博文部分参考链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/lidabo/p/8317196.html
Boost.Asio是一个跨平台的网络及底层IO的C++编程库。
头文件
#include <boost/asio.hpp>命名空间
using namespace boost::asio;
using boost::asio::ip::tcp;
ASIO库能够使用TCP、UDP、ICMP、串口来发送/接收数据,本文档介绍TCP协议的同步读写操作。
所有使用asio的程序都至少需要一个io_service 对象
boost::asio::io_service io_service;
服务端代码为:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
using namespace boost::asio;
int main()
{
typedef ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor_type;
typedef ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_type;
typedef ip::tcp::socket socket_type;
std::cout << "server.start." << std::endl;
io_service io; // asio程序必需的io_service对象
acceptor_type acceptor(io, endpoint_type(ip::tcp::v4(), 8016));
std::cout << "local address is: " <<
acceptor.local_endpoint().address() << std::endl;
try
{
while (true)
{
socket_type sock(io);
acceptor.accept(sock); // 阻塞等待socket连接
std::cout << "client:";
std::cout << sock.remote_endpoint().address() << std::endl;
// 业务处理
while (true)
{
char buf[128] = { 0 };
boost::system::error_code ec;
sock.read_some(buffer(buf), ec);
std::cout << "buf is: " << buf << std::endl;
memset(buf, 0, sizeof(buf)); // 将buf重置
sock.write_some(buffer("hello client"), ec);
if (ec)
{
std::cout << "system error is: " <<
boost::system::system_error(ec).what() << std::endl;
break;
}
}
}
}
catch (const std::exception& ex)
{
std::cout << ex.what() << std::endl;
}
return 0;
}客户端代码为:
#include <iostream>
#include <boost/asio.hpp>
#include <vector>
using namespace boost::asio;
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
typedef ip::tcp::acceptor acceptor_type;
typedef ip::tcp::endpoint endpoint_type;
typedef ip::tcp::socket socket_type;
typedef ip::address address_type;
io_service io;
while (true)
{
try
{
std::cout << "client start." << std::endl;
socket_type sock(io); // socket对象
// 连接端点,这里使用了本机连接,可以修改IP地址测试远程连接
endpoint_type ep(address_type::from_string("127.0.0.1"), 8016);
boost::system::error_code ec;
sock.connect(ep, ec); // 连接服务器
std::cout << sock.available() << std::endl;
// 如果出错,打印出错信息
if (ec)
{
std::cout << boost::system::system_error(ec).what() << std::endl;
return -1;
}
while (true)
{
// 收到数据
char buf[128] = { 0 };
std::cout << "please input: ";
std::cin.getline(buf, 128);
std::cout << std::endl;
sock.write_some(buffer(buf), ec);
memset(buf, 0, 128); // 将buf重置
sock.read_some(buffer(buf), ec);
std::cout << "receive message is :" << buf << std::endl;
}
}
catch (const std::exception& ex)
{
std::cout << ex.what() << std::endl;
}
}
return 0;
}演示如下:

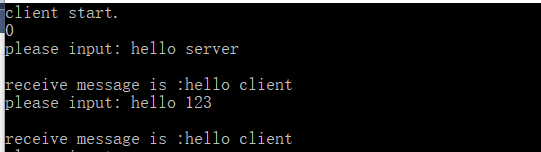
代码说明:
- ASIO的TCP协议通过boost::asio::ip名 空间下的tcp类进行通信。
- IP地址(address,address_v4,address_v6)、 端口号和协议版本组成一个端点(tcp:: endpoint)。用于在服务器端生成tcp::acceptor对 象,并在指定端口上等待连接;或者在客户端连接到指定地址的服务器上。
- socket是 服务器与客户端通信的桥梁,连接成功后所有的读写都是通过socket对 象实现的,当socket析 构后,连接自动断 开。
- ASIO读写所用的缓冲区用buffer函 数生成,这个函数生成的是一个ASIO内部使用的缓冲区类,它能把数组、指针(同时指定大 小)、std::vector、std::string、boost::array包装成缓冲区类。
- ASIO中的函数、类方法都接受一个boost::system::error_code类 型的数据,用于提供出错码。它可以转换成bool测试是否出错,并通过boost::system::system_error类 获得详细的出错信息。另外,也可以不向ASIO的函数或方法提供 boost::system::error_code,这时如果出错的话就会直 接抛出异常,异常类型就是boost::system:: system_error(它是从std::runtime_error继承的)。








 本文介绍如何使用Boost.Asio库实现TCP协议的同步读写操作,包括服务端和客户端的代码示例。通过创建io_service对象管理IO操作,使用socket对象进行通信。
本文介绍如何使用Boost.Asio库实现TCP协议的同步读写操作,包括服务端和客户端的代码示例。通过创建io_service对象管理IO操作,使用socket对象进行通信。

















 1391
1391

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








