帮我整理下面的help,配置参数的意义,可以设置的值,请详细介绍列出来:ubuntu@studyubuntu:~/gem5$ build/X86/gem5.opt configs/deprecated/example/se.py --help
gem5 Simulator System. https://www.gem5.org
gem5 is copyrighted software; use the --copyright option for details.
gem5 version 25.0.0.1
gem5 compiled Oct 15 2025 14:07:26
gem5 started Oct 22 2025 14:01:40
gem5 executing on studyubuntu, pid 3588
command line: build/X86/gem5.opt configs/deprecated/example/se.py --help
warn: The se.py script is deprecated. It will be removed in future releases of gem5.
usage: se.py [-h] [-n NUM_CPUS] [--sys-voltage SYS_VOLTAGE]
[--sys-clock SYS_CLOCK] [--list-mem-types]
[--mem-type {CfiMemory,DDR3_1600_8x8,DDR3_2133_8x8,DDR4_2400_16x4,DDR4_2400_4x16,DDR4_2400_8x8,DDR5_4400_4x8,DDR5_6400_4x8,DDR5_8400_4x8,DRAMInterface,GDDR5_4000_2x32,HBM_1000_4H_1x128,HBM_1000_4H_1x64,HBM_2000_4H_1x64,HMC_2500_1x32,LPDDR2_S4_1066_1x32,LPDDR3_1600_1x32,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_8B_BL32,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_BG_BL16,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_BG_BL32,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_8B_BL32,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_BG_BL16,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_BG_BL32,NVMInterface,NVM_2400_1x64,QoSMemSinkInterface,SimpleMemory,WideIO_200_1x128}]
[--mem-channels MEM_CHANNELS] [--mem-ranks MEM_RANKS]
[--mem-size MEM_SIZE] [--enable-dram-powerdown]
[--mem-channels-intlv MEM_CHANNELS_INTLV] [--memchecker]
[--external-memory-system EXTERNAL_MEMORY_SYSTEM]
[--tlm-memory TLM_MEMORY] [--caches] [--l2cache]
[--num-dirs NUM_DIRS] [--num-l2caches NUM_L2CACHES]
[--num-l3caches NUM_L3CACHES] [--l1d_size L1D_SIZE]
[--l1i_size L1I_SIZE] [--l2_size L2_SIZE] [--l3_size L3_SIZE]
[--l1d_assoc L1D_ASSOC] [--l1i_assoc L1I_ASSOC]
[--l2_assoc L2_ASSOC] [--l3_assoc L3_ASSOC]
[--cacheline_size CACHELINE_SIZE] [--ruby] [-m TICKS]
[--rel-max-tick TICKS] [--maxtime MAXTIME] [-P PARAM]
[--list-cpu-types]
[--cpu-type {AtomicSimpleCPU,BaseAtomicSimpleCPU,BaseMinorCPU,BaseNonCachingSimpleCPU,BaseO3CPU,BaseTimingSimpleCPU,DerivO3CPU,NonCachingSimpleCPU,O3CPU,TimingSimpleCPU,X86AtomicSimpleCPU,X86KvmCPU,X86MinorCPU,X86NonCachingSimpleCPU,X86O3CPU,X86TimingSimpleCPU}]
[--list-bp-types] [--list-indirect-bp-types]
[--bp-type {BiModeBP,LTAGE,LocalBP,MultiperspectivePerceptron64KB,MultiperspectivePerceptron8KB,MultiperspectivePerceptronTAGE64KB,MultiperspectivePerceptronTAGE8KB,TAGE,TAGE_SC_L_64KB,TAGE_SC_L_8KB,TournamentBP}]
[--indirect-bp-type {SimpleIndirectPredictor}] [--list-rp-types]
[--list-hwp-types]
[--l1i-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}]
[--l1d-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}]
[--l2-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}]
[--checker] [--cpu-clock CPU_CLOCK] [--smt] [--elastic-trace-en]
[--inst-trace-file INST_TRACE_FILE]
[--data-trace-file DATA_TRACE_FILE] [--dist]
[--dist-sync-on-pseudo-op] [--is-switch] [--dist-rank DIST_RANK]
[--dist-size DIST_SIZE] [--dist-server-name DIST_SERVER_NAME]
[--dist-server-port DIST_SERVER_PORT]
[--dist-sync-repeat DIST_SYNC_REPEAT]
[--dist-sync-start DIST_SYNC_START]
[--ethernet-linkspeed ETHERNET_LINKSPEED]
[--ethernet-linkdelay ETHERNET_LINKDELAY] [-I MAXINSTS]
[--work-item-id WORK_ITEM_ID] [--num-work-ids NUM_WORK_IDS]
[--work-begin-cpu-id-exit WORK_BEGIN_CPU_ID_EXIT]
[--work-end-exit-count WORK_END_EXIT_COUNT]
[--work-begin-exit-count WORK_BEGIN_EXIT_COUNT]
[--init-param INIT_PARAM] [--initialize-only]
[--simpoint-profile] [--simpoint-interval SIMPOINT_INTERVAL]
[--take-simpoint-checkpoints TAKE_SIMPOINT_CHECKPOINTS]
[--restore-simpoint-checkpoint]
[--take-checkpoints TAKE_CHECKPOINTS]
[--max-checkpoints MAX_CHECKPOINTS]
[--checkpoint-dir CHECKPOINT_DIR] [-r CHECKPOINT_RESTORE]
[--checkpoint-at-end]
[--work-begin-checkpoint-count WORK_BEGIN_CHECKPOINT_COUNT]
[--work-end-checkpoint-count WORK_END_CHECKPOINT_COUNT]
[--work-cpus-checkpoint-count WORK_CPUS_CHECKPOINT_COUNT]
[--restore-with-cpu {AtomicSimpleCPU,BaseAtomicSimpleCPU,BaseMinorCPU,BaseNonCachingSimpleCPU,BaseO3CPU,BaseTimingSimpleCPU,DerivO3CPU,NonCachingSimpleCPU,O3CPU,TimingSimpleCPU,X86AtomicSimpleCPU,X86KvmCPU,X86MinorCPU,X86NonCachingSimpleCPU,X86O3CPU,X86TimingSimpleCPU}]
[--repeat-switch REPEAT_SWITCH] [-s STANDARD_SWITCH]
[-p PROG_INTERVAL] [-W WARMUP_INSTS] [--bench BENCH]
[-F FAST_FORWARD] [-S] [--at-instruction]
[--spec-input {ref,test,train,smred,mdred,lgred}]
[--arm-iset {arm,thumb,aarch64}] [--stats-root STATS_ROOT]
[--override-vendor-string OVERRIDE_VENDOR_STRING] [-c CMD]
[-o OPTIONS] [-e ENV] [-i INPUT] [--output OUTPUT]
[--errout ERROUT] [--chroot CHROOT] [--interp-dir INTERP_DIR]
[--redirects REDIRECTS] [--wait-gdb]
options:
-h, --help show this help message and exit
-n NUM_CPUS, --num-cpus NUM_CPUS
--sys-voltage SYS_VOLTAGE
Top-level voltage for blocks running at system power
supply
--sys-clock SYS_CLOCK
Top-level clock for blocks running at system speed
--list-mem-types List available memory types
--mem-type {CfiMemory,DDR3_1600_8x8,DDR3_2133_8x8,DDR4_2400_16x4,DDR4_2400_4x16,DDR4_2400_8x8,DDR5_4400_4x8,DDR5_6400_4x8,DDR5_8400_4x8,DRAMInterface,GDDR5_4000_2x32,HBM_1000_4H_1x128,HBM_1000_4H_1x64,HBM_2000_4H_1x64,HMC_2500_1x32,LPDDR2_S4_1066_1x32,LPDDR3_1600_1x32,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_8B_BL32,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_BG_BL16,LPDDR5_5500_1x16_BG_BL32,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_8B_BL32,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_BG_BL16,LPDDR5_6400_1x16_BG_BL32,NVMInterface,NVM_2400_1x64,QoSMemSinkInterface,SimpleMemory,WideIO_200_1x128}
type of memory to use
--mem-channels MEM_CHANNELS
number of memory channels
--mem-ranks MEM_RANKS
number of memory ranks per channel
--mem-size MEM_SIZE Specify the physical memory size (single memory)
--enable-dram-powerdown
Enable low-power states in DRAMInterface
--mem-channels-intlv MEM_CHANNELS_INTLV
Memory channels interleave
--memchecker
--external-memory-system EXTERNAL_MEMORY_SYSTEM
use external ports of this port_type for caches
--tlm-memory TLM_MEMORY
use external port for SystemC TLM cosimulation
--caches
--l2cache
--num-dirs NUM_DIRS
--num-l2caches NUM_L2CACHES
--num-l3caches NUM_L3CACHES
--l1d_size L1D_SIZE
--l1i_size L1I_SIZE
--l2_size L2_SIZE
--l3_size L3_SIZE
--l1d_assoc L1D_ASSOC
--l1i_assoc L1I_ASSOC
--l2_assoc L2_ASSOC
--l3_assoc L3_ASSOC
--cacheline_size CACHELINE_SIZE
--ruby
-m TICKS, --abs-max-tick TICKS
Run to absolute simulated tick specified including
ticks from a restored checkpoint
--rel-max-tick TICKS Simulate for specified number of ticks relative to the
simulation start tick (e.g. if restoring a checkpoint)
--maxtime MAXTIME Run to the specified absolute simulated time in
seconds
-P PARAM, --param PARAM
Set a SimObject parameter relative to the root node.
An extended Python multi range slicing syntax can be
used for arrays. For example:
'system.cpu[0,1,3:8:2].max_insts_all_threads = 42'
sets max_insts_all_threads for cpus 0, 1, 3, 5 and 7
Direct parameters of the root object are not
accessible, only parameters of its children.
--list-cpu-types List available CPU types
--cpu-type {AtomicSimpleCPU,BaseAtomicSimpleCPU,BaseMinorCPU,BaseNonCachingSimpleCPU,BaseO3CPU,BaseTimingSimpleCPU,DerivO3CPU,NonCachingSimpleCPU,O3CPU,TimingSimpleCPU,X86AtomicSimpleCPU,X86KvmCPU,X86MinorCPU,X86NonCachingSimpleCPU,X86O3CPU,X86TimingSimpleCPU}
type of cpu to run with
--list-bp-types List available branch predictor types
--list-indirect-bp-types
List available indirect branch predictor types
--bp-type {BiModeBP,LTAGE,LocalBP,MultiperspectivePerceptron64KB,MultiperspectivePerceptron8KB,MultiperspectivePerceptronTAGE64KB,MultiperspectivePerceptronTAGE8KB,TAGE,TAGE_SC_L_64KB,TAGE_SC_L_8KB,TournamentBP}
type of branch predictor to run with (if not set, use
the default branch predictor of the selected CPU)
--indirect-bp-type {SimpleIndirectPredictor}
type of indirect branch predictor to run with
--list-rp-types List available replacement policy types
--list-hwp-types List available hardware prefetcher types
--l1i-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}
type of hardware prefetcher to use with the L1
instruction cache. (if not set, use the default
prefetcher of the selected cache)
--l1d-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}
type of hardware prefetcher to use with the L1 data
cache. (if not set, use the default prefetcher of the
selected cache)
--l2-hwp-type {AMPMPrefetcher,BOPPrefetcher,DCPTPrefetcher,IndirectMemoryPrefetcher,IrregularStreamBufferPrefetcher,MultiPrefetcher,PIFPrefetcher,SBOOEPrefetcher,STeMSPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcher,SignaturePathPrefetcherV2,SlimAMPMPrefetcher,SmsPrefetcher,StridePrefetcher,TaggedPrefetcher}
type of hardware prefetcher to use with the L2 cache.
(if not set, use the default prefetcher of the
selected cache)
--checker
--cpu-clock CPU_CLOCK
Clock for blocks running at CPU speed
--smt Only used if multiple programs are specified. If true,
then the number of threads per cpu is same as the
number of programs.
--elastic-trace-en Enable capture of data dependency and instruction
fetch traces using elastic trace probe.
--inst-trace-file INST_TRACE_FILE
Instruction fetch trace file input to Elastic Trace
probe in a capture simulation and Trace CPU in a
replay simulation
--data-trace-file DATA_TRACE_FILE
Data dependency trace file input to Elastic Trace
probe in a capture simulation and Trace CPU in a
replay simulation
--dist Parallel distributed gem5 simulation.
--dist-sync-on-pseudo-op
Use a pseudo-op to start dist-gem5 synchronization.
--is-switch Select the network switch simulator process for
adistributed gem5 run
--dist-rank DIST_RANK
Rank of this system within the dist gem5 run.
--dist-size DIST_SIZE
Number of gem5 processes within the dist gem5 run.
--dist-server-name DIST_SERVER_NAME
Name of the message server host DEFAULT: localhost
--dist-server-port DIST_SERVER_PORT
Message server listen port DEFAULT: 2200
--dist-sync-repeat DIST_SYNC_REPEAT
Repeat interval for synchronisation barriers among
dist-gem5 processes DEFAULT: --ethernet-linkdelay
--dist-sync-start DIST_SYNC_START
Time to schedule the first dist synchronisation
barrier DEFAULT:5200000000000t
--ethernet-linkspeed ETHERNET_LINKSPEED
Link speed in bps DEFAULT: 10Gbps
--ethernet-linkdelay ETHERNET_LINKDELAY
Link delay in seconds DEFAULT: 10us
-I MAXINSTS, --maxinsts MAXINSTS
Total number of instructions to simulate (default: run
forever)
--work-item-id WORK_ITEM_ID
the specific work id for exit & checkpointing
--num-work-ids NUM_WORK_IDS
Number of distinct work item types
--work-begin-cpu-id-exit WORK_BEGIN_CPU_ID_EXIT
exit when work starts on the specified cpu
--work-end-exit-count WORK_END_EXIT_COUNT
exit at specified work end count
--work-begin-exit-count WORK_BEGIN_EXIT_COUNT
exit at specified work begin count
--init-param INIT_PARAM
Parameter available in simulation with m5 initparam
--initialize-only Exit after initialization. Do not simulate time.
Useful when gem5 is run as a library.
--simpoint-profile Enable basic block profiling for SimPoints
--simpoint-interval SIMPOINT_INTERVAL
SimPoint interval in num of instructions
--take-simpoint-checkpoints TAKE_SIMPOINT_CHECKPOINTS
<simpoint file,weight file,interval-length,warmup-
length>
--restore-simpoint-checkpoint
restore from a simpoint checkpoint taken with --take-
simpoint-checkpoints
--take-checkpoints TAKE_CHECKPOINTS
<M,N> take checkpoints at tick M and every N ticks
thereafter
--max-checkpoints MAX_CHECKPOINTS
the maximum number of checkpoints to drop
--checkpoint-dir CHECKPOINT_DIR
Place all checkpoints in this absolute directory
-r CHECKPOINT_RESTORE, --checkpoint-restore CHECKPOINT_RESTORE
restore from checkpoint <N>
--checkpoint-at-end take a checkpoint at end of run
--work-begin-checkpoint-count WORK_BEGIN_CHECKPOINT_COUNT
checkpoint at specified work begin count
--work-end-checkpoint-count WORK_END_CHECKPOINT_COUNT
checkpoint at specified work end count
--work-cpus-checkpoint-count WORK_CPUS_CHECKPOINT_COUNT
checkpoint and exit when active cpu count is reached
--restore-with-cpu {AtomicSimpleCPU,BaseAtomicSimpleCPU,BaseMinorCPU,BaseNonCachingSimpleCPU,BaseO3CPU,BaseTimingSimpleCPU,DerivO3CPU,NonCachingSimpleCPU,O3CPU,TimingSimpleCPU,X86AtomicSimpleCPU,X86KvmCPU,X86MinorCPU,X86NonCachingSimpleCPU,X86O3CPU,X86TimingSimpleCPU}
cpu type for restoring from a checkpoint
--repeat-switch REPEAT_SWITCH
switch back and forth between CPUs with period <N>
-s STANDARD_SWITCH, --standard-switch STANDARD_SWITCH
switch from timing to Detailed CPU after warmup period
of <N>
-p PROG_INTERVAL, --prog-interval PROG_INTERVAL
CPU Progress Interval
-W WARMUP_INSTS, --warmup-insts WARMUP_INSTS
Warmup period in total instructions (requires
--standard-switch)
--bench BENCH base names for --take-checkpoint and --checkpoint-
restore
-F FAST_FORWARD, --fast-forward FAST_FORWARD
Number of instructions to fast forward before
switching
-S, --simpoint Use workload simpoints as an instruction offset for
--checkpoint-restore or --take-checkpoint.
--at-instruction Treat value of --checkpoint-restore or --take-
checkpoint as a number of instructions.
--spec-input {ref,test,train,smred,mdred,lgred}
Input set size for SPEC CPU2000 benchmarks.
--arm-iset {arm,thumb,aarch64}
ARM instruction set.
--stats-root STATS_ROOT
If given, dump only stats of objects under the given
SimObject. SimObjects are identified with Python
notation as in: system.cpu[0].mmu. All elements of an
array can be selected at once with: system.cpu[:].mmu.
If given multiple times, dump stats that are present
under any of the roots. If not given, dump all stats.
--override-vendor-string OVERRIDE_VENDOR_STRING
Override vendor string returned by CPUID instruction
in X86.
-c CMD, --cmd CMD The binary to run in syscall emulation mode.
-o OPTIONS, --options OPTIONS
The options to pass to the binary, use around the
entire string
-e ENV, --env ENV Initialize workload environment from text file.
-i INPUT, --input INPUT
Read stdin from a file.
--output OUTPUT Redirect stdout to a file.
--errout ERROUT Redirect stderr to a file.
--chroot CHROOT The chroot option allows a user to alter the search
path for processes running in SE mode. Normally, the
search path would begin at the root of the filesystem
(i.e. /). With chroot, a user can force the process to
begin looking atsome other location (i.e.
/home/user/rand_dir).The intended use is to trick
sophisticated software which queries the __HOST__
filesystem for information or functionality. Instead
of finding files on the __HOST__ filesystem, the
process will find the user's replacment files.
--interp-dir INTERP_DIR
The interp-dir option is used for setting the
interpreter's path. This will allow to load the guest
dynamic linker/loader itself from the elf binary. The
option points to the parent folder of the guest /lib
in the host fs
--redirects REDIRECTS
A collection of one or more redirect paths to be used
in syscall emulation.Usage: gem5.opt [...] --redirects
/dir1=/path/to/host/dir1 --redirects
/dir2=/path/to/host/dir2
--wait-gdb Wait for remote GDB to connect.
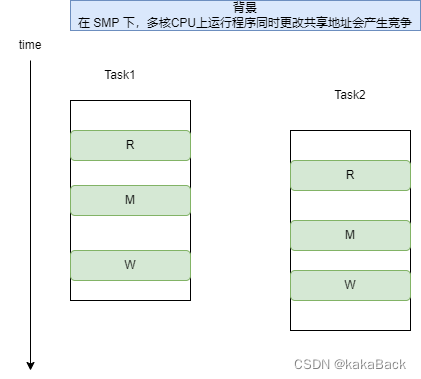
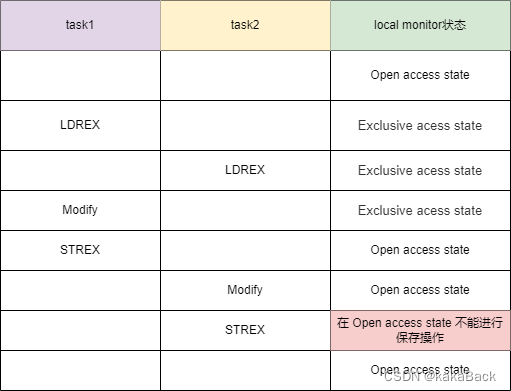
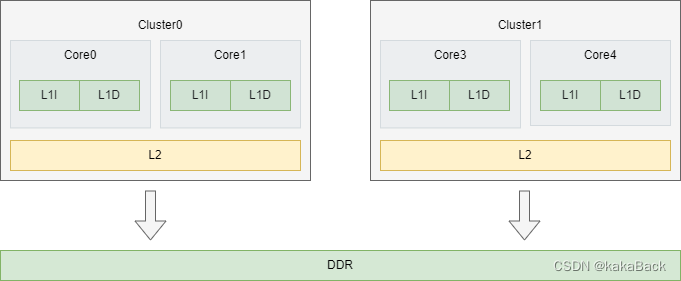
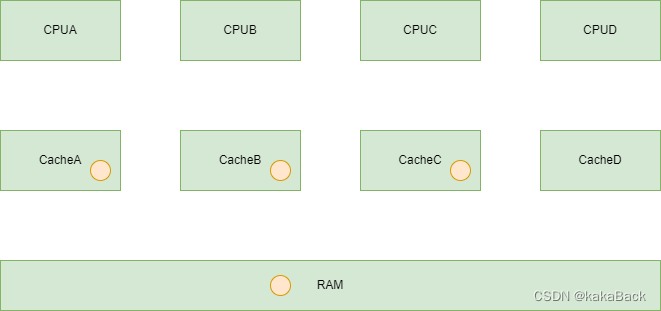







 本文详细介绍了Linux内核中的Atomic操作原理及其在ARM32与ARM64架构下的实现方式,并探讨了Per-CPU变量的设计理念及应用场景。
本文详细介绍了Linux内核中的Atomic操作原理及其在ARM32与ARM64架构下的实现方式,并探讨了Per-CPU变量的设计理念及应用场景。

















 487
487

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








