Problem
Given an m x n grid of characters board and a string word, return true if word exists in the grid.
The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. The same letter cell may not be used more than once.
Example 1:
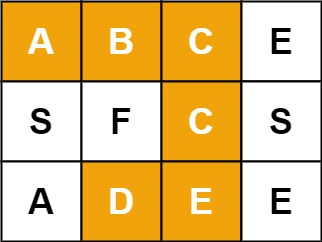
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCCED" Output: true
Example 2:
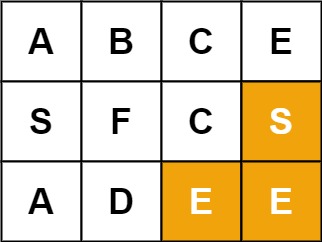
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "SEE" Output: true
Example 3:
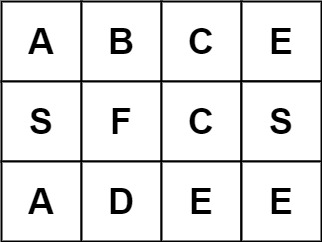
Input: board = [["A","B","C","E"],["S","F","C","S"],["A","D","E","E"]], word = "ABCB" Output: false
Intuition
The problem involves determining whether a given word exists in the provided grid. The word can be constructed from letters of sequentially adjacent cells, where adjacent cells are horizontally or vertically neighboring. Additionally, the same letter cell may not be used more than once. This problem can be solved using a depth-first search (DFS) approach.
Approach
DFS Function:
Implement a DFS function (dfs) that takes three parameters: the current row r, the current column c, and the index i representing the position in the word.
In the base case:
If i is equal to the length of the word, return True (the word has been found).
If the current cell (r, c) is out of bounds or has already been visited or contains a letter different from the corresponding letter in the word, return False.
Mark the current cell as visited by adding (r, c) to the set path.
Recursively call the dfs function for adjacent cells in all four directions (up, down, left, right) with the updated index i.
After the recursive calls, remove (r, c) from the set path to backtrack.
Iterate Over Grid:
Iterate over each cell in the grid and call the dfs function for each cell with the starting index i set to 0.
If the dfs function returns True for any cell, the word exists in the grid, and the function can return True.
Return Result:
If no cell results in a True return from the dfs function, return False, indicating that the word does not exist in the grid.
Complexity
- Time complexity:
The time complexity is O(M * N * 4^L), where M is the number of rows, N is the number of columns, and L is the length of the word. The factor of 4^L accounts for the branching factor of the DFS.
- Space complexity:
The space complexity is O(L), where L is the length of the word. This is due to the space required for the recursion stack and the set path used to track visited cells.
Code
class Solution:
def exist(self, board: List[List[str]], word: str) -> bool:
rows, cols = len(board), len(board[0])
path = set()
def dfs(r, c, i):
if i == len(word):
return True
if (r < 0 or c < 0 or
r >= rows or c >= cols or
word[i] != board[r][c] or (r, c) in path):
return False
path.add((r, c))
res = (dfs(r + 1, c, i + 1) or
dfs(r - 1, c, i + 1) or
dfs(r, c - 1, i + 1) or
dfs(r, c + 1, i + 1))
path.remove((r, c))
return res
for r in range(rows):
for c in range(cols):
if dfs(r, c, 0): return True
return False





















 1225
1225

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








