一、string 关系的运算
在实际编写代码的时候 , 经常会设计及两个字符串比较大小 , 比如 : 判断你输入的密码是否正确 , 就需要将输入的密码 和 数据库中正确的密码比较。
C++中为string 提供了一系列的关系运算 。这里涉及到了运算符重载 , 需要深入学习C++的内容 , 这里我们学会使用 ,竞赛中会使用即可 , 想深入了解可以在C++专栏里查看 。
1.1 支持的关系运算
string s1 = "abc" ;string s2 = "abcd" ;char s3[] = "abcdef" ; //C 风格的字符串// (1) s1 == s2bool operator== (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 == s2bool operator== (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 == s1bool operator== (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 == s3// (2) s1 != s2bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 != s2bool operator!= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 != s1bool operator!= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 != s3// (3) s1 < s2bool operator< (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 < s2bool operator< (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 < s1bool operator< (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 < s3// (4) s1 <= s2bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 <= s2bool operator<= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 <= s1bool operator<= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 <= s3// (5) s1 > s2bool operator> (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 > s2bool operator> (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 > s1bool operator> (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 > s3// (6) s1 >= s2bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s1 >= s2bool operator>= (const char* lhs, const string& rhs);//使用方式:s3 >= s1bool operator>= (const string& lhs, const char* rhs);//使用方式:s1 >= s3
注意:两字符串比较时 , 至少需要有一个 string 类型的字符串 。
字符串的比较是基于字典序进行的 , 比较是对应位置上字符的ASCII值的大小 ;比较的不是字符串的长度!!!

1.2 代码举例1
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "hello world";
string s2 = "hello";
if(s1 == (s2 + " world"))
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
return 0;
}
1.3 代码举例2
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1 = "abcd";
string s2 = "abbcdef";
char s3[] = "bbc";
if(s1 > s2)
cout << "s1 > s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 <= s2" << endl;
if(s1 == s2)
cout << "s1 == s2" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 != s2" << endl;
if(s1 <= s3)
cout << "s1 <= s3" << endl;
else
cout << "s1 > s3" << endl;
return 0;
}
二、和string 相关的函数

2.1 stoi/stol
1)stoi 是将字符串转换成 int 类型的值
2) stol是将字符串转换成 long int 类型的值
这两个函数用法非常相似 ,那么就以 stoi 为例讲解一下函数的使用方式 。
stoi 函数可以将一个string 类型的字符串 , 转化为整型 , 函数原型如下:
int stoi (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);long stol (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0, int base = 10);
参数解读:

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "11x22";
size_t pos = 0;
int n = stoi(s,&pos,2);
cout << n << endl;
cout << "pos: " << pos << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "11x22";
size_t pos = 0;
int n = stoi(s,&pos,2);
cout << n << endl;
cout << "pos: " << pos << endl;
string s1 = "11x22";
int n1 = stoi(s1,&pos,16);
cout << n1 << endl;
cout << "pos: " << pos << endl;
string s2 = "0x11x22";
int n2 = stoi(s2,&pos,0);
cout << n2 << endl;
cout << "pos: " << pos << endl;
return 0;
}如果不是想求出 非数字的字符所在的 pos 位置 , 可以不创建变量pos , 直接使用空指针(NULL) 或 0 作为参数 。
2.2 stod/stof
stod 是将字符串转换成double 类型的值 , 原型如下 , 和stoi 函数比较的化 , 少了描述字符串中数字进制的参数 , 其他参数一直 。 stof 是将字符串转换成 float 类型的值 。
double stod (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);float stof (const string& str, size_t* idx = 0);
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "3.14x456";
double ret = stod(s,NULL);
cout << ret << endl;
return 0;
}
2.3 to_string
tostring 函数可以将数字转换成字符串 , 从函数原型的角度看 ,可以将整型、浮点型的数字转换为字符串类型的 。
string to_string (int val);string to_string (long val);string to_string (long long val);string to_string (unsigned val);string to_string (unsigned long val);string to_string (unsigned long long val);string to_string (float val);string to_string (double val);string to_string (long double val);
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string pi = "pi is " + to_string(3.1415926);
cout << pi << endl;
return 0;
}

三、练习
3.1 练习一:标题统计
P5015 [NOIP 2018 普及组] 标题统计 - 洛谷


范围for :
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
int c = 0;//计数
for(auto e:s)
{
if(isspace(e))
continue;
else
c++;
}
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}for -- 通过下标遍历:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin , s);
int sz = s.size() ;
int c = 0 ;
for(int i = 0; i < sz ; i++)
{
if(isspace(s[i]))
continue;
else
c++;
}
cout << c << endl;
return 0;
}
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
int sum = 0;
while(cin >> s)
{
sum += s.size() ;
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}这个题解放在OJ平台可以通过 , 如果想要在控制台上检验 , 结束的时候要手动加上 Ctrl + Z , 来表示结束 。
1)cin 的特点就是 , 读取字符串的是时候 , 遇到空格就结束了 。在while 循环中 , 字符串前面有的空格也会自动跳过了 。所以 , 处理一个字符串的时候 , 也不一定要一次性读取完整个字符串 , 如果字符串中有空格的话 , 其实可以当做多个单词 , 一次读取 。
2)cin >> s 会返回一个流对象的引用 , 即cin 本身 。 在C++中 , 流对象(如 cin) 可以被用作布尔值来检查流的状态 , 如果流状态良好(没有发生错误) , 流对象的布尔值为 true , 如果发生错误 , 布尔值为 false
3 ) 在while (cin >> s ) 中 , 循环的条件部分检查 cin 流的状态 , 如果cin 被转化为false , 循环停止 。
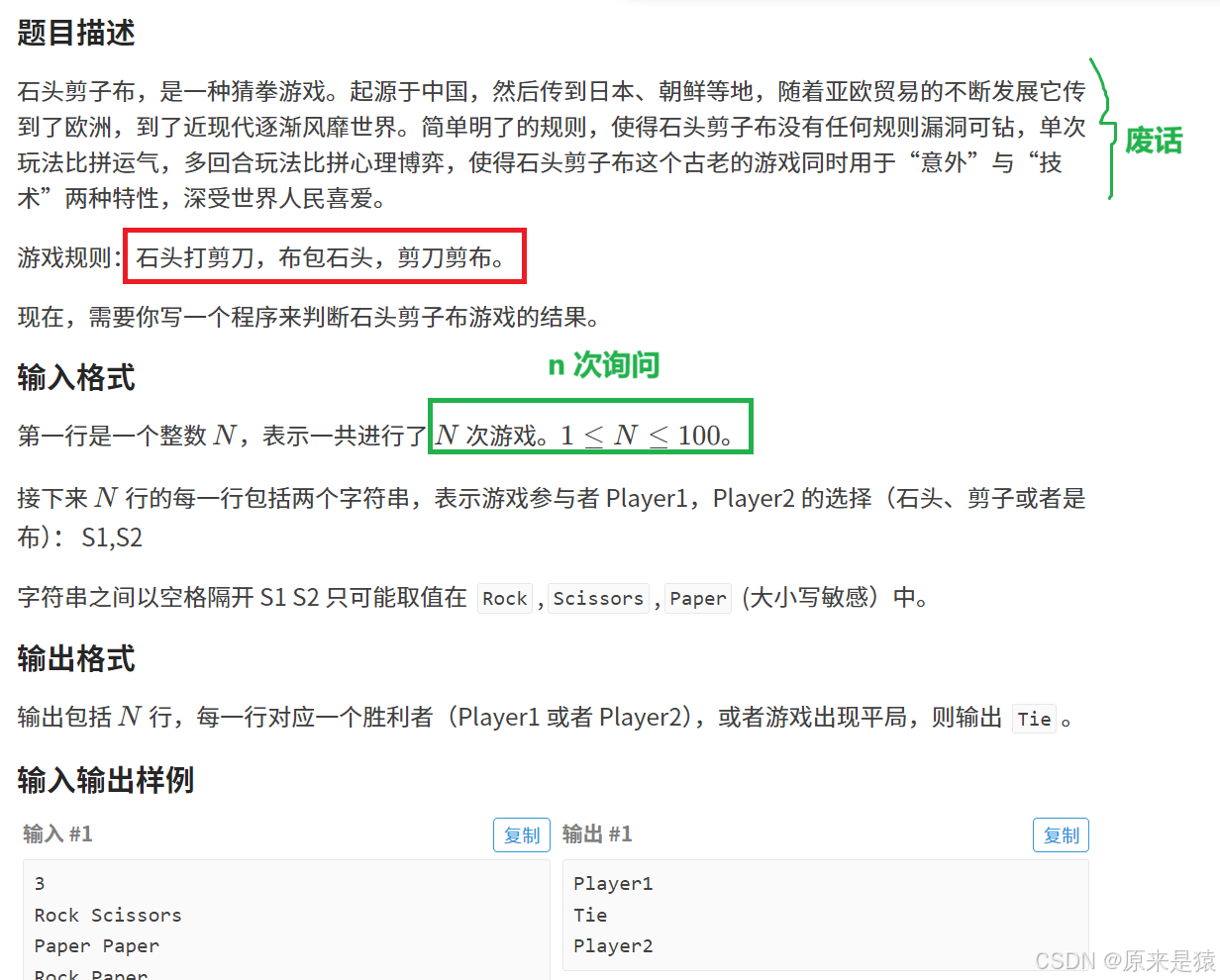
3.2 练习二:石头剪子布

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n ;
cin >> n;
string s1,s2;
while(n--)
{
cin >> s1 ;
cin >> s2 ;
if(s1 == s2)
cout << "Tie" << endl;
else if(s1 == "Rock" && s2 == "Scissors")
cout << "Player1" << endl;
else if(s1 == "Scissors" && s2 == "Paper")
cout << "Player1" << endl;
else if(s1 == "Paper" && s2 == "Rock")
cout << "Player1" << endl;
else
cout << "Player2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}把玩家一赢的条件写在一起也是可以的:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n ;
cin >> n;
string s1,s2;
while(n--)
{
cin >> s1 ;
cin >> s2 ;
if(s1 == s2)
cout << "Tie" << endl;
else if(s1 == "Rock" && s2 == "Scissors"
||s1 == "Scissors" && s2 == "Paper"
||s1 == "Paper" && s2 == "Rock")
cout << "Player1" << endl;
else
cout << "Player2" << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.3 练习三:密码翻译

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
for(int i = 0;i < s.size() ;i++)
{
if((s[i] >= 'b' && s[i] <= 'z') || (s[i] >= 'B' && s[i] <= 'Z'))
s[i] -= 1;
else if(s[i] == 'a')
s[i] = 'z';
else if(s[i] == 'A')
s[i] = 'Z';
}
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}
3.4 练习四:文字处理软件

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int q;
cin >> q;
string s;
cin >> s; //原始字符串
string str;
int a,b;
//q次询问/循环
int m = 0;
while(q--)
{
//处理一次操作
cin >> m;
switch(m)
{
case 1:
cin >> str;
s += str;
cout << s << endl;
break;
case 2:
cin >> a >> b;
s = s.substr(a,b);
cout << s << endl;
break;
case 3:
cin >> a >> str;
s.insert(a,str);
cout << s << endl;
break;
case 4:
cin >> str;
size_t pos = s.find(str);
if(pos != string::npos)
cout << pos << endl;
else
cout << -1 << endl;
break;
}
}
return 0;
}
3.5 练习五:单词的长度

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
//先处理第一个单词
cin >> s;
cout << s.size();
while(cin >> s)
{
size_t n = s.size();
cout << "," << n ;
}
return 0;
}还有一种思路 , 就是如果不想特殊出来处理第一次单词 , 我们可以创建一个布尔变量,初始化为真 , 进入循环之后 , 如果布尔变量为true ,打印长度并把布尔变量置为false , 之后再进入循环 , 进入else 语句即可 。
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
bool flag = true;
while(cin >> s)
{
if(flag)
{
cout << s.size();
flag = false;
}
else
{
cout << "," << s.size() ;
}
}
return 0;
}
3.6 练习六:单词翻转

方法一:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while(cin >> s)
{
int left = 0;
int right = s.size() -1;
while(left < right)
{
char tmp = s[left];
s[left] = s[right];
s[right] = tmp;
left++;
right--;
}
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}方法二:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cctype>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while(cin >> s)
{
for(int i = s.size()-1;i >= 0;i--)
{
cout << s[i];
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}方法三:
其实在C++的STL中 , 包含一个算法叫 reverse , 可以完成字符串的逆序(反转)。
需要的头文件是<algorithm>

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s = "abcdef";
cout << s << endl;
reverse(s.begin() ,s.end());
cout << s << endl;
return 0;
}

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
//反转字符串
string s = "hello world";
cout << s << endl;
reverse(s.begin() ,s.end());
cout << s << endl;
//反转数组
int arr[] = {1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10};
int size = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
//对数组中的元素进行逆序
reverse(arr,arr+size);
for(auto e:arr)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
掌握了这种方法 , 我们再来看看这道题目, 大大减少了代码的复杂度:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
while(cin >> s)
{
reverse(s.begin() ,s.end());
cout << s << endl;
}
return 0;
}
3.7 练习七:判断字符串是否为回文
回文 --> 顺着读倒着读都一样 !!!

#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s1;
cin >> s1;
string s2 = s1;
reverse(s2.begin() ,s2.end());
if(s1 == s2)
cout << "yes" << endl;
else
cout << "no" << endl;
return 0;
}如果麻烦一些,就定两个变量 , 一个left , 指向第一个元素;一个right , 指向最后一个元素;进入循环 , 比较 , 相等就继续比较 , 不相等就直接输出 no ,并return 。(return 比 break 的威力更大 , break 是跳出循环 , return 直接结束了程序)
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
cin >> s;
int left = 0;
int right = s.size() -1;
while(left < right)
{
if(s[left] == s[right])
{
left++;
right--;
}
else
{
cout << "no" << endl;
return 0;
}
}
cout << "yes" << endl;
return 0;
}
3.8 练习八:手机


#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
string s;
getline(cin,s);
int count[26] = {1,2,3, 1,2,3, 1,2,3, 1,2,3, 1,2,3, 1,2,3,4, 1,2,3, 1,2,3,4};
int sum = 0;
for(auto e:s)
{
if(e == ' ')
sum += 1;
else
sum += count[e - 'a'];
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}3.9 练习九:口算练习题



#include <iostream>
#include <cstdio>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
cin >> i;
string op;//操作
string last;
string num1;
string num2;
int r = 0;
while(i--)
{
//输入数据
string ans;
cin >> op;
if(op == "a" || op == "b" || op =="c")
{
cin >> num1 >> num2;
int n1 = stoi(num1);
int n2 = stoi(num2);
ans += num1;
if(op == "a")
r = n1 + n2,ans += "+";
else if(op == "b")
r = n1 - n2,ans += "-";
else
r = n1 * n2,ans += "*";
last = op;
}
else
{
num1 = op;
cin >> num2;
int n1 = stoi(num1);
int n2 = stoi(num2);
ans += num1;
if(last == "a")
r = n1 + n2,ans += "+";
else if(last == "b")
r = n1 - n2,ans += "-";
else
r = n1 * n2,ans += "*";
}
ans += (num2 + "=" + to_string(r));
cout << ans << endl;
cout << ans.size() << endl;
}
return 0;
}
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








