在学习OVS VXLAN实现之前,我们先回顾一下传统VTEP设备是如何处理VXLAN报文的。如下图所示: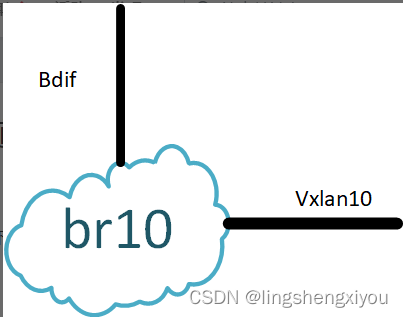
vxlan报文进入交换机端口后,根据报文头部信息进行vxlan隧道终结。隧道终结后,根据underlay信息进行overlay映射,得到overlay的bd和vrf.对于上图来说,报文隧道终结后从vxlan10进入br10,就为overlay报文绑定了br10和bdif。其中br10进行同子网FDB转发,如果overlay报文的目的MAC为bdif的mac,那么报文将从bdif进入其所属的vrf进行三层路由。这个过程就是VTEP接收到vxlan报文后的处理流程。
对于overlay报文,在经过overlay路由后,如果其目的bd为br10。那么报文将会从bdif进入br10,经过fdb后从vxlan10输出。vxlan10接口负责为报文构建vxlan封装。vxlan报文封装好后进入underlay路由转发,离开VTEP。
(免费订阅,永久学习)学习地址: Dpdk/网络协议栈/vpp/OvS/DDos/NFV/虚拟化/高性能专家-学习视频教程-腾讯课堂
更多DPDK相关学习资料有需要的可以自行报名学习,免费订阅,永久学习,或点击这里加qun免费
领取,关注我持续更新哦! !
VTEP组成要素
tunnel-terminate table
隧道终结表用于剥掉vxlan报文的underlay报文头。
VXLAN报文进入VTEP后,需要进行隧道终结。VXLAN属于P2MP(点到多点)隧道。进行隧道终结时只需要校验目的IP是本机的IP即可(目的MAC必定是本机的)。当然隧道终结之前,需要确定报文是否为VXLAN报文。隧道终结一般有两种形式:
- 像linux内核那样,不管报文是否为vxlan报文,当成常规的报文进行处理,因为vxlan报文的目的IP是本机,报文将会被送往local的udp进行处理,在udp处理时,根据目的端口为4789,然后将报文转入vlxan端口进行处理,这时overlay报文将会从vxlan中进入协议栈进行第二遍处理。
- 向传统硬件厂商一样,在parser阶段就已经将整个报文的内外层报文头都提取出来,如果是vxlan报文,直接进入tunnel-terminate表进行终结。
tunnel-decap-map table
隧道解封装映射表,用于确定overlay报文的二层广播域和三层路由域,即bd和vrf。
vxlan隧道时点到多点的隧道,可以根据vni来映射其所属的BD和VRF,用于overlay报文的同子网FDB和不同子网的路由。
tunnel-encap table
隧道封装表负责对fdb转发后或者路由后的报文进行vxlan报文封装。对于同子网的报文需要确定vni,underlay源IP,underlay目的IP即可,一般来说同子网转发,vni是不会变的。对于跨子网转发,需要借助路由,路由后确定了overlay-smac,overlay-dmac。对于vni,underlay-sip,underlay-dip的确定,不同的转发模型有很大的不同。传统的转发模型是,overlay-route只负责路由,路由后封装好链路层。报文从bdif输出,bdif连接到一个桥,由桥的vni决定报文的vni。还有一些厂商可以直接由路由决定vni,underlay-sip和underlay-dip,具体可以参考sonic的sai接口设计。
underlay route table
overlay报文封装好后,进入underlay进行路由转发,所以需要underlay路由。传统网络设备需要给vxlan隧道携带一个underlay rif,通过该rif指定underlay vrf。
underlay neighbor
underlay路由后,需要邻居进行underlay链路封装,需要邻居表。
OVS DPDK VXLAN
ovs要实现vtep功能,必定需要实现上面的要素。
主要数据结构
struct tnl_match {
ovs_be64 in_key;//vni
struct in6_addr ipv6_src;//源IP
struct in6_addr ipv6_dst;//目的IP
odp_port_t odp_port;//对应的接口编号
bool in_key_flow;//该标志位false,表示vni需要严格匹配,为true,表示希望流表设置vni。
bool ip_src_flow;//为false表示必须匹配源IP,如果源IP为0表示通配所有源IP。为true表示使用openflow流表设置隧道
//tunnel-id进行进一步匹配。
bool ip_dst_flow;//为false表示必须匹配目的IP,为true表示使用openflow流表设置隧道的目的IP。
};
struct tnl_port {
struct hmap_node ofport_node;
struct hmap_node match_node;
const struct ofport_dpif *ofport;
uint64_t change_seq;
struct netdev *netdev;
struct tnl_match match;//隧道认证元素,唯一标识一个隧道
};
// ovs将vxlan port存在一个hash表中:
/* Each hmap contains "struct tnl_port"s.
* The index is a combination of how each of the fields listed under "Tunnel
* matches" above matches, see the final paragraph for ordering.
* vxlan端口映射表。根据in_key_flow,in_dst_flow,in_src_flow三个参数分成12个
* 优先级。
*/
static struct hmap *tnl_match_maps[N_MATCH_TYPES] OVS_GUARDED_BY(rwlock);
详细说明
struct tnl_match 结构为vxlan端口的核心结构。in_key,ipv6_src,ipv6_dst指定了vxlan封装的核心成员,这些是传统VTEP的vxlan接口必须的成员。它们用于隧道终结和隧道封装。但是在ovs中,设计者添加了是三个重要的标志:
- in_key_flow:有两种取值false表示该隧道VNI由vxlan端口创建时设置,该值会用来进行隧道终结,如果报文从该接口出去的话,会使用该值进行封装。所以为false的时候,优先级会更高。如果为true,则表示隧道终结不匹配vni,具体vni的操作由流表进行处理,封装报文时,vni由流表进行设置。
- ip_src_flow:有三种取值,如果为false,表示隧道终结时需要使用该IP与vxlan报文的目的IP进行匹配。报文封装时,使用该IP作为该vxlan端口出去报文的隧道源IP。为true时有两种情况,src_ip为0表示通配所有IP,否则,只能匹配确定IP。
- ip_dst_flow:有两种值,如果为false,表示隧道终结时需要匹配报文的源IP为该IP。报文从该接口输出时,隧道目的接口为该接口。如果为true的话,都由flow进行处理。
vxlan端口创建示例:
admin@ubuntu:$ sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 vxlan1 -- set interface vxlan1 type=vxlan options:remote_ip=flow options:key=flow options:dst_port=8472 options:local_ip=flow admin@ubuntu:$ sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 vxlan2 -- set interface vxlan2 type=vxlan options:remote_ip=flow options:key=flow options:dst_port=8472 admin@ubuntu:/var/log/openvswitch$ sudo ovs-vsctl add-port br0 vxlan13 -- set interface vxlan13 type=vxlan options:remote_ip=flow options:key=191 options:dst_port=8472 admin@ubuntu:/var/log/openvswitch$
ovs交换机是一个sdn交换机,其需要核心动作是openflow流表来完成。引入这三个标志正是用来解除传统vxlan设备的限制。这三个要素根据取值的不同,可以有2*2*3=12种组合,即tnl_match_maps数组的大小。
隧道端口查找过程
/* Returns a pointer to the 'tnl_match_maps' element corresponding to 'm''s
* matching criteria.
* 根据三个标志和配置决定其优先级,即map的索引。这个函数在vxlan接口添加时会调用,决定vxlan接口加入到那个map中
*/
static struct hmap **
tnl_match_map(const struct tnl_match *m)
{
enum ip_src_type ip_src;
ip_src = (m->ip_src_flow ? IP_SRC_FLOW
: ipv6_addr_is_set(&m->ipv6_src) ? IP_SRC_CFG
: IP_SRC_ANY);
return &tnl_match_maps[6 * m->in_key_flow + 3 * m->ip_dst_flow + ip_src];
}
/* Returns the tnl_port that is the best match for the tunnel data in 'flow',
* or NULL if no tnl_port matches 'flow'.
* 隧道终结过程,根据报文信息查找对应的vxlan端口,进行隧道终结
*/
static struct tnl_port *
tnl_find(const struct flow *flow) OVS_REQ_RDLOCK(rwlock)
{
enum ip_src_type ip_src;
int in_key_flow;
int ip_dst_flow;
int i;
i = 0;
for (in_key_flow = 0; in_key_flow < 2; in_key_flow++) {//in_key_flow优先级最高,0优先级高于1
for (ip_dst_flow = 0; ip_dst_flow < 2; ip_dst_flow++) {//ip_dst_flow优先级次之,即vxlan报文源IP
for (ip_src = 0; ip_src < 3; ip_src++) {//ip_src优先级最低,可能的取值可以查看IP_SRC_CFG
struct hmap *map = tnl_match_maps[i];
if (map) {
struct tnl_port *tnl_port;
struct tnl_match match;
memset(&match, 0, sizeof match);
/* The apparent mix-up of 'ip_dst' and 'ip_src' below is
* correct, because "struct tnl_match" is expressed in
* terms of packets being sent out, but we are using it
* here as a description of how to treat received
* packets.
* in_key_flow为真的时候,不需要匹配vni
*/
match.in_key = in_key_flow ? 0 : flow->tunnel.tun_id;
if (ip_src == IP_SRC_CFG) {
match.ipv6_src = flow_tnl_dst(&flow->tunnel);
}
if (!ip_dst_flow) {/* */
match.ipv6_dst = flow_tnl_src(&flow->tunnel);
}
match.odp_port = flow->in_port.odp_port;
match.in_key_flow = in_key_flow;
match.ip_dst_flow = ip_dst_flow;
match.ip_src_flow = ip_src == IP_SRC_FLOW;
//进行精确匹配
tnl_port = tnl_find_exact(&match, map);
if (tnl_port) {
return tnl_port;
}
}
i++;
}
}
}
return NULL;
}
优势
ovs通过这三个标志的加入,极大的简化了vxlan端口的配置,使得全局一个vxlan端口足以满足应用,其它参数通过流表来操作,突出了SDN的优势,可以适应大规模场景。
terminate table
ovs的隧道终结表是在创建vxlan port的时候构建。
//隧道全局信息初始化。ovs采用分类器来构建隧道终结表cls。全局变量addr_list保存了本地所有的underlay ip地址。
//underlay ip将来会作为隧道终结的目的地址,也会作为隧道封装的源IP地址。
//port_list保存了使用传输层端口的隧道,比如vxlan隧道。
void
tnl_port_map_init(void)
{
classifier_init(&cls, flow_segment_u64s);//隧道终结表
ovs_list_init(&addr_list);//underlay ip链表
ovs_list_init(&port_list);//tnl_port控制块链表
unixctl_command_register("tnl/ports/show", "-v", 0, 1, tnl_port_show, NULL);
}
隧道端口添加
/* Adds 'ofport' to the module with datapath port number 'odp_port'. 'ofport's
* must be added before they can be used by the module. 'ofport' must be a
* tunnel.
*
* Returns 0 if successful, otherwise a positive errno value.
* native_tnl表示是否开启了隧道终结
*/
int
tnl_port_add(const struct ofport_dpif *ofport, const struct netdev *netdev,
odp_port_t odp_port, bool native_tnl, const char name[]) OVS_EXCLUDED(rwlock)
{
bool ok;
fat_rwlock_wrlock(&rwlock);
ok = tnl_port_add__(ofport, netdev, odp_port, true, native_tnl, name);
fat_rwlock_unlock(&rwlock);
return ok ? 0 : EEXIST;
}
//添加隧道端口
static bool
tnl_port_add__(const struct ofport_dpif *ofport, const struct netdev *netdev,
odp_port_t odp_port, bool warn, bool native_tnl, const char name[])
OVS_REQ_WRLOCK(rwlock)
{
const struct netdev_tunnel_config *cfg;
struct tnl_port *existing_port;
struct tnl_port *tnl_port;
struct hmap **map;
cfg = netdev_get_tunnel_config(netdev);
ovs_assert(cfg);
tnl_port = xzalloc(sizeof *tnl_port);
tnl_port->ofport = ofport;
tnl_port->netdev = netdev_ref(netdev);
tnl_port->change_seq = netdev_get_change_seq(tnl_port->netdev);
//这些参数不会影响隧道终结
tnl_port->match.in_key = cfg->in_key;
tnl_port->match.ipv6_src = cfg->ipv6_src;
tnl_port->match.ipv6_dst = cfg->ipv6_dst;
tnl_port->match.ip_src_flow = cfg->ip_src_flow;
tnl_port->match.ip_dst_flow = cfg->ip_dst_flow;
tnl_port->match.in_key_flow = cfg->in_key_flow;
tnl_port->match.odp_port = odp_port;
//根据隧道的匹配条件查找其在map中的位置
map = tnl_match_map(&tnl_por








 本文详细介绍了OVS DPDK如何处理VXLAN隧道,包括VTEP组成要素如tunnel-terminate、tunnel-decap-map等表的操作,以及OVS在VXLAN报文的隧道终结、解封装、封装和路由转发过程中的工作原理。通过理解这些概念,可以更好地了解SDN环境下VXLAN的工作机制。
本文详细介绍了OVS DPDK如何处理VXLAN隧道,包括VTEP组成要素如tunnel-terminate、tunnel-decap-map等表的操作,以及OVS在VXLAN报文的隧道终结、解封装、封装和路由转发过程中的工作原理。通过理解这些概念,可以更好地了解SDN环境下VXLAN的工作机制。
 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 1123
1123

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








