SpringBoot 源码解析2:启动流程1
1.启动方式
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
SpringBoot启动方式,这里就不多做说明了
2.@SpringBootApplication
@SpringBootConfiguration
@EnableAutoConfiguration
@ComponentScan(excludeFilters = { @Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = TypeExcludeFilter.class),
@Filter(type = FilterType.CUSTOM, classes = AutoConfigurationExcludeFilter.class) })
public @interface SpringBootApplication {
xxxxx
}
- 可以看到SpringBootApplication注解由三个注解标注,@SpringBootConfiguration、@EnableAutoConfiguration、@ComponentScan。
- 简要说明一下这三个注解的作用:
2.1. SpringBootConfiguration由Configuration标注,而Configuration又是由Component标注,Component表明这个类要被Spring管理。同时Configuration注解还能对当前类进行代理。
2.2. EnableAutoConfiguration是由@Import注解所标注,而Import注解的作用是告诉Spring容器需要注入哪些bean。
2.3. ComponentScan是用来配置扫描Component资源的策略,包含策略和剔除策略,剔除策略优先及高。
3.SpringApplication
3.1 构造器SpringApplication
@SuppressWarnings({ "unchecked", "rawtypes" })
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
- 参数说明:resourceLoader写死null,primarySources为启动类MyApplication。
- 通过classLoader判断当前的WebApplicationType,这里返回的是WebApplicationType.SERVLET。
- 从spring.factories文件中拿到ApplicationContextInitializer和ApplicationListener。spring.factories文件解析可参考 SpringBoot 基础概念:SpringApplication#getSpringFactoriesInstances
- 推断出主类,通过RuntimeException的栈帧信息找到第一个"main"方法所属的类,也就是MyApplication。
3.2 SpringApplication#run
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
configureHeadlessProperty();
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting();
try {
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
context = createApplicationContext();
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
refreshContext(context);
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
listeners.started(context);
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
- 这是SpringBoot真正启动的总流程。
- 从spring.factories文件中获取SpringApplicationRunListener对应的类,通过参数类型为SpringApplication.class, String[].class的构造器实例化,其中值为当前的SpringApplication对象和启动参数args,封装在SpringApplicationRunListeners里。其实是实例化了EventPublishingRunListener,从名字上可知,它是用来分发事件的。

- 调用SpringApplicationRunListeners#starting发布"正在启动"事件,事件为ApplicationStartingEvent。
- prepareEnvironment方法发布"环境准备"事件,由ConfigFileApplicationListener监听,然后解析配置文件(如yml、bootstrap、properties、xml等),将解析的信息存放到Environment里面。
- printBanner方法打印banner
- createApplicationContext创建ApplicationContext,判断的依据是webApplicationType。由于是Servlet类型的,创建的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext。
- 获取异常报告事件监听器,在catch到异常监听failed。
- 准备applicationContext
- refreshContext(context)刷新容器
- listeners.started(context) 发布"已启动"事件
- 调用ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner
- listeners.running发送"running事件"
3.3 SpringApplication#run 中关键方法
3.1 SpringApplication#prepareEnvironment
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners,
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments) {
// Create and configure the environment
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = getOrCreateEnvironment();
configureEnvironment(environment, applicationArguments.getSourceArgs());
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
listeners.environmentPrepared(environment);
bindToSpringApplication(environment);
if (!this.isCustomEnvironment) {
environment = new EnvironmentConverter(getClassLoader()).convertEnvironmentIfNecessary(environment,
deduceEnvironmentClass());
}
ConfigurationPropertySources.attach(environment);
return environment;
}
- getOrCreateEnvironment为Spring创建了环境StandardServletEnvironment,环境变量中有四个propertySources,servletContextInitParams、servletConfigInitParams、systemProperties、systemEnvironment,在Environment的propertySources中存放的是具体的配置信息。
- configureEnvironment方法为environment配置了转换器ConversionService,解析启动参数args保存到环境变量(保存在SimpleCommandLinePropertySource,其name为commandLineArgs)。解析启动参数args中的spring.profiles.active。
- ConfigurationPropertySources#attach,获取到name=configurationProperties的propertySource,如果与environment里面的propertySources不想同就remove。重新添加name=configurationProperties的propertySource,值为environment里面所有的propertySources。
- 发送environmentPrepared事件,ConfigFileApplicationListener监听到该事件,会对配置文件解析,下面会对ConfigFileApplicationListener进行解析。监听器原理可参考:SpringBoot 源码解析4:事件监听器
- 绑定环境变量,属性为spring.main,绑定对象为当前的SpringApplication。
- 如果是自定义environment(配置文件中配置spring.main.isCustomEnvironment),可自定义environment的类型。
3.1.1 环境准备监听器 ConfigFileApplicationListener
//EventPublishingRunListener#environmentPrepared
@Override
public void environmentPrepared(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
this.initialMulticaster
.multicastEvent(new ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, environment));
}
//ConfigFileApplicationListener#onApplicationEvent
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationEvent event) {
if (event instanceof ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent((ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent) event);
}
if (event instanceof ApplicationPreparedEvent) {
onApplicationPreparedEvent(event);
}
}
//ConfigFileApplicationListener#onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent
private void onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
List<EnvironmentPostProcessor> postProcessors = loadPostProcessors();
postProcessors.add(this);
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(postProcessors);
for (EnvironmentPostProcessor postProcessor : postProcessors) {
postProcessor.postProcessEnvironment(event.getEnvironment(), event.getSpringApplication());
}
}
可以看到,发布的是ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent事件,所以会回调onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法。
在onApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent方法中,加载了spring.factories文件中的所有EnvironmentPostProcessor,并且把当前对象放入到集合中,然后根据order排序,再回调postProcessEnvironment方法。
protected void addPropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
RandomValuePropertySource.addToEnvironment(environment);
new Loader(environment, resourceLoader).load();
}
先在systemEnvironment的propertySource后面增加random的propertySource,然后在通过Loader去加载。具体的加载逻辑在Loader里面。
3.1.2 加载配置文件 Loader
构造器
Loader(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, ResourceLoader resourceLoader) {
this.environment = environment;
this.placeholdersResolver = new PropertySourcesPlaceholdersResolver(this.environment);
this.resourceLoader = (resourceLoader != null) ? resourceLoader : new DefaultResourceLoader();
this.propertySourceLoaders = SpringFactoriesLoader.loadFactories(PropertySourceLoader.class,
getClass().getClassLoader());
}
- 保存了当前的环境
- 创建了占位符解析器placeholdersResolver ,${属性:默认属性值}
- 从spring.factories文件中获取了所有的属性资源加载器PropertySourceLoader。

其中PropertiesPropertySourceLoader负责加载properties和xml文件,YamlPropertySourceLoader负责加载yml和yaml文件

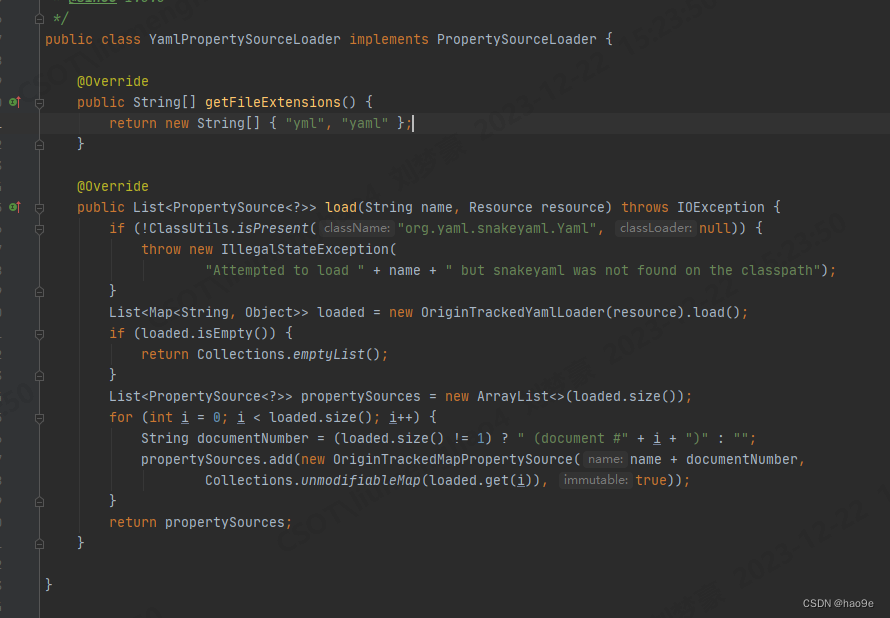
配置文件加载原理请参考:SpringBoot 扩展篇:ConfigFileApplicationListener源码解析
3.2 SpringApplication#createApplicationContext
该方法创建了ApplicationContext
3.2.1 SpringApplication#createApplicationContext
protected ConfigurableApplicationContext createApplicationContext() {
Class<?> contextClass = this.applicationContextClass;
if (contextClass == null) {
try {
switch (this.webApplicationType) {
case SERVLET:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_SERVLET_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
case REACTIVE:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_REACTIVE_WEB_CONTEXT_CLASS);
break;
default:
contextClass = Class.forName(DEFAULT_CONTEXT_CLASS);
}
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Unable create a default ApplicationContext, please specify an ApplicationContextClass", ex);
}
}
return (ConfigurableApplicationContext) BeanUtils.instantiateClass(contextClass);
}
根据不同的webApplicationType创建不同的ApplicationContext,这里创建的是AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
3.2.2 AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext构造器
public AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext() {
this.reader = new AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader(this);
this.scanner = new ClassPathBeanDefinitionScanner(this);
}
从名字上来看AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext是支持注解式的appicationContext。reader负责的是对BeanDefinition的注解进行解析,而scanner进行扫描(看哪些class需要生成BeanDifinition)。
3.2.3 org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigUtils#registerAnnotationConfigProcessors
public static Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> registerAnnotationConfigProcessors(
BeanDefinitionRegistry registry, @Nullable Object source) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory beanFactory = unwrapDefaultListableBeanFactory(registry);
if (beanFactory != null) {
if (!(beanFactory.getDependencyComparator() instanceof AnnotationAwareOrderComparator)) {
beanFactory.setDependencyComparator(AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.INSTANCE);
}
if (!(beanFactory.getAutowireCandidateResolver() instanceof ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver)) {
beanFactory.setAutowireCandidateResolver(new ContextAnnotationAutowireCandidateResolver());
}
}
Set<BeanDefinitionHolder> beanDefs = new LinkedHashSet<>(8);
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(ConfigurationClassPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, CONFIGURATION_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, AUTOWIRED_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JSR-250 support, and if present add the CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jsr250Present && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, COMMON_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
// Check for JPA support, and if present add the PersistenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.
if (jpaPresent && !registry.containsBeanDefinition(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition();
try {
def.setBeanClass(ClassUtils.forName(PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME,
AnnotationConfigUtils.class.getClassLoader()));
}
catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Cannot load optional framework class: " + PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_CLASS_NAME, ex);
}
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, PERSISTENCE_ANNOTATION_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(EventListenerMethodProcessor.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_PROCESSOR_BEAN_NAME));
}
if (!registry.containsBeanDefinition(EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME)) {
RootBeanDefinition def = new RootBeanDefinition(DefaultEventListenerFactory.class);
def.setSource(source);
beanDefs.add(registerPostProcessor(registry, def, EVENT_LISTENER_FACTORY_BEAN_NAME));
}
return beanDefs;
}
- 在创建AnnotatedBeanDefinitionReader的同时,Spring还注册了一些及其重要的后置处理器,这些postProcessor及其重要,后面会一一解析其源码。
- ConfigurationClassPostProcessor:负责注解的解析,生成BeanDefinition,比如@Component、@ConponentScan、@Configuration、@Import等注解。
- AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:解析@Autowired、@Value、@Inject(JSR)注解,初始化字段或调用方法。
- CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor:解析@Resource注解。
- EventListenerMethodProcessor、DefaultEventListenerFactory:对注解式事件监听器的支持EventListener。
3.3 SpringApplication#prepareContext
private void prepareContext(ConfigurableApplicationContext context, ConfigurableEnvironment environment,
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners, ApplicationArguments applicationArguments, Banner printedBanner) {
context.setEnvironment(environment);
postProcessApplicationContext(context);
applyInitializers(context);
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
logStartupInfo(context.getParent() == null);
logStartupProfileInfo(context);
}
// Add boot specific singleton beans
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// Load the sources
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources();
Assert.notEmpty(sources, "Sources must not be empty");
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
listeners.contextLoaded(context);
}
- 对已经创建好的applicationContext进行准备和初始化。
- applyInitializers方法:负责对applicationContext初始化。在SpringApplication对象创建的时候,从spring.factories文件中配置的多个ApplicationContextInitializer,调用了initialize方法。可以addApplicationListener、registerSingleton、addBeanFactoryPostProcessor,甚至可以从环境变量context.initializer.classes中读取自定义的ApplicationContextInitializer进行回调(DelegatingApplicationContextInitializer)。
- 之前对SpringApplication对象绑定的spring.main.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding,对beanfactory设置了allowBeanDefinitionOverriding初始化。
- 创建了BeanDefinitionLoader,并且加载当前的source(MyApplication),注册BeanDenition。
- listeners.contextLoaded(context)方法不仅仅触发了监听器。还将当前的监听器add到ApplicationContext中,以便后续ApplicationContext容器刷新使用这些监听器。
public void contextLoaded(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
for (ApplicationListener<?> listener : this.application.getListeners()) {
if (listener instanceof ApplicationContextAware) {
((ApplicationContextAware) listener).setApplicationContext(context);
}
context.addApplicationListener(listener);
}
this.initialMulticaster.multicastEvent(new ApplicationPreparedEvent(this.application, this.args, context));
}
3.4 SpringApplication#refreshContext
负责对Spring容器的刷新,注册和实例化bean的核心逻辑
3.5 callRunners
private void callRunners(ApplicationContext context, ApplicationArguments args) {
List<Object> runners = new ArrayList<>();
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(ApplicationRunner.class).values());
runners.addAll(context.getBeansOfType(CommandLineRunner.class).values());
AnnotationAwareOrderComparator.sort(runners);
for (Object runner : new LinkedHashSet<>(runners)) {
if (runner instanceof ApplicationRunner) {
callRunner((ApplicationRunner) runner, args);
}
if (runner instanceof CommandLineRunner) {
callRunner((CommandLineRunner) runner, args);
}
}
}
回调ApplicationRunner和CommandLineRunner的run方法,参数为启动参数args,可通过Order控制回调顺序。Run方法的回调是在主线程完成的。




 本文详细分析了SpringBoot应用的启动过程,重点讲解了@SpringBootApplication注解的构成和作用,以及SpringApplication#run方法中的关键步骤,包括环境准备、配置文件加载、ApplicationContext创建等。
本文详细分析了SpringBoot应用的启动过程,重点讲解了@SpringBootApplication注解的构成和作用,以及SpringApplication#run方法中的关键步骤,包括环境准备、配置文件加载、ApplicationContext创建等。
















 2万+
2万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








