一、概述
在本章中,大量用了截图记录笔记信息,原因在于,本章作为C++基础,在理解定义和关键字的方面十分重要。本书满满的干货,深入c++介绍的很详细,可见作者的大师水平,建议还是有些编程基础的会回味受益良多,基础比较差的需要多读几遍,回味编程的魅力。



二、变量和基本类型
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int i = 42;
std::cout << i << std::endl; // prints 42
if (i) // condition will evaluate as true
i = 0;
std::cout << i << std::endl; // prints 0
bool b = 42; // b is true
std::cout << b << std::endl; // prints 1
int j = b; // j has value 1
std::cout << j << std::endl; // prints 1
double pi = 3.14; // pi has value 3.14
std::cout << pi << std::endl; // prints 3.14
j = pi; // j has value 3
std::cout << j << std::endl; // prints 3
unsigned char c = -1; // assuming 8-bit chars, c has value 255
i = c; // the character with value 255 is an unprintable character
// assigns value of c (i.e., 255) to an int
std::cout << i << std::endl; // prints 255
return 0;
}
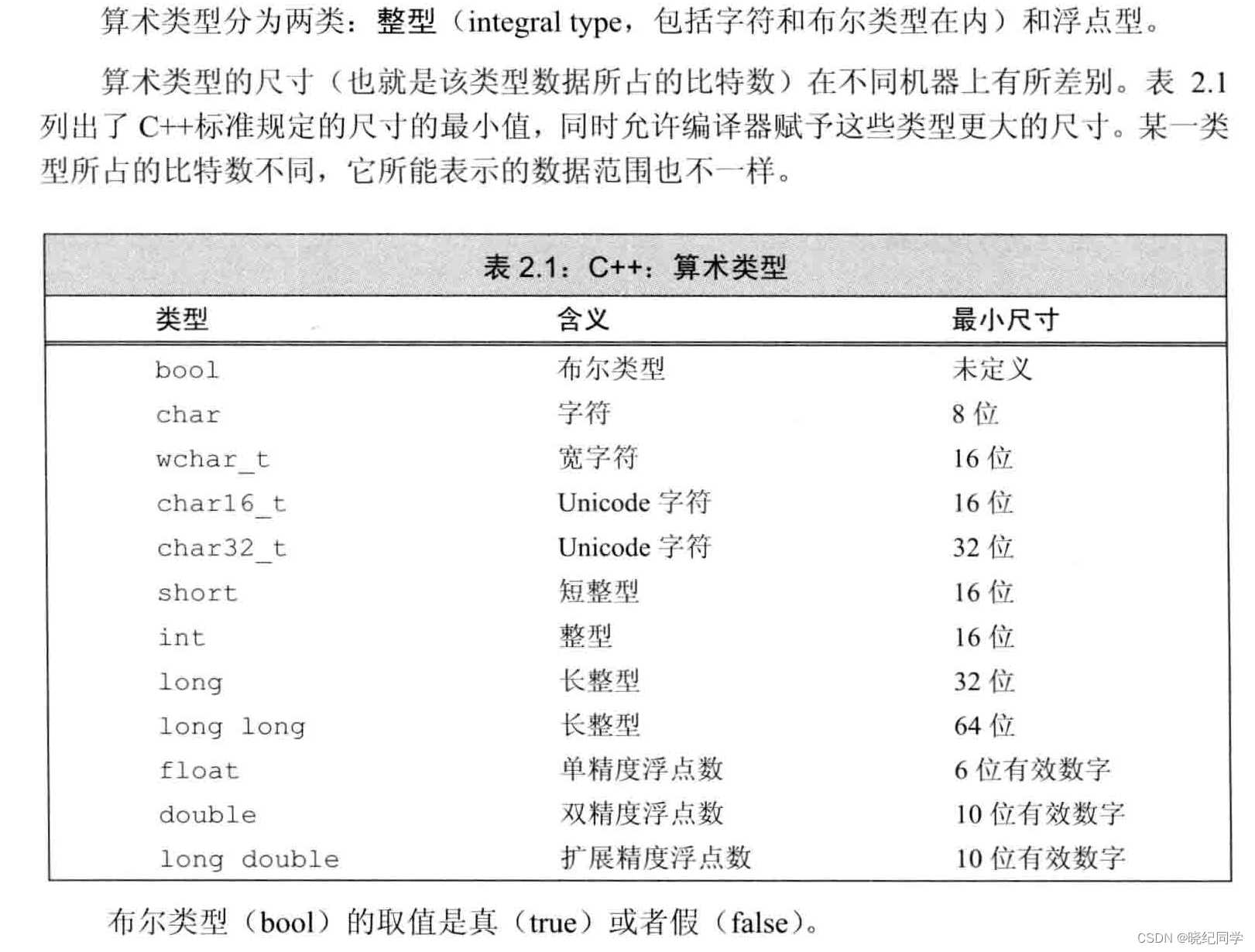
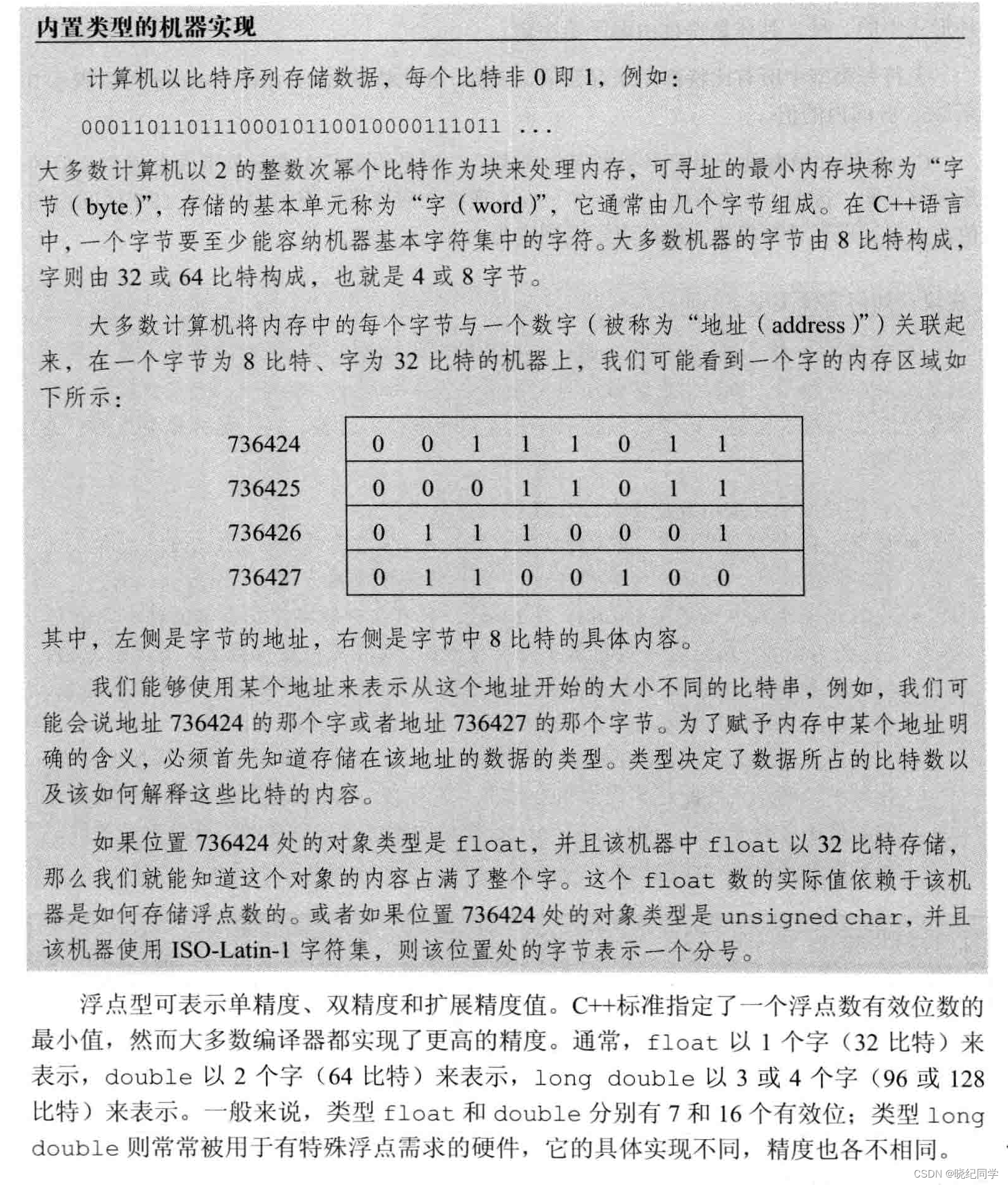
2.1、基本内置类型





#include <iostream>
int main()
{
unsigned u = 10, u2 = 42;
std::cout << u2 - u << std::endl;
std::cout << u - u2 << std::endl;
int i = 10, i2 = 42;
std::cout << i2 - i << std::endl;
std::cout << i - i2 << std::endl;
u = 42;
i = 10;
std::cout << i - u << std::endl;
std::cout << u - i << std::endl;
u = 10;
i = -42;
std::cout << i + i << std::endl; // prints -84
std::cout << u + i << std::endl; // if 32-bit ints, prints 4294967264
i = 10;
std::cout << "good" << std::endl;
while (i >= 0) {
std::cout << i << std::endl;
--i;
}
for (int i = 10; i >= 0; --i)
std::cout << i << std::endl;
for (unsigned u = 0; u <= 10; ++u)
std::cout << u << std::endl; // prints 0 . . . 10
/* NOTE: the condition in the following loop
will run indefinitely
// WRONG: u can never be less than 0; the condition will always succeed
for (unsigned u = 10; u >= 0; --u)
std::cout << u << std::endl;
*/
u = 11; // start the loop one past the first element we want to print
while (u > 0) {
--u; // decrement first, so that the last iteration will print 0
std::cout << u << std::endl;
}
// be wary of comparing ints and unsigned
u = 10;
i = -42;
if (i < u) // false: i is converted to unsigned
std::cout << i << std::endl;
else
std::cout << u << std::endl; // prints 10
u = 42; u2 = 10;
std::cout << u - u2 << std::endl; // ok: result is 32
std::cout << u2 - u << std::endl; // ok: but the result will wrap around
}
字面值
形如42的之被称为 字面值常量




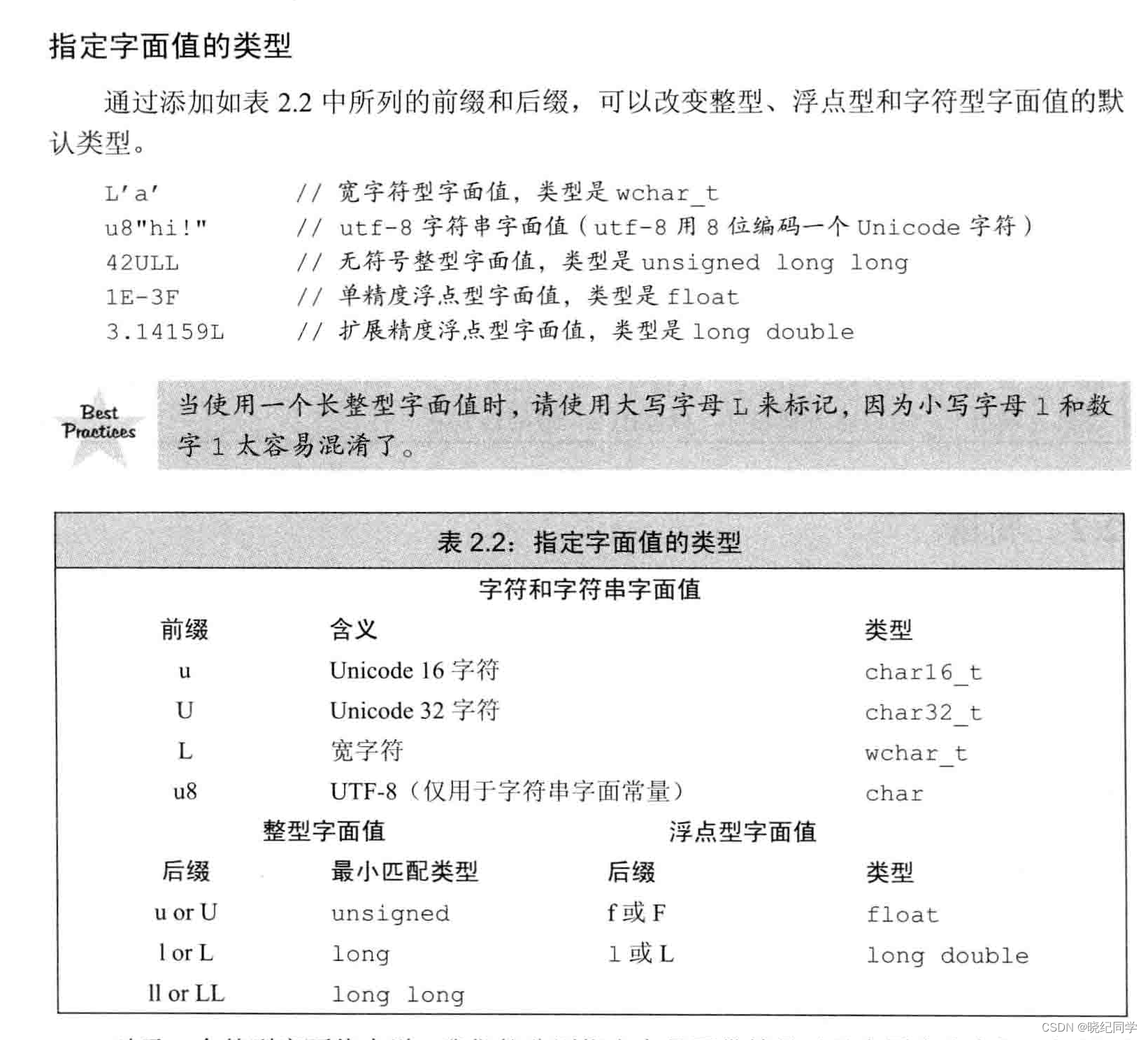


nullptr是指针的字面值
2.2、变量


列表初始化

重要:


默认初始化


标识符

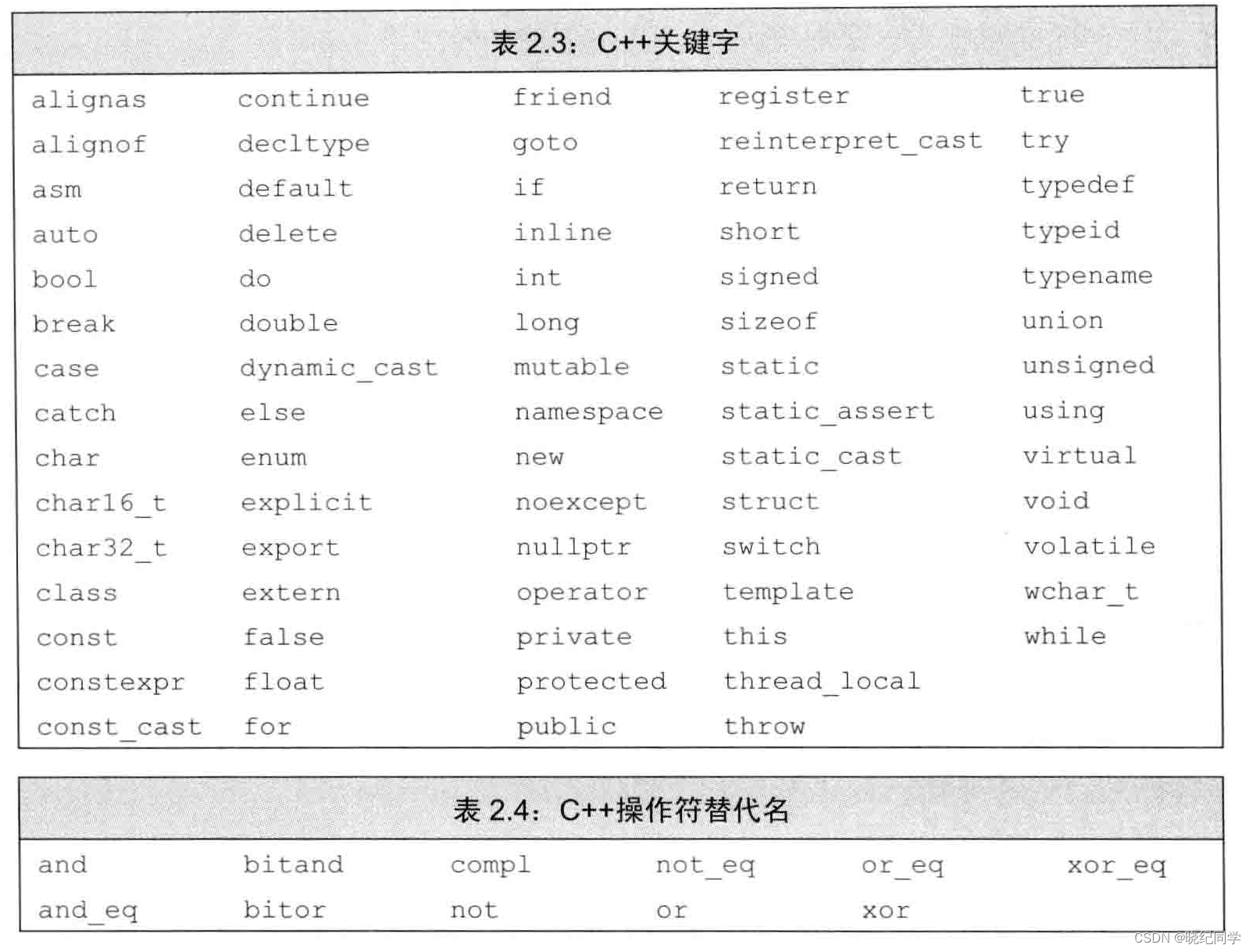
名字作用域


嵌套作用域

#include <iostream>
// Program for illustration purposes only: It is bad style for a function
// to use a global variable and also define a local variable with the same name
int reused = 42; // reused has global scope
int main()
{
int unique = 0; // unique has block scope
// output #1: uses global reused; prints 42 0
std::cout << reused << " " << unique << std::endl;
int reused = 0; // new, local object named reused hides global reused
// output #2: uses local reused; prints 0 0
std::cout << reused << " " << unique << std::endl;
// output #3: explicitly requests the global reused; prints 42 0
std::cout << ::reused << " " << unique << std::endl;
return 0;
}

2.3、复合类型

引用




#include <iostream>
int main()
{
int i = 0, &ri = i; // ri is a reference to i
// ri is just another name for i;
// this statement prints the value of i twice
std::cout << i << " " << ri << std::endl;
i = 5; // changing i is reflected through ri as well
std::cout << i << " " << ri << std::endl;
ri = 10; // assigning to ri actually assigns to i
std::cout << i << " " << ri << std::endl;
return 0;
}
指针







空指针



#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// i is an int; p is a pointer to int; r is a reference to int
int i = 1024, *p = &i, &r = i;
// three ways to print the value of i
std::cout << i << " " << *p << " " << r << std::endl;
int j = 42, *p2 = &j;
int *&pref = p2; // pref is a reference to the pointer p2
// prints the value of j, which is the int to which p2 points
std::cout << *pref << std::endl;
// pref refers to a pointer; assigning &i to pref makes p point to i
pref = &i;
std::cout << *pref << std::endl; // prints the value of i
// dereferencing pref yields i, the int to which p2 points;
*pref = 0; // changes i to 0
std::cout << i << " " << *pref << std::endl;
return 0;
}
void*指针







#include <iostream>
int main()
{
// i is an int; p is a pointer to int; r is a reference to int
int i = 1024, *p = &i, &r = i;
// three ways to print the value of i
std::cout << i << " " << *p << " " << r << std::endl;
int j = 42, *p2 = &j;
int *&pref = p2; // pref is a reference to the pointer p2
// prints the value of j, which is the int to which p2 points
std::cout << *pref << std::endl;
// pref refers to a pointer; assigning &i to pref makes p point to i
pref = &i;
std::cout << *pref << std::endl; // prints the value of i
// dereferencing pref yields i, the int to which p2 points;
*pref = 0; // changes i to 0
std::cout << i << " " << *pref << std::endl;
return 0;
}

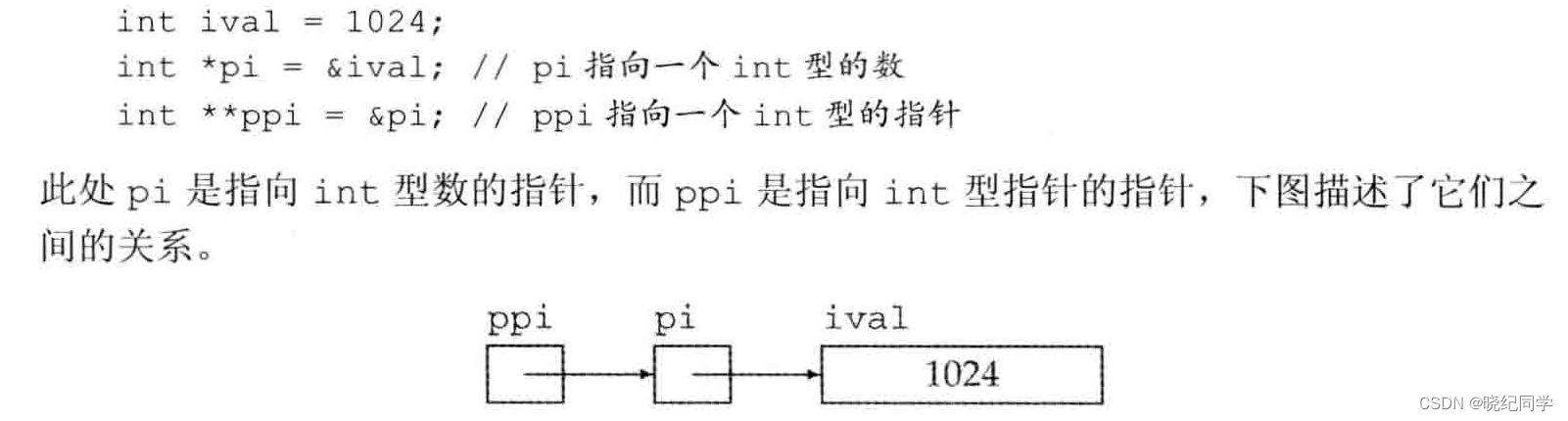
#include <iostream>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
int main()
{
int ival = 1024;
int *pi = &ival; // pi points to an int
int **ppi = π // ppi points to a pointer to an int
cout << "The value of ival\n"
<< "direct value: " << ival << "\n"
<< "indirect value: " << *pi << "\n"
<< "doubly indirect value: " << **ppi
<< endl;
int i = 2;
int *p1 = &i; // p1 points to i
*p1 = *p1 * *p1; // equivalent to i = i * i
cout << "i = " << i << endl;
*p1 *= *p1; // equivalent to i *= i
cout << "i = " << i << endl;
return 0;
}


2.4 const限定符

**
const 定义变量的值不能被修改
const变量必须初始化
**




const的引用








指针和const



顶层consrt


constexpr和常量表达式



2.5、处理类型
类型别名为了简化类型名称,便于理解



auto类型说明符





decltype类型指示符



2.6自定义数据类型



编写自己的头文件



2.7小结

2.8、术语表








 本文深入讲解C++的基础知识,包括变量、基本类型、复合类型等内容,并通过实例演示了如何使用这些概念进行编程。
本文深入讲解C++的基础知识,包括变量、基本类型、复合类型等内容,并通过实例演示了如何使用这些概念进行编程。


















 33万+
33万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










