WordSearch
问题描述:给定一个二维数字,每个元素都是字符char, 再给定一个字符串s,问在二维数组中能否找到一条路径刚好是s。每次可以走四个方向,二维数组中的每个字符最多走一次(不能重复)。
例如ABCCED就是从(0, 0)开始的红线 SEE是绿线 思路:利用DFS,找到与word相同的路径返回即可,找不到返回false。利用visit来控制每个位置仅能走一次。注意,我们只要找到一条路径可以构成word就可以返回了,不需要找到所有可能存在的路径。 代码: class Solution {
public:
int dxs[ 4 ] = { 1 , 0 , - 1 , 0 } ;
int dys[ 4 ] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 } ;
bool isValid ( int x, int y, int m, int n) {
if ( 0 <= x && x < m && 0 <= y && y < n)
return true;
return false;
}
bool existBase ( vector< vector< char >> & board, string word, int cur_idx, bool* visits, int x, int y,
const int & m, const int & n) {
if ( cur_idx == word. length ( ) )
return true;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< 4 ; i++ ) {
int new_x = x + dxs[ i] ;
int new_y = y + dys[ i] ;
if ( isValid ( new_x, new_y, m, n) && ! visits[ new_x * n + new_y] && board[ new_x] [ new_y] == word[ cur_idx] ) {
visits[ new_x * n + new_y] = true;
if ( existBase ( board, word, cur_idx + 1 , visits, new_x, new_y, m, n) )
return true;
visits[ new_x * n + new_y] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
bool exist ( vector< vector< char >> & board, string word) {
int m = board. size ( ) ;
if ( m == 0 && word. length ( ) == 0 )
return true;
if ( m == 0 )
return false;
int n = board[ 0 ] . size ( ) ;
bool visits[ m * n] ;
memset ( visits, false, sizeof ( visits) ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< m; i++ ) {
for ( int j= 0 ; j< n; j++ ) {
if ( board[ i] [ j] == word[ 0 ] ) {
visits[ i * n + j] = true;
if ( existBase ( board, word, 1 , visits, i, j, m, n) )
return true;
visits[ i * n + j] = false;
}
}
}
return false;
}
vector< string> findWords ( vector< vector< char >> & board, vector< string> & words) {
vector< string> res;
for ( auto s: words) {
if ( exist ( board, s) ) {
res. push_back ( s) ;
}
}
return res;
}
static void solution ( ) {
vector< vector< char > > board = {
{ 'A' , 'B' , 'C' , 'E' } ,
{ 'S' , 'F' , 'C' , 'S' } ,
{ 'A' , 'D' , 'E' , 'E' }
} ;
string word = "ABCF" ;
Solution solution1;
cout<< solution1. exist ( board, word) << endl;
}
} ;
WordSearch II
问题描述:与I不同的是,II要求我们在一个word的list中找到通过二维数组可以构成的word. 思路:
最直接的方法是我们可以调用I中的exit方法,判断list中的每个word是否存在,然后把存在的word放入res中。并返回。代码如上一段代码中的findWords所示。
一般来说,这种最直接的方法都会超时…当然此题也不意外Orz. 我们尝试分析一个时间复杂度,list的长度是K,二维数组的大小是M*N。所以时间复杂度应该是O(KM*N*M*N) 明显这个时间复杂度太高,不能接受。 另一种方法就是利用字典树(Trie). 关于字典树的介绍可以看第三段。
我们从二维数组的每个点开始遍历
如果当前路径形成的字符串不在Trie的perfix中,我们直接可以终止本次循环,因为需要查找的字符串肯定不存在。 如果当前路径形成的字符串在Trie的perfix中且我们可以找到它,则我们将当前字符串加入set中,继续下一步。这里有两点需要注意:
是我们这里要继续进行下一步,而不能终止掉,避免因为abc的出现,而终止了abcd; 是我们使用set,便于我们最后去重用。因为同一个word可能存在多条路径。 四个方向,利用dfs的方法尝试走每个方向。 时间复杂度是O(M*N*M*N) + O(K*L) L是word的平均长度。 代码: class Solution {
public:
int dxs[ 4 ] = { 1 , 0 , - 1 , 0 } ;
int dys[ 4 ] = { 0 , 1 , 0 , - 1 } ;
bool isValid ( int x, int y, int m, int n) {
if ( 0 <= x && x < m && 0 <= y && y < n)
return true;
return false;
}
bool findWordsBase ( vector< vector< char >> & board, bool* visits, int x, int y, int m, int n, string string1,
Trie* & root, set< string> & set_res) {
if ( ! root-> hasPerfix ( string1) )
return false;
if ( root-> hasStr ( string1) ) {
set_res. insert ( string1) ;
}
for ( int i= 0 ; i< 4 ; i++ ) {
int new_x = x + dxs[ i] ;
int new_y = y + dys[ i] ;
if ( isValid ( new_x, new_y, m, n) && ! visits[ new_x * n + new_y] ) {
visits[ new_x * n + new_y] = true;
findWordsBase ( board, visits, new_x, new_y, m, n, string1 + board[ new_x] [ new_y] ,
root, set_res) ;
visits[ new_x * n + new_y] = false;
}
}
return false;
}
vector< string> findWords ( vector< vector< char >> & board, vector< string> & words) {
set< string> set_res;
Trie* root = new Trie ( ) ;
for ( auto s: words) {
root-> insert ( s) ;
}
int m = ( int ) board. size ( ) ;
if ( m == 0 )
return { } ;
int n = ( int ) board[ 0 ] . size ( ) ;
bool visits[ m* n] ;
memset ( visits, false, sizeof ( visits) ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< m; i++ ) {
for ( int j= 0 ; j< n; j++ ) {
visits[ i* n + j] = true;
string cur_init = "" ;
cur_init = cur_init + board[ i] [ j] ;
findWordsBase ( board, visits, i, j, m, n, cur_init, root, set_res) ;
visits[ i* n + j] = false;
}
}
vector< string> res ( set_res. size ( ) ) ;
copy ( set_res. begin ( ) , set_res. end ( ) , res. begin ( ) ) ;
return res;
}
} ;
Trie: 字典树
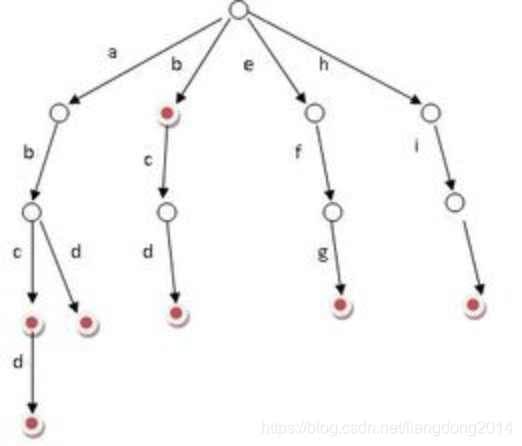
一般用于大规模字符串的查找,匹配。 他是树的一种形式,每个node存储的是
char,当前节点所代表的字符串 children,每个节点有26个子节点,代表a->b, a->c这种路径。 isEnd, 代表从root节点到当前节点的路径所构成的字符串是否存在在字典里面。或者说是否要字符串终结于此。 便于大家理解,附上一张百度百科的图片: 实现代码: class Trie {
public:
Trie* letters[ 26 ] ;
bool isEnd;
char c;
Trie ( ) {
this-> isEnd = false;
memset ( letters, 0 , sizeof ( letters) ) ;
}
Trie ( char c) {
this-> c = c;
this-> isEnd = false;
memset ( letters, 0 , sizeof ( letters) ) ;
}
void insert ( string word) {
Trie* root = this;
for ( auto c: word) {
if ( root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] == NULL ) {
root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] = new Trie ( c) ;
}
root = root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] ;
}
root-> isEnd = true;
}
bool hasStr ( string word) {
Trie* root = this;
for ( auto c: word) {
if ( root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] == NULL )
return false;
root = root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] ;
}
return root-> isEnd;
}
bool hasPerfix ( string prefix) {
Trie* root = this;
for ( auto c: prefix) {
if ( root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] == NULL )
return false;
root = root-> letters[ c- 'a' ] ;
}
return true;
}
} ;
分析
实现Trie有三种方法:
前两种是限制了字符的个数,利用map我们可以不限字符的个数。 时间复杂度的话如下所示,分布是使用[], vector, unorder_map去解决Word SearchII的耗时.

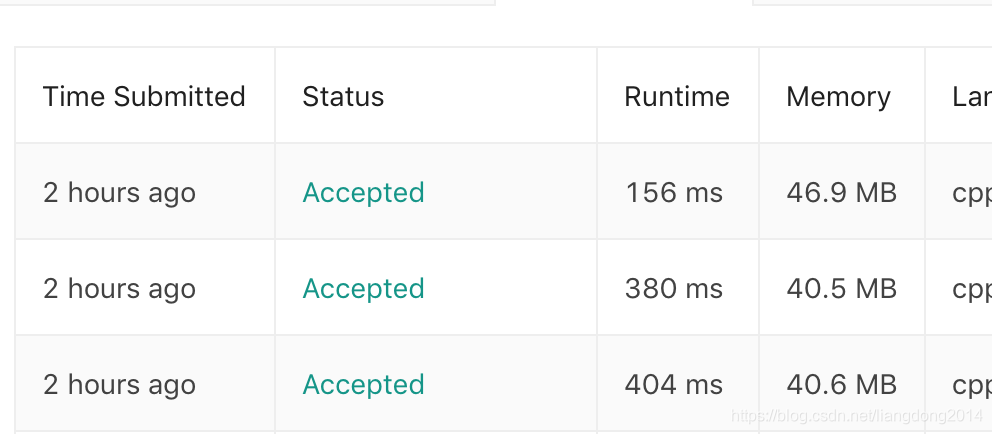





 本文详细解析了WordSearch问题及其进阶版WordSearchII的解决方案,包括利用深度优先搜索(DFS)查找指定单词路径,以及如何通过字典树(Trie)优化查找大量单词的效率,特别适用于大规模字符串查找和匹配场景。
本文详细解析了WordSearch问题及其进阶版WordSearchII的解决方案,包括利用深度优先搜索(DFS)查找指定单词路径,以及如何通过字典树(Trie)优化查找大量单词的效率,特别适用于大规模字符串查找和匹配场景。
















 840
840

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








