相关文章
Jdbc工具类的简单例子
封装方法
- 创建连接,共用调用
- 静态代码块,只需调用一次,账号密码等配置文件获取,不需更改代码
- 关闭资源方法
配置文件:
driver=com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/study?useSSL=false&serverTimezone=UTC&characterEncoding=utf-8 user=root password=password
工具类代码
package com.lingaolu.Utils;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.net.URL;
import java.sql.*;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* @author 林高禄
* @create 2020-06-23-11:12
*/
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driver;
private static String url;
private static String userName;
private static String pw;
static{
try {
Properties p = new Properties();
ClassLoader classLoader = JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader();
// 这个路径相对于src的路径来说,classLoader.getResource只能获取src下的目录
URL resource = classLoader.getResource("com/lingaolu/file/jdbc.properties");
String path = resource.getPath();
p.load(new FileReader(path));
driver = p.getProperty("driver");
url = p.getProperty("url");
userName = p.getProperty("user");
pw = p.getProperty("password");
Class.forName(driver);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static Connection createConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, userName, pw);
}
public static void close(Statement stmt,Connection con){
if(null != stmt){
try {
stmt.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(null != con){
try {
con.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public static void close(ResultSet set,Statement s,Connection con){
if(null != set){
try {
set.close();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
close(s,con);
}
}
测试demo2代码
package com.lingaolu.jdbcConnector;
import com.lingaolu.Utils.JdbcUtils;
import java.sql.*;
/**
* @author 林高禄
* @create 2020-06-23-17:27
*/
public class Demo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Connection con = null;
Statement stmt = null;
try {
con = JdbcUtils.createConnection();
String sql = "insert into account value(null,'林帅',20000)";
String sql2 = "select * from account";
stmt = con.createStatement();
// 如果是查询的话返回true,如果是更新或插入的话就返回false
boolean execute = stmt.execute(sql);
boolean execute2 = stmt.execute(sql2);
System.out.println(execute);
System.out.println(execute2);
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally {
JdbcUtils.close(stmt,con);
}
}
}
运行前数据库数据
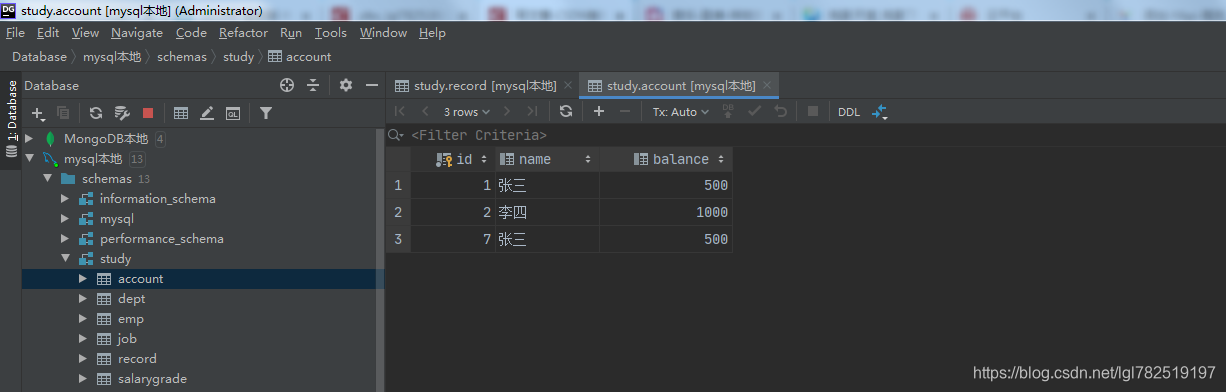
运行输出:
false
true
运行后数据库数据
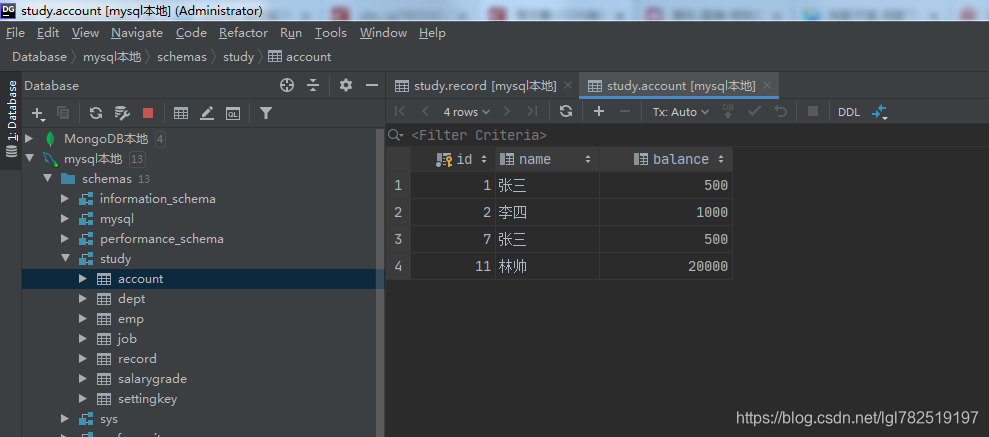
简单的jdbc工具类就介绍到这





 本文介绍了JDBC连接数据库时可能出现的异常处理,详细讲解了JDBC工具类的封装,包括创建连接、ResultSet的使用、防止SQL注入的PreparedStatement、事务管理,并给出了具体的代码实现和测试案例,展示了如何通过工具类简化数据库操作。
本文介绍了JDBC连接数据库时可能出现的异常处理,详细讲解了JDBC工具类的封装,包括创建连接、ResultSet的使用、防止SQL注入的PreparedStatement、事务管理,并给出了具体的代码实现和测试案例,展示了如何通过工具类简化数据库操作。

















 652
652

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










