1. 前言
输入序列检测,主要包括两种方法
- 状态机法
- 序列缓存对比法
牛客网上有Verilog编程的题可以刷,刷了以后将笔记统一到一篇博客上来。
题目链接:牛客网Verilog刷题
2. 例题1
2.1 题目
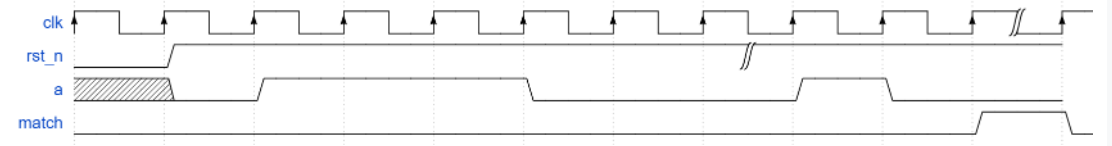
请编写一个序列检测模块,检测输入信号a是否满足01110001序列,当信号满足该序列,给出指示信号match。
模块的接口信号图如下:
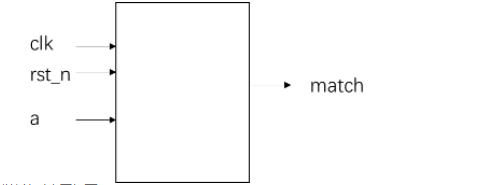
模块的时序图如下:
2.2 解题思路
2.3 代码
2.3.1 序列缓冲对比法
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
reg [7:0] a_tem;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
begin
match <= 1'b0;
end
else if (a_tem == 8'b0111_0001)
begin
match <= 1'b1;
end
else
begin
match <= 1'b0;
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)
if (!rst_n)
begin
a_tem <= 8'b0;
end
else
begin
a_tem <= {a_tem[6:0],a};
end
endmodule
2.3.1 状态机法
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
reg [1:0] state;
reg [1:0] cnt;
//状态转换
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
state <= 0;
else begin
case(state)
0: begin //0
if(!a)
state <= 1;
else
state <= 0;
end
1: begin //01110
if(cnt == 3) begin
if(!a)
state <= 2;
else
state <= 0;
end
else
state <= 1;
end
2: begin //01110001
if(a) begin
if(cnt == 2)
state <= 3;
else
state <= 1;
end
else
state <= 2;
end
3: begin
state <= 0;
end
endcase
end
end
//计数器计数
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
cnt <= 0;
else begin
case(state)
1: begin
if(a)
cnt <= cnt + 1;
else
cnt <= 0;
end
2: begin
if(!a)
cnt <= cnt + 1;
else //检测到a == 1必然切换至1或3,若转换至1则因已检测一个高电平故cnt <= 1
cnt <= 1;
end
default: cnt <= 0;
endcase
end
end
//输出
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n)
match <= 0;
else if(state == 3)
match <= 1;
else
match <= 0;
end
endmodule
3. 例题2
3.1 题目
请编写一个序列检测模块,检测输入信号a是否满足011XXX110序列(长度为9位数据,前三位是011,后三位是110,中间三位不做要求),当信号满足该序列,给出指示信号match。
程序的接口信号图如下

模块的时序图如下:

3.2 解题思路
状态机法的过程类似于题意理解中提到的过程:在初始状态中,先判断第一位是否符合,若符合则进入下一个状态,判断第二位是否符合;若第一位不符合则保持在初始状态,直到第一位匹配。如前两位匹配,则判断第三位是否符合,若第一位匹配,最新输入的数值和目标序列的第二位不匹配,则根据最新一位是否匹配第一位,进入第一位匹配状态或者初始状态。依次类推。
序列缓存对比法,则是将九个时刻的数据缓存,作为一个数组,每个时刻的输入位于数组的末尾,数组其它元素左移,把最早输入的数据移出。然后截取数组的前三位和目标序列011对比,截取数组的后三位和目标序列110对比,如果两段数组都和目标序列相等,则说明出现目标序列。
3.3 代码
3.3.1 序列缓冲对比法
序列缓存对比法在实现上比较简单,本题采用该方法实现。首先声明一个数组,缓存九个时刻的a输入的数值。移位可以通过位截取操作和位拼接操作实现:a_tem[7:0]表示截取a_tem的低7位,{a_tem[7:0],a}表示把a_tem[7:0]和新输入的数值a拼接,a位于低位。
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
reg [8:0]a_temp;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
match<=1'b0;
else if(a_temp[8:6]==3'b011 && a_temp[2:0]==3'b110)
match<=1'b1;
else
match<=1'b0;
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(!rst_n)
a_temp<=9'd0;
else
a_temp<={a_temp[7:0],a};
end
endmodule
这里也可以在casex中进行判断:
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
reg [8:0] a_temp;
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
a_temp<= 9'b0;
end else begin
a_temp <= {a_temp[7:0],a};
end
end
always @(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if (!rst_n) begin
match <= 1'b0;
end else begin
casex (a_temp)
9'b011xxx110 : match <= 1'b1;
default : match <= 1'b0;
endcase
end
end
endmodule
状态机法
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input a,
output reg match
);
parameter ZERO=0, ONE=1, TWO=2, THREE=3, FOUR=4, FIVE=5, SIX=6, SEVEN=7, EIGHT=8, NINE=9;
reg [3:0] state, nstate;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n)
state <= ZERO;
else
state <= nstate;
end
always@(*) begin
case(state)
ZERO : nstate = a? ZERO : ONE;
ONE : nstate = a? TWO : ONE;
TWO : nstate = a? THREE: ONE;
THREE : nstate = FOUR;
FOUR : nstate = FIVE;
FIVE : nstate = SIX;
SIX : nstate = a? SEVEN: ONE;
SEVEN : nstate = a? EIGHT: ONE;
EIGHT : nstate = a? ZERO: NINE;
NINE : nstate = a? TWO : ONE;
default: nstate = ZERO;
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(~rst_n)
match = 0;
else
match = state==NINE;
end
endmodule
4. 例题3
4.1 题目
请编写一个序列检测模块,检测输入信号(a)是否满足011100序列, 要求以每六个输入为一组,不检测重复序列,例如第一位数据不符合,则不考虑后五位。一直到第七位数据即下一组信号的第一位开始检测。当信号满足该序列,给出指示信号match。当不满足时给出指示信号not_match。
模块的接口信号图如下:
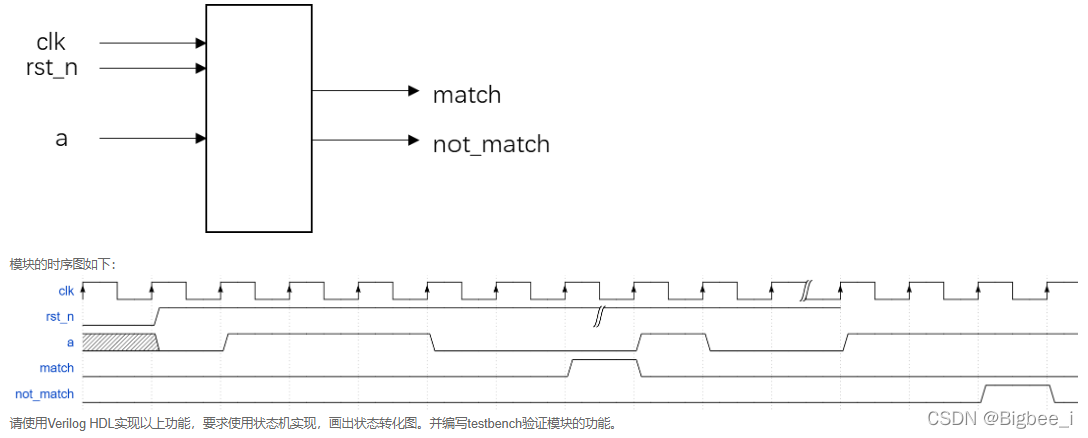
4.2 解题思路
题目要求使用状态机的方向进行实现,但是其实也可以使用序列缓冲对比法
4.3 代码
4.3.1 缓冲对比法
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data,
output reg match,
output reg not_match
);
reg [5:0] seq;
reg [3:0] counter;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
seq <= 6'b0;
end
else
seq <= { seq[4:0], data };
end
always@(posedge clk) begin
if(!rst_n) begin
counter <= 0;
end
else if(counter=='d5)
counter <= 0;
else begin
counter <= counter + 1;
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(!rst_n) begin
match <= 0;
end
else if( {seq[4:0],data}==6'b011100 && counter=='d5 ) begin
match <= 1;
end
else begin
match <= 0;
end
end
always@(posedge clk)begin
if(!rst_n) begin
not_match <= 0;
end
else if( {seq[4:0],data}!=6'b011100 && counter=='d5 ) begin
not_match <= 1;
end
else begin
not_match <= 0;
end
end
endmodule
4.3.2 状态机法
`timescale 1ns/1ns
module sequence_detect(
input clk,
input rst_n,
input data,
output reg match,
output reg not_match
);
reg [2:0] cnt;
reg [5:0] ram;
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(! rst_n)
cnt <= 3'd0;
else if(cnt == 3'd5)
cnt <= 3'd0;
else
cnt <= cnt + 3'd1;
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n)begin
if(! rst_n)
ram <= 6'd0;
else
case(cnt)
3'd0:ram <= {ram[5:1],data};
3'd1:ram <= {ram[5:2],data,ram[0]};
3'd2:ram <= {ram[5:3],data,ram[1:0]};
3'd3:ram <= {ram[5:4],data,ram[2:0]};
3'd4:ram <= {ram[5],data,ram[3:0]};
3'd5:ram <= {data,ram[4:0]};
endcase
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(! rst_n)
match <= 1'd0;
else if((ram == 6'b001110 )&&(cnt == 3'd5))
match <= 1'd1;
else
match <= 1'd0;
end
always@(posedge clk or negedge rst_n) begin
if(! rst_n)
not_match <= 1'd0;
else if((ram != 6'b001110)&&(cnt == 3'd5))
not_match <= 1'd1;
else
not_match <= 1'd0;
end
endmodule





 本文详细介绍了使用Verilog编程实现序列检测模块的方法,包括状态机法和序列缓存对比法。通过三个例题,分别展示了如何检测特定序列,如01110001、011XXX110和011100,并考虑了不检测重复序列的情况。每个例题提供了清晰的解题思路和完整的代码实现。
本文详细介绍了使用Verilog编程实现序列检测模块的方法,包括状态机法和序列缓存对比法。通过三个例题,分别展示了如何检测特定序列,如01110001、011XXX110和011100,并考虑了不检测重复序列的情况。每个例题提供了清晰的解题思路和完整的代码实现。

















 1325
1325

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










