K/N 的内存管理器和 GC,和主流虚拟机基本一样,主要功能如:K/N 使用自己的 custom 内存分配器,每个线程有自己的 tlab;默认垃圾回收器通过 Stop-the-world 标记和并发清除收集器,并且不会将堆分代;当前只支持弱引用,当标记阶段完成后,GC 会处理弱引用,并使指向未标记对象的引用无效。

引言
K/N 的内存管理器和 GC,和主流虚拟机基本一样,主要功能如下:
- K/N 使用自己的 custom 内存分配器,每个线程有自己的 tlab
- 默认垃圾回收器通过 Stop-the-world 标记和并发清除收集器,并且不会将堆分代
- 当前只支持弱引用,当标记阶段完成后,GC 会处理弱引用,并使指向未标记对象的引用无效
要监控 GC 性能,需要在 Gradle 构建脚本中设置以下编译器选项。
代码块:
-Xruntime-logs=gc=info为了提高 GC 性能,可以在 Gradle 构建脚本启用 cms 垃圾回收器,将存活对象标记与应用程序线程并行运行,减少 GC 暂停时间。
代码块:
kotlin.native.binary.gc=cms从文档看,内存分配器已经比较完善了,但是 GC 性能比较差,默认垃圾回收器是 STW,cms 还需要手动配置。我们从代码层面看一下。
Runtime
通过抓取过 kmp trace,可以看到 runtime 入口。
- 鸿蒙 linker 是 ld-musl-aarch64.so,加载 libbenchmark.so,这是 kmp 的编译产物
- 之后执行 workRoutine 方法,这是 Runtime 的入口方法

抖音仓库用的是 kotlin2.0.20, workerRoutine 代码在 kotlin-native 项目 Worker.cpp 文件。
- 先调用 Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded 初始化 Runtime
- 然后通过 do/while 循环调用 processQueueElement 处理任务,类似消息循环
代码块:
void* workerRoutine(void* argument){
Worker* worker = reinterpret_cast<Worker*>(argument);
// Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded calls WorkerInit that needs
// to see there's already a worker created for this thread.
::g_worker = worker;
Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded();
// Only run this routine in the runnable state. The moment between this routine exiting and thread
// destructors running will be spent in the native state. `Kotlin_deinitRuntimeCallback` ensures
// that runtime deinitialization switches back to the runnable state.
kotlin::ThreadStateGuard guard(worker->memoryState(), ThreadState::kRunnable);
do {
if (worker->processQueueElement(true) == JOB_TERMINATE) break;
} while (true);
returnnullptr;
}而 Kotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded 会调用 initRuntime,每个线程有独立的 runtimeState 变量,通过判断 runtimeState 变量状态避免多次调用 initRuntime。
代码块:
RUNTIME_NOTHROW voidKotlin_initRuntimeIfNeeded(){
if (!isValidRuntime()) {
initRuntime();
// Register runtime deinit function at thread cleanup.
konan::onThreadExit(Kotlin_deinitRuntimeCallback, runtimeState);
}
}
THREAD_LOCAL_VARIABLE RuntimeState* runtimeState = kInvalidRuntime;
inlineboolisValidRuntime(){
return ::runtimeState != kInvalidRuntime;
}initRuntime 具体功能如下:
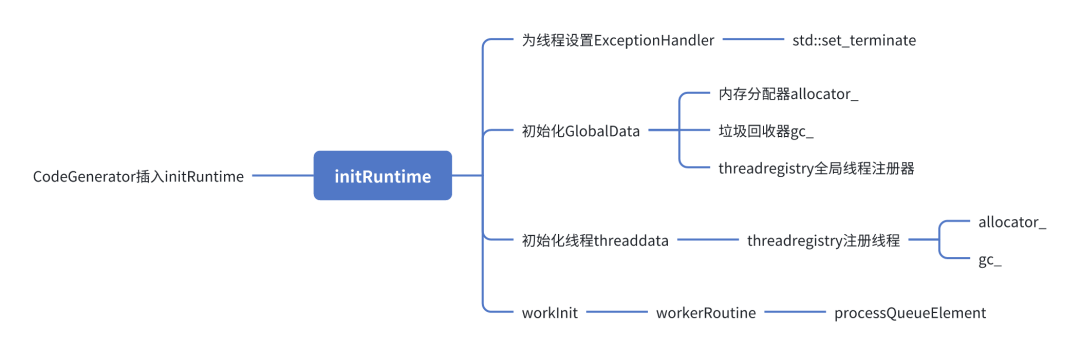
- SetKonanTerminateHandler 为线程设置异常处理 Handler,这样可以捕获 kotlin excepiton
- 设置 runtimeState
- initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded 初始化全局变量
- InitMemory 初始化线程内存分配器
- WorkInit 初始化
代码块:
RuntimeState* initRuntime(){
SetKonanTerminateHandler();
RuntimeState* result = new RuntimeState();
if (!result) return kInvalidRuntime;
::runtimeState = result;
bool firstRuntime = initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded();
result->memoryState = InitMemory();
// Switch thread state because worker and globals inits require the runnable state.
// This call may block if GC requested suspending threads.
ThreadStateGuard stateGuard(result->memoryState, kotlin::ThreadState::kRunnable);
result->worker = WorkerInit(result->memoryState);
result->status = RuntimeStatus::kRunning;
return result;
}initRuntime 过程如图,我们接下来分别分析。
ExceptionHandler
SetKonanTerminateHandler 通过 TerminateHandler 调用 std::set_terminate 设置 kotlinHandler 来处理异常。
代码块:
// Use one public function to limit access to the class declaration
voidSetKonanTerminateHandler(){
TerminateHandler::install();
}
/// Use machinery like Meyers singleton to provide thread safety
TerminateHandler()
: queuedHandler_((QH)std::set_terminate(kotlinHandler)) {}GlobalData
initializeGlobalRuntimeIfNeeded 调用 initGlobalMemory 初始化 GlobalData,GlobalData 包括 allocator_内存分配器,gc_垃圾回收器,threadRegistry_线程列表等。GlobalData 是全局变量,所有线程共用,还有 ThreadData 是线程私有的,后续分析。
代码块:
voidkotlin::initGlobalMemory()noexcept{
mm::GlobalData::init();
}
// Global (de)initialization is undefined in C++. Use single global singleton to define it for simplicity.
classGlobalData :private Pinned {
public:
ThreadRegistry& threadRegistry()noexcept{ return threadRegistry_; }
GlobalsRegistry& globalsRegistry()noexcept{ return globalsRegistry_; }
SpecialRefRegistry& specialRefRegistry()noexcept{ return specialRefRegistry_; }
gcScheduler::GCScheduler& gcScheduler()noexcept{ return gcScheduler_; }
alloc::Allocator& allocator()noexcept{ return allocator_; }
gc::GC& gc()noexcept{ return gc_; }ThreadData
InitMemory 通过上面分析的 ThreadRegistry 全局变量的 RegisterCurrentThread 方法,生成 ThreadData,并注册到 list_列表里,这样 gc 时可以访问到 ThreadData 中的 gc root。currentThreadDataNode 是 thread local 变量,每个线程有独立的变量。
代码块:
extern"C"MemoryState* InitMemory(){
mm::GlobalData::waitInitialized();
return mm::ToMemoryState(mm::ThreadRegistry::Instance().RegisterCurrentThread());
}
mm::ThreadRegistry::Node* mm::ThreadRegistry::RegisterCurrentThread() noexcept {
auto lock = list_.LockForIter();
auto* threadDataNode = list_.Emplace(konan::currentThreadId());
Node*& currentDataNode = currentThreadDataNode_;
currentDataNode = threadDataNode;
threadDataNode->Get()->gc().onThreadRegistration();
return threadDataNode;
}
// static
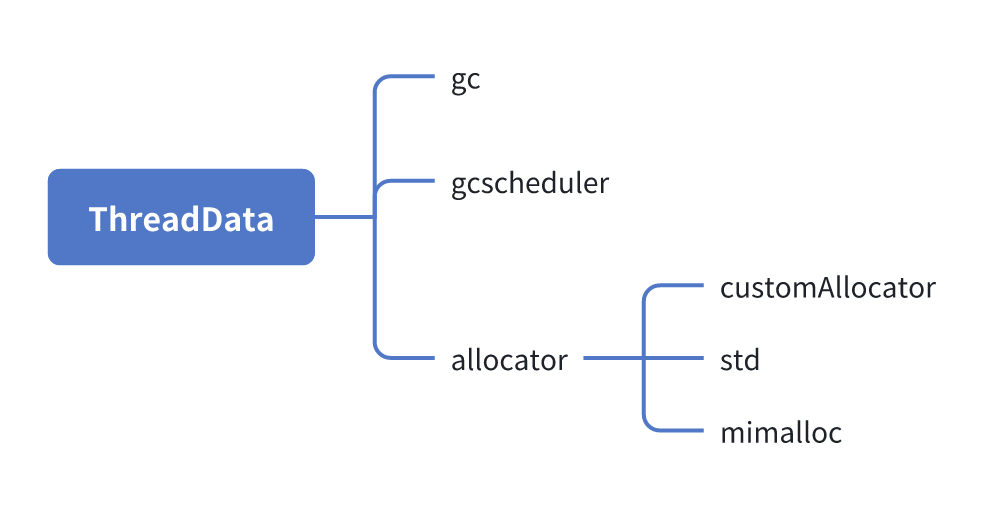
THREAD_LOCAL_VARIABLE mm::ThreadRegistry::Node* mm::ThreadRegistry::currentThreadDataNode_ = nullptr;ThreadData 包括 threadId_,allocator_, gc_等,每个线程一个对象,这样 allocator_每个线程私有就实现了 tlab。
代码块:
// `ThreadData` is supposed to be thread local singleton.
// Pin it in memory to prevent accidental copying.
classThreadDatafinal : privatePinned{
public:
explicit ThreadData(int threadId) noexcept :
threadId_(threadId),
globalsThreadQueue_(GlobalsRegistry::Instance()),
specialRefRegistry_(SpecialRefRegistry::instance()),
gcScheduler_(GlobalData::Instance().gcScheduler(), *this),
allocator_(GlobalData::Instance().allocator()),
gc_(GlobalData::Instance().gc(), *this),
suspensionData_(ThreadState::kNative, *this){}总结一下,ThreadData 在每个线程内部定义了内存分配器和 GC,关于内存分配器我们后续分析。
WorkInit
WorkInit 将 Work 的 thread_变量设置为线程自己,workRoutine 通过 pthread_create 创建新线程 thread_来执行。线程通过 kotlin 代码/c++代码创建,创建好线程之后调用 initRuntime 来初始化。
代码块:
Worker* WorkerInit(MemoryState* memoryState){
Worker* worker;
if (::g_worker != nullptr) {
worker = ::g_worker;
} else {
worker = theState()->addWorkerUnlocked(workerExceptionHandling(), nullptr, WorkerKind::kOther);
::g_worker = worker;
}
worker->setThread(pthread_self());
worker->setMemoryState(memoryState);
return worker;
}
voidWorker::startEventLoop(){
kotlin::ThreadStateGuard guard(ThreadState::kNative);
pthread_create(&thread_, nullptr, workerRoutine, this);
}这里有个问题,既然 workerRoutine 通过 runtime 初始化调用,哪里真正调用 Runtime 呢?
CodeGenerator 会将每个方法中的 kotlin ir 转换为 llvm ir,在这个过程中会插入 initRuntimeIfNeeded 调用。所以每个方法执行时都会先调用 initRuntimeIfNeeded。
代码块:
if (needsRuntimeInit || switchToRunnable) {
check(!forbidRuntime) { "Attempt to init runtime where runtime usage is forbidden" }
call(llvm.initRuntimeIfNeeded, emptyList())
}Runtime 这里分析完了,我们继续看一下 allocator_内存分配器。
内存分配
K/N 有 3 种内存分配器:
- Custom:K/N 自己开发的内存分配器,也是默认的内存分配器
- Std:标准库内存分配器,在鸿蒙上是 jemalloc
- Mimalloc:mimalloc 是微软开源的 native 分配器
每个内存分配器都会实现一个 Allocator::ThreadData::Impl 类,比如 CustomAllocator 就对应 Custom 内存分配器,这样 allocator_可以和特定的内存分配器关联。
代码块:
classAllocator::ThreadData::Impl : private Pinned {
public:
explicitImpl(Allocator::Impl& allocator)noexcept : alloc_(allocator.heap()){}
alloc::CustomAllocator& alloc()noexcept{ return alloc_; }
private:
CustomAllocator alloc_;
};
ALWAYS_INLINE ObjHeader* alloc::Allocator::ThreadData::allocateObject(const TypeInfo* typeInfo) noexcept {
return impl_->alloc().CreateObject(typeInfo);
}我们主要看一下 Custom 内存分配器,每个线程有独立的 threadata,通过 threaddata 创建独立的 allocator_。allocator_每次从 heap 申请一个 page





 最低0.47元/天 解锁文章
最低0.47元/天 解锁文章

















 992
992

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








