maxout
m
a
x
o
u
t
的论文,参考 Goodfellow et al., 2013a
上述论文的基本翻译,参考知乎回答
本质上讲,
maxout
m
a
x
o
u
t
的核心在于:
其中:

其中,
j
j
为 的
cursor
c
u
r
s
o
r
,
i
i
为
layer
l
a
y
e
r
的
cursor
c
u
r
s
o
r
, 表示
zij
z
i
j
由输入张量
x
x
与第 个
W
W
矩阵的第项相称,在
k
k
个相乘的结果中取最大值为隐藏层的值。
其他计算
hidden layer
h
i
d
d
e
n
l
a
y
e
r
的方法:
即直接
x
x
与 相乘
对上图所示的神经元的
maxout
m
a
x
o
u
t
的计算方法:
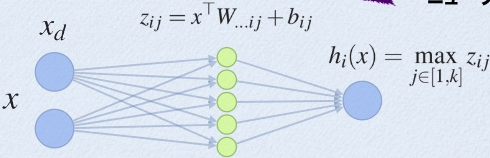
x
x
与多个 相乘,取最大值得到
zij
z
i
j
值得注意的是,此处为
Wi
W
i
,即为某一向量,而非需要多个
W
W
矩阵
因而在实践中,常常将 的规模乘以 k k 倍(需要手动设置), 得到 倍的 zij z i j 后, 每 k k 个选出其中最大的,作为对应的的值。这一行为和max-pooling 表现一致
tensorflow
t
e
n
s
o
r
f
l
o
w
实现:
基于
max−pooling
m
a
x
−
p
o
o
l
i
n
g
import numpy as np
import tensorflow as tf
"""
Maxout OP from https://arxiv.org/abs/1302.4389
Max pooling is performed in given filter/channel dimension. This can also be
used after fully-connected layers to reduce number of features.
Args:
inputs: A Tensor on which maxout will be performed
num_units: Specifies how many features will remain after max pooling at the
channel dimension. This must be multiple of number of channels.
axis: The dimension where max pooling will be performed. Default is the
last dimension.
outputs_collections: The collections to which the outputs are added.
scope: Optional scope for name_scope.
Returns:
A `Tensor` representing the results of the pooling operation.
Raises:
ValueError: if num_units is not multiple of number of features.
"""
def max_out(inputs, num_units, axis=None):
shape = inputs.get_shape().as_list()
if shape[0] is None:
shape[0] = -1
if axis is None: # Assume that channel is the last dimension
axis = -1
num_channels = shape[axis]
if num_channels % num_units:
raise ValueError('number of features({}) is not '
'a multiple of num_units({})'.format(num_channels, num_units))
shape[axis] = num_units
shape += [num_channels // num_units]
outputs = tf.reduce_max(tf.reshape(inputs, shape), -1, keep_dims=False)
return outputsanother intuitive implementation:
def maxout(x, k, m):
d = x.get_shape().as_list()[-1]
W = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape=[d, m, k]))
b = tf.Variable(tf.random_normal(shape = [m, k]))
z = tf.tensordot(x, W, axes=1) + b
z = tf.reduce_max(z, axis=2)
return z




















 1174
1174

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








