG("Will revert to oldest state at " << lastHistoryState->latestControlTime_ << ".\n");
ROS_WARN_STREAM_DELAYED_THROTTLE(historyLength_, "Could not revert to state with time " <<
std::setprecision(20) << time << ". Instead reverted to state with time " <<
lastHistoryState->lastMeasurementTime_ << ". History size was " << history_size);
}
}
// 如果我们有一个有效的恢复状态,恢复
if (lastHistoryState)
{
// 重置滤波器到队列中的最新状态。
const FilterStatePtr &state = lastHistoryState;
filter_.setState(state->state_);
filter_.setEstimateErrorCovariance(state->estimateErrorCovariance_);
filter_.setLastMeasurementTime(state->lastMeasurementTime_);
RF_DEBUG("Reverted to state with time " << std::setprecision(20) << state->lastMeasurementTime_ << "\n");
//把历史测量中 晚于给定时间戳,且 晚于滤波器最新状态时间(应该是早于给定时间的) 的测量,重新放入测量队列
int restored_measurements = 0;
while (!measurementHistory_.empty() && measurementHistory_.back()->time_ > time)
{
// 不需要恢复早于滤波器最新状态时间的测量
if (state->lastMeasurementTime_ <= measurementHistory_.back()->time_)
{
measurementQueue_.push(measurementHistory_.back());
restored_measurements++;
}
measurementHistory_.pop_back();
}
RF_DEBUG("Restored " << restored_measurements << " to measurement queue.\n");
}
RF_DEBUG("\n----- /RosFilter::revertTo\n");
return retVal;
}1.1.14 测量队列、历史测量队列和历史状态队列
这个是在ros_filter.h文件中的,补充一下
typedef std::priority_queue<MeasurementPtr, std::vector<MeasurementPtr>, Measurement> MeasurementQueue;
typedef std::deque<MeasurementPtr> MeasurementHistoryDeque;
typedef std::deque<FilterStatePtr> FilterStateHistoryDeque;第一个是一个按照时间戳排序的队列,越早的数据优先级更高,优先被处理。三个模板参数分别是,Measurement的智能指针,存放指针的容器和比较器的类型【重载operater()函数】。
第二三是双端队列,放测量和状态的历史数据。
1.2 Ekf类继承了FilterBase()类
1.2.1 FilterBase类
1.2.1.1 processMeasurement函数
首先如果没有初始化:
FB_DEBUG("First measurement. Initializing filter.\n");
// Initialize the filter, but only with the values we're using
//源代码如果updateVector_中的值为true,则使用测量值初始化状态,否则用默认值初始化状态。(这个默认值可以用服务设置)
size_t measurementLength = measurement.updateVector_.size();
for (size_t i = 0; i < measurementLength; ++i)
{
state_[i] = (measurement.updateVector_[i] ? measurement.measurement_[i] : state_[i]);
}
// Same for covariance
for (size_t i = 0; i < measurementLength; ++i)
{
for (size_t j = 0; j < measurementLength; ++j)
{
estimateErrorCovariance_(i, j) = (measurement.updateVector_[i] && measurement.updateVector_[j] ?
measurement.covariance_(i, j) :
estimateErrorCovariance_(i, j));
}
}
initialized_ = true;已经初始化了:
//确定自上次测量以来经过了多少时间
delta = measurement.time_ - lastMeasurementTime_;
FB_DEBUG("Filter is already initialized. Carrying out predict/correct loop...\n"
"Measurement time is " << std::setprecision(20) << measurement.time_ <<
", last measurement time is " << lastMeasurementTime_ << ", delta is " << delta << "\n");
//如果data>0,进行预测和更新。否则,只是更新。
if (delta > 0)
{
validateDelta(delta);
predict(measurement.time_, delta);
// Return this to the user
predictedState_ = state_;
}
correct(measurement);最后就是data如果大于0,就更新最新的测量时间。
1.2.2 predict函数
计算转移矩阵、雅可比矩阵、动态调整过程噪声、预测状态和预测协方差。
其中有个noalias()函数,还有一个eval()函数,需要再学习一下。
void Ekf::predict(const double referenceTime, const double delta)
{
FB_DEBUG("---------------------- Ekf::predict ----------------------\n" <<
"delta is " << delta << "\n" <<
"state is " << state_ << "\n");
double roll = state_(StateMemberRoll);
double pitch = state_(StateMemberPitch);
double yaw = state_(StateMemberYaw);
double xVel = state_(StateMemberVx);
double yVel = state_(StateMemberVy);
double zVel = state_(StateMemberVz);
double pitchVel = state_(StateMemberVpitch);
double yawVel = state_(StateMemberVyaw);
double xAcc = state_(StateMemberAx);
double yAcc = state_(StateMemberAy);
double zAcc = state_(StateMemberAz);
// 我们需要经常进行三角函数计算
double sp = ::sin(pitch);
double cp = ::cos(pitch);
double cpi = 1.0 / cp;
double tp = sp * cpi;
double sr = ::sin(roll);
double cr = ::cos(roll);
double sy = ::sin(yaw);
double cy = ::cos(yaw);
prepareControl(referenceTime, delta);
// 转移方程,可以看成是状态转移矩阵
//在构造函数中reset函数完成了transferFunction_和transferFunctionJacobian_的初始化(单位矩阵)
// 以第一个为例,就是x方向的位移 = x方向的速度乘以时间间隔
//由于X是在世界坐标系下,所以还要乘以cos(yaw)和cos(pitch)旋转到世界坐标系中。
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVx) = cy * cp * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVy) = (cy * sp * sr - sy * cr) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVz) = (cy * sp * cr + sy * sr) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberAx) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVx) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberAy) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVy) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberAz) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberX, StateMemberVz) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVx) = sy * cp * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVy) = (sy * sp * sr + cy * cr) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVz) = (sy * sp * cr - cy * sr) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberAx) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVx) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberAy) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVy) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberAz) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberY, StateMemberVz) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVx) = -sp * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVy) = cp * sr * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVz) = cp * cr * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberAx) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVx) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberAy) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVy) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberAz) = 0.5 * transferFunction_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberVz) * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberRoll, StateMemberVroll) = delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberRoll, StateMemberVpitch) = sr * tp * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberRoll, StateMemberVyaw) = cr * tp * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberPitch, StateMemberVpitch) = cr * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberPitch, StateMemberVyaw) = -sr * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberYaw, StateMemberVpitch) = sr * cpi * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberYaw, StateMemberVyaw) = cr * cpi * delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberVx, StateMemberAx) = delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberVy, StateMemberAy) = delta;
transferFunction_(StateMemberVz, StateMemberAz) = delta;
// 准备转移函数雅克比矩阵。该函数是从转移函数解析导出的。
double xCoeff = 0.0;
double yCoeff = 0.0;
double zCoeff = 0.0;
double oneHalfATSquared = 0.5 * delta * delta;
yCoeff = cy * sp * cr + sy * sr;
zCoeff = -cy * sp * sr + sy * cr;
//x对roll求导
double dFx_dR = (yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
//roll对roll求导
double dFR_dR = 1.0 + (cr * tp * pitchVel - sr * tp * yawVel) * delta;
xCoeff = -cy * sp;
yCoeff = cy * cp * sr;
zCoeff = cy * cp * cr;
//x对pitch求导
double dFx_dP = (xCoeff * xVel + yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(xCoeff * xAcc + yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
//Roll对pitch求导
double dFR_dP = (cpi * cpi * sr * pitchVel + cpi * cpi * cr * yawVel) * delta;
xCoeff = -sy * cp;
yCoeff = -sy * sp * sr - cy * cr;
zCoeff = -sy * sp * cr + cy * sr;
//x对yaw求导
double dFx_dY = (xCoeff * xVel + yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(xCoeff * xAcc + yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
yCoeff = sy * sp * cr - cy * sr;
zCoeff = -sy * sp * sr - cy * cr;
//y对roll求导
double dFy_dR = (yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
//pitch对roll求导
double dFP_dR = (-sr * pitchVel - cr * yawVel) * delta;
xCoeff = -sy * sp;
yCoeff = sy * cp * sr;
zCoeff = sy * cp * cr;
//y对pitch求导
double dFy_dP = (xCoeff * xVel + yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(xCoeff * xAcc + yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
xCoeff = cy * cp;
yCoeff = cy * sp * sr - sy * cr;
zCoeff = cy * sp * cr + sy * sr;
//y对yaw求导
double dFy_dY = (xCoeff * xVel + yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(xCoeff * xAcc + yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
yCoeff = cp * cr;
zCoeff = -cp * sr;
//z对roll求导
double dFz_dR = (yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
//yall对roll求导
double dFY_dR = (cr * cpi * pitchVel - sr * cpi * yawVel) * delta;
xCoeff = -cp;
yCoeff = -sp * sr;
zCoeff = -sp * cr;
//z对pitch求导
double dFz_dP = (xCoeff * xVel + yCoeff * yVel + zCoeff * zVel) * delta +
(xCoeff * xAcc + yCoeff * yAcc + zCoeff * zAcc) * oneHalfATSquared;
//yaw对pitch求导
double dFY_dP = (sr * tp * cpi * pitchVel + cr * tp * cpi * yawVel) * delta;
// Much of the transfer function Jacobian is identical to the transfer function
transferFunctionJacobian_ = transferFunction_;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberX, StateMemberRoll) = dFx_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberX, StateMemberPitch) = dFx_dP;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberX, StateMemberYaw) = dFx_dY;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberY, StateMemberRoll) = dFy_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberY, StateMemberPitch) = dFy_dP;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberY, StateMemberYaw) = dFy_dY;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberRoll) = dFz_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberZ, StateMemberPitch) = dFz_dP;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberRoll, StateMemberRoll) = dFR_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberRoll, StateMemberPitch) = dFR_dP;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberPitch, StateMemberRoll) = dFP_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberYaw, StateMemberRoll) = dFY_dR;
transferFunctionJacobian_(StateMemberYaw, StateMemberPitch) = dFY_dP;
FB_DEBUG("Transfer function is:\n" << transferFunction_ <<
"\nTransfer function Jacobian is:\n" << transferFunctionJacobian_ <<
"\nProcess noise covariance is:\n" << processNoiseCovariance_ <<
"\nCurrent state is:\n" << state_ << "\n");
Eigen::MatrixXd *processNoiseCovariance = &processNoiseCovariance_;
//计算动态过程噪声协方差
if (useDynamicProcessNoiseCovariance_)
{
computeDynamicProcessNoiseCovariance(state_, delta);
processNoiseCovariance = &dynamicProcessNoiseCovariance_;
}
// (1) Apply control terms, which are actually accelerations
// 加上控制加速度,没有使用控制,所以是0
state_(StateMemberVroll) += controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVroll) * delta;
state_(StateMemberVpitch) += controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVpitch) * delta;
state_(StateMemberVyaw) += controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVyaw) * delta;
state_(StateMemberAx) = (controlUpdateVector_[ControlMemberVx] ?
controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVx) : state_(StateMemberAx));
state_(StateMemberAy) = (controlUpdateVector_[ControlMemberVy] ?
controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVy) : state_(StateMemberAy));
state_(StateMemberAz) = (controlUpdateVector_[ControlMemberVz] ?
controlAcceleration_(ControlMemberVz) : state_(StateMemberAz));
// (2) Project the state forward: x = Ax + Bu (really, x = f(x, u))
// 计算预测状态
state_ = transferFunction_ * state_;
// 保持欧拉角在[-pi,pi]之间
wrapStateAngles();
FB_DEBUG("Predicted state is:\n" << state_ <<
"\nCurrent estimate error covariance is:\n" << estimateErrorCovariance_ << "\n");
// (3) Project the error forward: P = J * P * J' + detaT * Q
// 计算预测误差协方差
// 这里noalias()函数是确定不会出现混淆,不创建中间临时对象,提高速度、降低内存消耗
// 矩阵乘法可能出现混淆,如matrix1 = matrix1 * matrix2
estimateErrorCovariance_ = (transferFunctionJacobian_ *
estimateErrorCovariance_ *
transferFunctionJacobian_.transpose());
estimateErrorCovariance_.noalias() += delta * (*processNoiseCovariance);
FB_DEBUG("Predicted estimate error covariance is:\n" << estimateErrorCovariance_ <<
"\n\n--------------------- /Ekf::predict ----------------------\n");
}
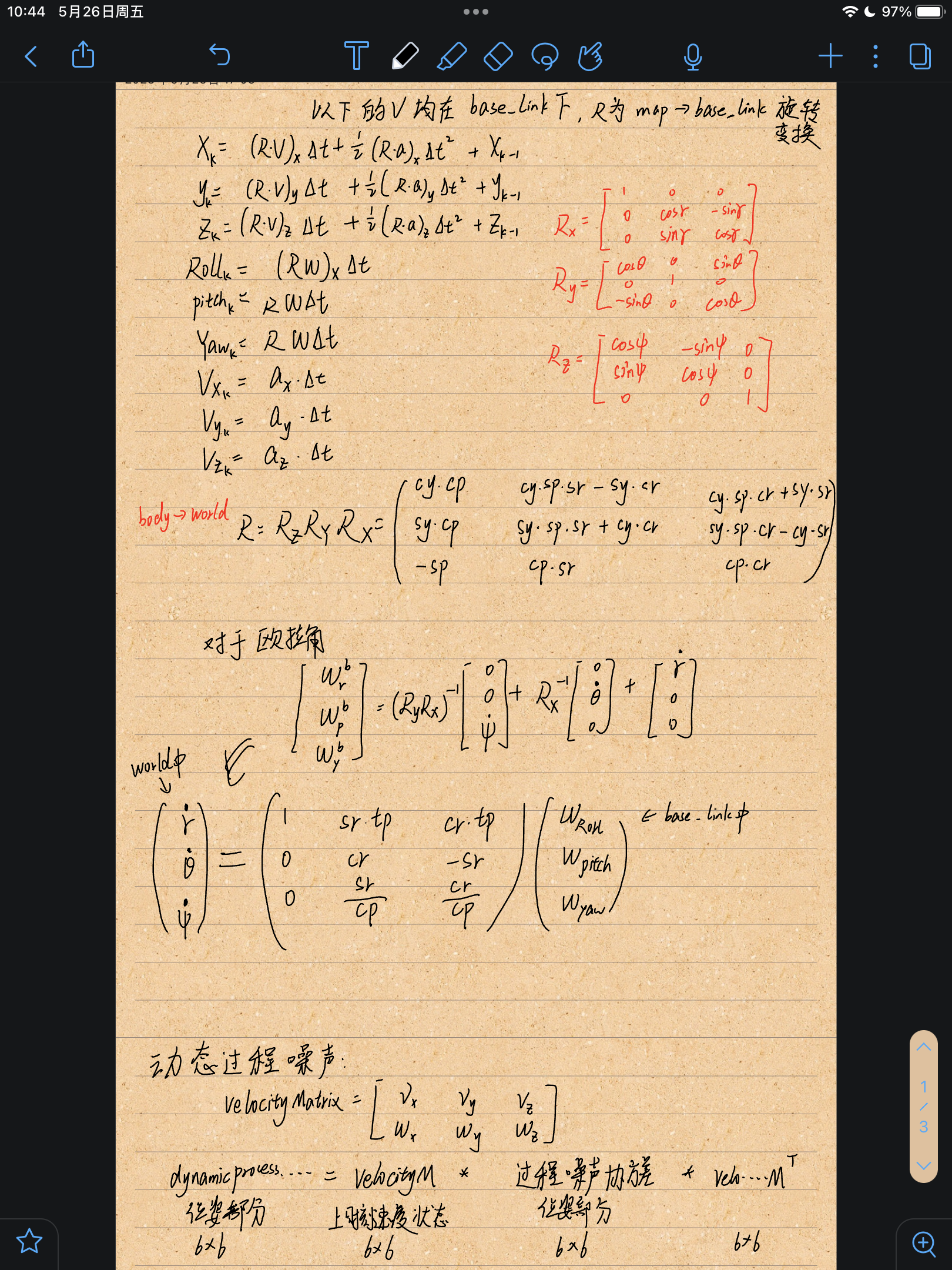
1.2.3 correct函数
void Ekf::correct(const Measurement &measurement)
{
FB_DEBUG("---------------------- Ekf::correct ----------------------\n" <<
"State is:\n" << state_ << "\n"
"Topic is:\n" << measurement.topicName_ << "\n"
"Measurement is:\n" << measurement.measurement_ << "\n"
"Measurement topic name is:\n" << measurement.topicName_ << "\n\n"
"Measurement covariance is:\n" << measurement.covariance_ << "\n");
// 我们不想更新所有内容,因此我们需要构建仅更新状态向量的测量部分的矩阵。
// 在整个预测和校正过程中,我们尝试在Eigen中最大化效率。
// 首先,确定我们正在更新多少个状态向量值
std::vector<size_t> updateIndices;
for (size_t i = 0; i < measurement.updateVector_.size(); ++i)
{
if (measurement.updateVector_[i])
{
// 处理测量中的nan和inf值
if (std::isnan(measurement.measurement_(i)))
{
FB_DEBUG("Value at index " << i << " was nan. Excluding from update.\n");
}
else if (std::isinf(measurement.measurement_(i)))
{
FB_DEBUG("Value at index " << i << " was inf. Excluding from update.\n");
}
else
{
updateIndices.push_back(i);
}
}
}
FB_DEBUG("Update indices are:\n" << updateIndices << "\n");
size_t updateSize = updateIndices.size();
// 现在设置相关矩阵
Eigen::VectorXd stateSubset(updateSize); // x (in most literature)
Eigen::VectorXd measurementSubset(updateSize); // z
Eigen::MatrixXd measurementCovarianceSubset(updateSize, updateSize); // R
Eigen::MatrixXd stateToMeasurementSubset(updateSize, state_.rows()); // H
Eigen::MatrixXd kalmanGainSubset(state_.rows(), updateSize); // K
Eigen::VectorXd innovationSubset(updateSize); // z - Hx残差,测量-预测
stateSubset.setZero();
measurementSubset.setZero();
measurementCovarianceSubset.setZero();
stateToMeasurementSubset.setZero();
kalmanGainSubset.setZero();
innovationSubset.setZero();
// 现在从全尺寸矩阵构建子矩阵
for (size_t i = 0; i < updateSize; ++i)
{
measurementSubset(i) = measurement.measurement_(updateIndices[i]);
stateSubset(i) = state_(updateIndices[i]);
for (size_t j = 0; j < updateSize; ++j)
{
measurementCovarianceSubset(i, j) = measurement.covariance_(updateIndices[i], updateIndices[j]);
}
// 处理测量中的负(坏)协方差。与其排除测量或构成协方差,不如取绝对值。
// 例如,如果我们有一个测量值为1,但协方差为-0.01,则将其更改为0.01。
if (measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i) < 0)
{
FB_DEBUG("WARNING: Negative covariance for index " << i <<
" of measurement (value is" << measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i) <<
"). Using absolute value...\n");
measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i) = ::fabs(measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i));
}
// 如果给定变量的测量方差非常接近0(如e-50或更高),并且协方差矩阵中该变量的方差也接近0,
// 则卡尔曼增益计算将会爆炸。实际上,没有测量可以完全没有误差,因此在这种情况下添加一小部分。
if (measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i) < 1e-9)
{
FB_DEBUG("WARNING: measurement had very small error covariance for index " << updateIndices[i] <<
". Adding some noise to maintain filter stability.\n");
measurementCovarianceSubset(i, i) = 1e-9;
}
}
// 状态到测量函数h现在将是一个measurement_size x full_state_size矩阵,其中(i,i)位置的值将被更新
for (size_t i = 0; i < updateSize; ++i)
{
stateToMeasurementSubset(i, updateIndices[i]) = 1;
}
FB_DEBUG("Current state subset is:\n" << stateSubset <<
"\nMeasurement subset is:\n" << measurementSubset <<
"\nMeasurement covariance subset is:\n" << measurementCovarianceSubset <<
"\nState-to-measurement subset is:\n" << stateToMeasurementSubset << "\n");
// (1) Compute the Kalman gain: K = (PH') / (HPH' + R)
Eigen::MatrixXd pht = estimateErrorCovariance_ * stateToMeasurementSubset.transpose();
Eigen::MatrixXd hphrInv = (stateToMeasurementSubset * pht + measurementCovarianceSubset).inverse();
kalmanGainSubset.noalias() = pht * hphrInv;
innovationSubset = (measurementSubset - stateSubset);//残差
// Wrap angles in the innovation
for (size_t i = 0; i < updateSize; ++i)
{
if (updateIndices[i] == StateMemberRoll ||
updateIndices[i] == StateMemberPitch ||
updateIndices[i] == StateMemberYaw)
{
while (innovationSubset(i) < -PI)
{
innovationSubset(i) += TAU;
}
while (innovationSubset(i) > PI)
{
innovationSubset(i) -= TAU;
}
}
}
// (2) Check Mahalanobis distance between mapped measurement and state.
//检查 测量 和 状态 之间的马氏距离。
if (checkMahalanobisThreshold(innovationSubset, hphrInv, measurement.mahalanobisThresh_))
{
// (3) Apply the gain to the difference between the state and measurement: x = x + K(z - Hx)
//将增益应用于状态和测量之间的差值
state_.noalias() += kalmanGainSubset * innovationSubset;
// (4) Update the estimate error covariance using the Joseph form: (I - KH)P(I - KH)' + KRK'
//使用Joseph形式更新估计误差协方差
Eigen::MatrixXd gainResidual = identity_;
gainResidual.noalias() -= kalmanGainSubset * stateToMeasurementSubset;
estimateErrorCovariance_ = gainResidual * estimateErrorCovariance_ * gainResidual.transpose();
estimateErrorCovariance_.noalias() += kalmanGainSubset *
measurementCovarianceSubset *
kalmanGainSubset.transpose();
// Handle wrapping of angles
//保持角度在[-pi,pi]之间
wrapStateAngles();
FB_DEBUG("Kalman gain subset is:\n" << kalmanGainSubset <<
"\nInnovation is:\n" << innovationSubset <<
"\nCorrected full state is:\n" << state_ <<
"\nCorrected full estimate error covariance is:\n" << estimateErrorCovariance_ <<
"\n\n---------------------- /Ekf::correct ----------------------\n");
}
}1.2.4 computeDynamicProcessNoiseCovariance函数
动态调整过程噪声协方差矩阵,逻辑是速度越快,位置和角度的噪声越大。(感觉怪怪的)
Eigen::MatrixXd velocityMatrix(TWIST_SIZE, TWIST_SIZE);
velocityMatrix.setIdentity();
velocityMatrix.diagonal() *= state.segment(POSITION_V_OFFSET, TWIST_SIZE).norm();
dynamicProcessNoiseCovariance_.block<TWIST_SIZE, TWIST_SIZE>(POSITION_OFFSET, POSITION_OFFSET) =
velocityMatrix *
processNoiseCovariance_.block<TWIST_SIZE, TWIST_SIZE>(POSITION_OFFSET, POSITION_OFFSET) *
velocityMatrix.transpose();这段代码定义了一个大小为6x6的矩阵velocityMatrix,并将其初始化为单位矩阵。然后,它将velocityMatrix对角线上的元素乘以状态向量segment(6, 6)的范数,也就是速度和角速度的范数
@todo:理解其中过程噪声协方差Q自适应调整逻辑,修改测量噪声协方差R改为自适应调整,




 ekf_localization_node节点主要功能是集成各种传感器数据,如odom、imu等,利用扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)进行定位。它涉及到的主要函数包括初始化、回调函数处理数据、加速度处理、测量队列管理、周期性更新滤波器状态等。节点会根据传感器数据的时间戳和设置进行处理,如差分模式、坐标变换、测量值的马氏距离检查等。滤波器通过predict和correct步骤更新状态和协方差矩阵。
ekf_localization_node节点主要功能是集成各种传感器数据,如odom、imu等,利用扩展卡尔曼滤波(EKF)进行定位。它涉及到的主要函数包括初始化、回调函数处理数据、加速度处理、测量队列管理、周期性更新滤波器状态等。节点会根据传感器数据的时间戳和设置进行处理,如差分模式、坐标变换、测量值的马氏距离检查等。滤波器通过predict和correct步骤更新状态和协方差矩阵。


















 7403
7403

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










