动态规划(Dynamic Programming)
什么是动态规划,我们要如何描述它?
动态规划算法通常基于一个递推公式及一个或多个初始状态。当前子问题的解将由上一次子问题的解推出。
动态规划和分治法相似,都是通过组合子问题的解来求解原问题。分治法将问题划分成互不相交的子问题,递归求解子问题,再将他们的解组合起来,求出原问题的解。与之相反,动态规划应用于子问题重叠的情况,即不同的子问题具有公共的子子问题。在这种情况下,分治算法会做出许多不必要的工作,它会反复的求解那些公共子问题。而动态规划算法对每个子子问题只求解一次,将结果保存到表格中,从而无需每次求解一个子子问题都要重新计算。
动态规划 - 钢条切割问题
假定我们知道sering公司出售一段长度为I英寸的钢条的价格为pi(i=1,2,3….)钢条长度为整英寸如图给出价格表的描述(任意长度的钢条价格都有)
| 长度 i | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 |
| 价格p[i] | 1 | 5 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 17 | 17 | 20 | 24 | 30 |
先给我们一段长度为n的钢条,问怎么切割,获得的收益最大 rn?
考虑n=4的时候
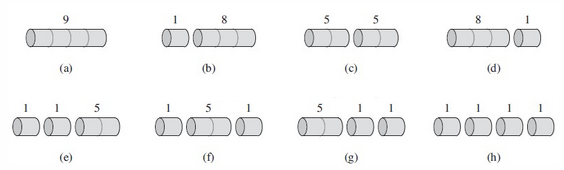
假如一个最优解把n段七个成了k段(1<=k<=n),那么最优切割方案:
![]()
最大收益:
![]()

第一种求最优解方案:
对于 r n (n>=1),最优切割收益:
![]()
将切割方案分成下面几种
1,不切割 收益为pn
2,将它切割成两半,切割成两半的情况有,对每种情况求最优解
(1,n-1) (2,n-2) (3,n-3) (4,n-4) ..... (n-1,1)
对这两半分别求最优解,最优解的和就是当前情况的最优解
第二种求最优解方案:
我们从钢条的左边切下长度为i的一段,只对右边剩下长度为n-i的一段继续进行切割,对左边的不再切割。这样,不做任何切割的方案就是:当第一段长度为n的时候,收益为pn,剩余长度为0,对应的收益为0。如果第一段长度为i,收益为pi:
![]()
代码实现 - 自顶向下递归实现
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 钢条切割问题_递归实现
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int n = 5;//我们要切割售卖的钢条的长度
int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 };//索引代表 钢条的长度,值代表价格
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(0, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(1, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(2, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(6, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(8, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(9, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(10, p));
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static int UpDown(int n,int[] p)//求得长度为n的最大收益
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
int tempMaxPrice = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n+1; i++)
{
int maxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p);
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;
}
return tempMaxPrice;
}
}
}
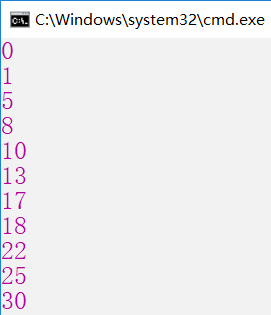
分析效率,关于上述方法的运行性能时间问题。
动态规划的方法进行求解
上面的方法之所以效率很低,是因为它反复求解相同的子问题。因此,动态规划算法安排求解的顺序,对每个子问题只求解一次,并将结果保存下来。如果随后再次需要此子问题的解,只需查找保存的结果,不必重新计算。因此动态规划的方法是付出额外的内存空间来节省计算时间。
动态规划有两种等价的实现方法(我们使用上面的钢条切割问题为例,实现这两种方法)
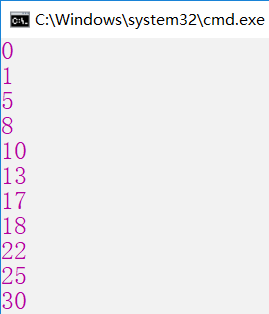
第一种方法是 带备忘的自顶向下法
此方法依然是按照自然的递归形式编写过程,但过程中会保存每个子问题的解(通常保存在一个数组中)。当需要计算一个子问题的解时,过程首先检查是否已经保存过此解。如果是,则直接返回保存的值,从而节省了计算时间;如果没有保存过此解,按照正常方式计算这个子问题。我们称这个递归过程是带备忘的。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 钢条切割问题_带备忘的自顶向下法_动态规划_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
//int n = 5;//我们要切割售卖的钢条的长度
int[] result = new int[11];
int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 };//索引代表 钢条的长度,值代表价格
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(0, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(1, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(2, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(6, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(8, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(9, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(10, p, result));
Console.ReadKey();
}
//带备忘的自顶向下
public static int UpDown(int n, int[] p, int[] result)//求得长度为n的最大收益
{
if (n == 0) return 0;
if (result[n] != 0)
{
return result[n];
}
int tempMaxPrice = 0;
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)
{
int maxPrice = p[i] + UpDown(n - i, p, result);
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;
}
result[n] = tempMaxPrice;
return tempMaxPrice;
}
}
}
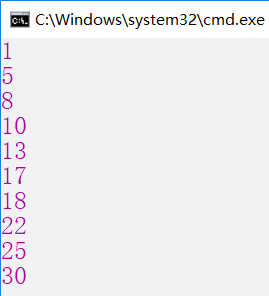
第二种方法是 自底向上法
首先恰当的定义子问题的规模,使得任何问题的求解都只依赖于更小的子问题的解。因而我们将子问题按照规模排序,按从小到大的顺序求解。当求解某个问题的时候,它所依赖的更小的子问题都已经求解完毕,结果已经保存。
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 钢条切割问题_自底向上法_动态规划算法_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] result = new int[11];
int[] p = { 0, 1, 5, 8, 9, 10, 17, 17, 20, 24, 30 };//索引代表 钢条的长度,值代表价格
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(1, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(2, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(3, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(4, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(5, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(6, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(7, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(8, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(9, p, result));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(10, p, result));
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static int BottomUp(int n, int[] p, int[] result)
{
for (int i = 1; i < n + 1; i++)
{
//下面取得 钢条长度为i时最大的收益
int tempMaxPrice = -1;
for(int j = 1; j <= i; j++)
{
int maxPrice = p[j] + result[i - j];
if (maxPrice > tempMaxPrice)
tempMaxPrice = maxPrice;
}
result[i] = tempMaxPrice;
}
return result[n];
}
}
}
动态规划 - 01背包问题
问题描述:
假设现有容量m kg的背包,另外有i个物品,重量分别为w[1] w[2] ... w[i] (kg),价值分别为p[1] p[2] ... p[i] (元),将哪些物品放入背包可以使得背包的总价值最大?最大价值是多少?
(示例一:m=10 i=3 重量和价值分别为 3kg-4元 4kg-5元 5kg-6元 )
1,穷举法(把所有情况列出来,比较得到 总价值最大的情况)
如果容量增大,物品增多,这个方法的运行时间将成指数增长
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _01背包问题_穷举法
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m;
int[] w = { 0, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] p = { 0, 4, 5, 6 };
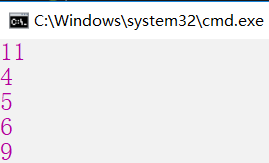
Console.WriteLine(Exhaustivity(10, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(Exhaustivity(3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(Exhaustivity(4, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(Exhaustivity(5, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(Exhaustivity(7, w, p));
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static int Exhaustivity(int m, int[] w, int[] p)
{
int i = w.Length - 1;//物品的个数
int maxPrice = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < Math.Pow(2,m); j++)
{
//取得j上某一个位的二进制值
int weightTotal = 0;
int priceTotal = 0;
for(int number = 1;number <=i;number++)
{
int result = Get2(j, number);
if(result == 1)
{
weightTotal += w[number];
priceTotal += p[number];
}
}
if(weightTotal <=m&&priceTotal > maxPrice)
{
maxPrice = priceTotal;
}
}
return maxPrice;
}
//取得j上第number位上的二进制值,是1还是0
//比如85的二进制为1010101.
//w我们要求第五位二进制位数上是0还是1,那么我们可以通过位运算符的移位操作来进行
//比如我们可以将85的二进制1010101与1向左移4位来做与运算
//就是1010101 与 0010000做与运算,看第五位是0还是1,
//得出这个结果,我们可以将结果0010000右移4位然后将结果与1进行比较即可
public static int Get2(int j,int number)
{
int A = j;
int B = (int)Math.Pow(2, number - 1);
int result = A & B;
if (result == 0)
return 0;
return 1;
}
}
}
2,动态规划算法
我们要求得i个物体放入容量为m(kg)的背包的最大价值(记为 c[i,m])。在选择物品的时候,对于每种物品i只有两种选择,即装入背包或不装入背包。某种物品不能装入多次(可以认为每种物品只有一个),因此该问题被称为0-1背包问题
对于c[i,m]有下面几种情况:
a、c[i,0]=c[0,m]=0
b、c[i,m]=c[i-1,m] w[i]>m(最后一个物品的重量大于容量,直接舍弃不用)
w[i]<=m的时候有两种情况,一种是放入i,一种是不放入i
不放入i c[i,m]=c[i-1,m]
放入i c[i,m]=c[i-1,m-w[i]]+p[i]
c[i,m]=max(不放入i,放入i)
不带备忘的自顶向下法的实现
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _01背包问题_递归实现_不带备忘的自顶向下法_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m;
int[] w = { 0, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] p = { 0, 4, 5, 6 };
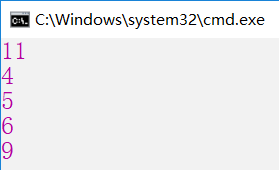
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(10, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, 3, w, p));
Console.ReadKey();
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回值是m可以存储的最大值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="m">背包容量</param>
/// <param name="i">物品个数</param>
/// <param name="w">物品的重量</param>
/// <param name="p">物品的价值</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int UpDown(int m, int i, int[] w, int[] p)
{
if (i == 0 || m == 0) return 0;
if (w[i] > m)//如果第i个重量超过剩余的重量
{
return UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = UpDown(m - w[i], i - 1, w, p) + p[i];//放入第i个物品
int maxValue2 = UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);//不放入第i个物品
if (maxValue1 > maxValue2)
return maxValue1;
else
return maxValue2;
}
}
}
}
带备忘的自顶向下法的实现
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _01背包问题_递归实现_带备忘的自顶向下法_
{
class Program
{
//用来存储已经计算的最大价值
//第一个是背包的容量m,第二个是物品的个数i
public static int[,] result = new int[11, 4];
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m;
int[] w = { 0, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] p = { 0, 4, 5, 6 };
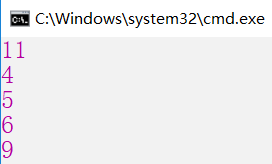
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(10, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(3, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(4, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(5, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(UpDown(7, 3, w, p));
Console.ReadKey();
}
/// <summary>
/// 返回值是m可以存储的最大值
/// </summary>
/// <param name="m">背包容量</param>
/// <param name="i">物品个数</param>
/// <param name="w">物品的重量</param>
/// <param name="p">物品的价值</param>
/// <returns></returns>
public static int UpDown(int m, int i, int[] w, int[] p)
{
if (i == 0 || m == 0) return 0;
if (result[m, i] != 0)
return result[m, i];
if (w[i] > m)//如果第i个重量超过剩余的重量
{
result[m,i] = UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);
return result[m, i];
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = UpDown(m - w[i], i - 1, w, p) + p[i];//放入第i个物品
int maxValue2 = UpDown(m, i - 1, w, p);//不放入第i个物品
if (maxValue1 > maxValue2)
result[m, i] = maxValue1;
else
result[m, i] = maxValue2;
return result[m, i];
}
}
}
}
自底向上法的实现(动态规划)
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace _01背包问题_自底向上法_动态规划_
{
class Program
{
public static int[,] result = new int[11, 4];
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int m;
int[] w = { 0, 3, 4, 5 };
int[] p = { 0, 4, 5, 6 };
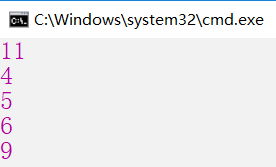
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(10, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(3, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(4, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(5, 3, w, p));
Console.WriteLine(BottomUp(7, 3, w, p));
}
public static int BottomUp(int m,int i,int []w,int[] p)
{
if (result[m, i] != 0) return result[m, i];
for (int tempM = 1; tempM < m+1; tempM++)
{
for (int tempI = 1; tempI < i+1; tempI++)
{
if (result[tempM, tempI] != 0) continue;
if (w[tempI] > tempM)
{
result[tempM, tempI] = result[tempM, tempI - 1];
}
else
{
int maxValue1 = result[tempM - w[tempI], tempI - 1] + p[tempI];
int maxValue2 = result[tempM, tempI - 1];
if (maxValue1 > maxValue2)
result[tempM, tempI] = maxValue1;
else
result[tempM, tempI] = maxValue2;
}
}
}
return result[m, i];
}
}
}
贪心算法
对于许多最优化问题,使用动态规划算法来求最优解有些杀鸡用牛刀了,可以使用更加简单、更加高效的算法。贪心算法就是这样的算法,它在每一步做出当时看起来最佳的选择。也就是说它总是做出局部最优的选择,从而得到全局最优解。
对于某些问题并不保证得到最0优解,但对很多问题确实可以求得最优解。
贪心算法 - 活动选择问题
有n个需要在同一天使用同一个教室的活动a1,a2,…,an,教室同一时刻只能由一个活动使用。每个活动ai都有一个开始时间si和结束时间fi 。一旦被选择后,活动ai就占据半开时间区间[si,fi)。如果[si,fi]和[sj,fj]互不重叠,ai和aj两个活动就可以被安排在这一天。该问题就是要安排这些活动使得尽量多的活动能不冲突的举行(最大兼容活动子集)。例如下图所示的活动集合S,其中各项活动按照结束时间单调递增排序。
{a3,a9,a11}是一个兼容的活动子集,但它不是最大子集,因为子集{a1,a4,a8,a11}更大,实际上它是我们这个问题的最大兼容子集,但它不是唯一的一个{a2,a4,a9,a11}
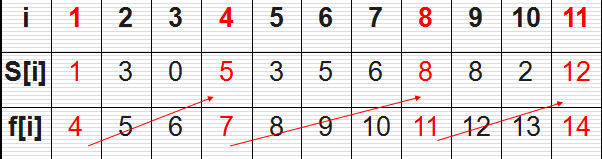
1,动态规划算法解决思路
我们使用Sij代表在活动ai结束之后,且在aj开始之前的那些活动的集合,我们使用c[i,j]代表Sij的最大兼容活动子集的大小,对于上述问题就是求c[0,12]的解
a, 当i>=j-1或者Sij 中没有任何活动元素的时候, c[i,j]=0
b,当i<j-1
1,Sij不存在活动,c[i,j]=0
2,Sij存在活动的时候,c[i,j]= max{c[i,k]+c[k,j]+1} ak属于Sij,这里是遍历Sij的集合,然后求得最大兼容子集
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 活动选择问题_动态规划思路_自底向上_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] s = { 0, 1, 3, 0, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2, 12, 24 };
int[] f = { 0, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14, 24 };
List<int>[,] result = new List<int>[13, 13];//默认值null
for(int m = 0; m < 13; m++)
{
for (int n = 0; n < 13; n++)
{
result[m, n] = new List<int>();
}
}//默认值是空list集合
for (int j = 0; j < 13; j++)
{
for (int i = 0; i < j - 1; i++)
{
//S[ij] i结束之后 j开始之前的活动集合
//f[i] s[j]这个时间区间内的所有活动
List<int> sij = new List<int>();
for (int number = 1; number < s.Length - 1; number++)
{
if (s[number] >= f[i] && f[number] <= s[j])
sij.Add(number);
}
if (sij.Count > 0)
{
//result[i,j] = max{ result[i,k]+result[k,j]+1}
int maxCount = 0;
List<int> tempList = new List<int>();
foreach (int number in sij)
{
int count = result[i, number].Count + result[number, j].Count + 1;
if (maxCount < count)
{
maxCount = count;
tempList = result[i, number].Union<int>(result[number, j]).ToList<int>();
tempList.Add(number);
}
}
result[i, j] = tempList;
}
}
}
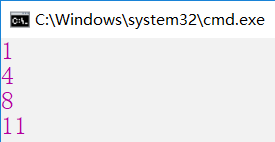
List<int> l = result[0, 12];
foreach (int temp in l)
{
Console.WriteLine(temp);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
2,贪心算法
想要使用贪心算法的话,得先找到适合贪心算法的规律(局部最优选择)
对于任何非空的活动集合S,假如am是S中结束时间最早的活动,则am一定在S的某个最大兼容活动子集中。
(如何证明上面的结论?反证法)
递归解决
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 活动选择问题_贪心算法_递归解决_
{
class Program
{
static int[] s = { 0, 1, 3, 0, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2, 12 };
static int[] f = { 0, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14 };
public static List<int> ActivitySelection(int startActivityNumber, int endActivityNumber, int startTime, int endTime)
{
if (startActivityNumber > endActivityNumber || startTime >= endTime)
return new List<int>();
//找到结束时间最早的活动
int tempNumber = 0;
for (int number = startActivityNumber; number <= endActivityNumber; number++)
{
if(s[number]>=startTime && f[number] <= endTime)
{
tempNumber = number;
break;
}
}
List<int> list = ActivitySelection(tempNumber + 1, endActivityNumber, f[tempNumber], endTime);
list.Add(tempNumber);
return list;
}
static void Main(string[] args)
{
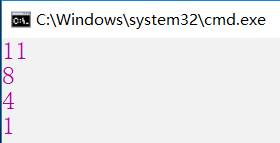
List<int> list = ActivitySelection(1, 11, 0, 24);
foreach (int temp in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(temp);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
迭代解决
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 活动选择问题_贪心算法_迭代解决_
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] s = { 0, 1, 3, 0, 5, 3, 5, 6, 8, 8, 2, 12 };
int[] f = { 0, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12, 13, 14};
int startTime = 0;
int endTime = 24;
List<int> list = new List<int>();
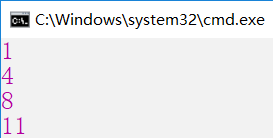
for (int number = 1; number <=11; number++)
{
if(s[number]>= startTime && f[number] <= endTime)
{
list.Add(number);
startTime = f[number];
}
}
foreach(int i in list)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
Console.ReadKey();
}
}
}
贪心算法 - 钱币找零问题
这个问题在我们的日常生活中就更加普遍了。假设1元、2元、5元、10元、20元、50元、100元的纸币分别有c0, c1, c2, c3, c4, c5, c6张。现在要用这些钱来支付K元,至少要用多少张纸币?用贪心算法的思想,很显然,每一步尽可能用面值大的纸币即可。
int Count[N]={3,0,2,1,0,3,5};
int Value[N]={1,2,5,10,20,50,100};
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace 钱币找零问题_贪心算法
{
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
int[] amount = { 1, 2, 5, 10, 20, 50, 100 };
int[] count = { 3, 0, 2, 1, 0, 3, 5 };
int[] result = Change(204, count, amount);
foreach (int i in result)
{
Console.Write(i + " ");
}
Console.WriteLine();
Console.ReadKey();
}
public static int[] Change(int k, int[] count, int[] amount)
{
if (k == 0) return new int[amount.Length + 1];
int total = 0;
int index = amount.Length - 1;
int[] result = new int[amount.Length+1];
while (true)
{
if (k <= 0 || index <= -1) break;
if(k > count[index] * amount[index])//我们有的纸币的钱的总额,比k要小
{
result[index] = count[index];
k -= count[index] * amount[index];
}
else
{
result[index] = k / amount[index];
k -= result[index] * amount[index];
}
index--;
}
result[amount.Length] = k;
return result;
}
}
}
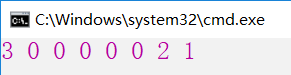
图





 本文介绍了动态规划和贪心算法的基本概念、特点及其在实际问题中的应用,包括钢条切割问题、01背包问题和活动选择问题等,并提供了详细的算法实现。
本文介绍了动态规划和贪心算法的基本概念、特点及其在实际问题中的应用,包括钢条切割问题、01背包问题和活动选择问题等,并提供了详细的算法实现。
















 531
531

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








