List 接口
一、List 接口
1. 基本介绍
-
(1) List 集合类中元素有序(即添加顺序和取出顺序一致)、且可重复
-
(2) List 集合中的每个元素都有其对应的顺序索引,即支持索引
-
(3) List 容器中的元素都对应一个整数型的序号记载其在容器中的位置,可以根据序号存取容器中的元素
2. 常用方法
List接口是Collection接口的子接口,即也实现了Collection接口的方法
以下是List独有的方法
| 方法签名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
get(int index) | 返回列表中指定索引位置的元素。索引从 0 开始,超出范围会抛出 IndexOutOfBoundsException |
set(int index, E element) | 用指定元素替换列表中指定位置的元素,并返回被替换的原元素 |
remove(int index) | 移除并返回列表中指定索引位置的元素。后续元素的索引会自动递减 |
void add(int index, E element) | 在列表的指定索引位置插入指定元素。后续元素的索引会自动递增 |
boolean addAll(int index, Collection<? extends E> c) | 从指定位置开始,将指定集合中的所有元素插入到列表中 |
int indexOf(Object o) | 返回指定元素在列表中第一次出现的索引,不存在则返回 -1 |
int lastIndexOf(Object o) | 返回指定元素在列表中最后一次出现的索引,不存在则返回 -1 |
List<E> subList(int fromIndex, int toIndex) | 返回列表中指定范围的子列表(fromIndex,toIndex)左闭右开 |
3. 代码示例
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class practise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list.add("jack");
list.add("computer");
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
list1.add("list2 - 1");
list1.add("list2 - 2");
System.out.println("list[0] = " + list.get(0));
System.out.println("subList(0,1):" + list.subList(0,1));
list.add(list.size() - 1,"list");
System.out.println("add(list.size() - 1,\"list\"):" + list);
list.remove(list.size() - 1);
System.out.println("remove(list.size() - 1):" + list);
list.add("jack");
list.set(list.size() - 1,"jack");
list.addAll(0,list1);
System.out.println("addAll(list1):" + list);
System.out.println("indexOf(\"jack\") :" + list.indexOf("jack"));
System.out.println("lastIndexOf(\"jack\") :" + list.lastIndexOf("jack"));
}
}
// 输出结果
list[0] = jack
subList(0,1):[jack]
add(list.size() - 1,"list"):[jack, computer, hello, list, java]
remove(list.size() - 1):[jack, computer, hello, list]
addAll(list1):[list2 - 1, list2 - 2, jack, computer, hello, list, jack]
indexOf("jack") :2
lastIndexOf("jack") :6
4. List接口遍历对象的方法
方法一:Iterator (迭代器)
返回一个 List 对象的迭代器,方法和 Collection 中的相同
方法二:增强 for循环
返回一个 List 对象的迭代器,方法和 Collection 中的相同
方法三:普通 for 循环
使用get 方法取值
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class practise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
List list1 = new ArrayList();
list.add("jack");
list.add("computer");
list.add("hello");
list.add("java");
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
System.out.println(list.get(i));
}
}
}
5. 练习:创建 book 对象(名称,价格),添加到 List 结合中,按照价格从低到高输出
关键点
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.List;
@SuppressWarnings("all")
public class practise {
public static void main(String[] args) {
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add(new book("西游记", 18));
list.add(new book("水浒传", 20));
list.add(new book("红楼梦", 30));
for (int i = 0; i < list.size() - 1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < list.size() - 1 - i; j++) {
// 向下转型
book book1 = (book) (list.get(i));
book book2 = (book) (list.get(i));
if (book1.price > book2.price) {
// 用 set() 方法交换位置
list.set(j + 1, book1);
list.set(j, book2);
}
}
}
// 使用迭代器遍历
Iterator iterator = list.iterator();
while(iterator.hasNext()){
Object obj = iterator.next();
System.out.println(obj);
}
}
}
class book {
String name;
double price;
public book(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public double getPrice() {
return price;
}
public void setPrice(double price) {
this.price = price;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "book{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", price=" + price +
'}';
}
}
// 输出结果
book{name='西游记', price=18.0}
book{name='水浒传', price=20.0}
book{name='红楼梦', price=30.0}
二、实现 List 接口的子类
说明:这三个是实现接口的类,自然会实现接口的方法,Collection和List接口的方法都可以使用
1. Arraylist
1. 基本介绍
(1) permits all elements, including null,ArrayList可以加入 null,并且多个
(2) ArrayList 是由数组来实现数据存储的
(3) ArrayList 基本等同于 Vector,除了 ArrayList 是线程不安全,但是执行效率高。在多线程情况下,不建议使用 ArrayList
2. 重点理解: ArrayList的底层操作机制源码分析
结论如下
-
(1) ArrayList 中维护了一个 Object 类型的数组 elementData(
transient Object[] elementData) -
(2)当创建 ArrayList 对象时,如果使用的是无参构造器,则初始 elementData 容量为 0,第 1 次添加,则扩容 elementData 为 10,如需要再次扩容,则扩容 elementData 为 1.5 倍。
-
(3)如果使用的是指定大小的构造器,则初始 elementData 容量为指定大小,如果需要再次扩容,则直接扩容 elementData 为 1.5 倍。
源码剖析
(预备工作)IDEA 设置:在调试时显示隐藏的数据
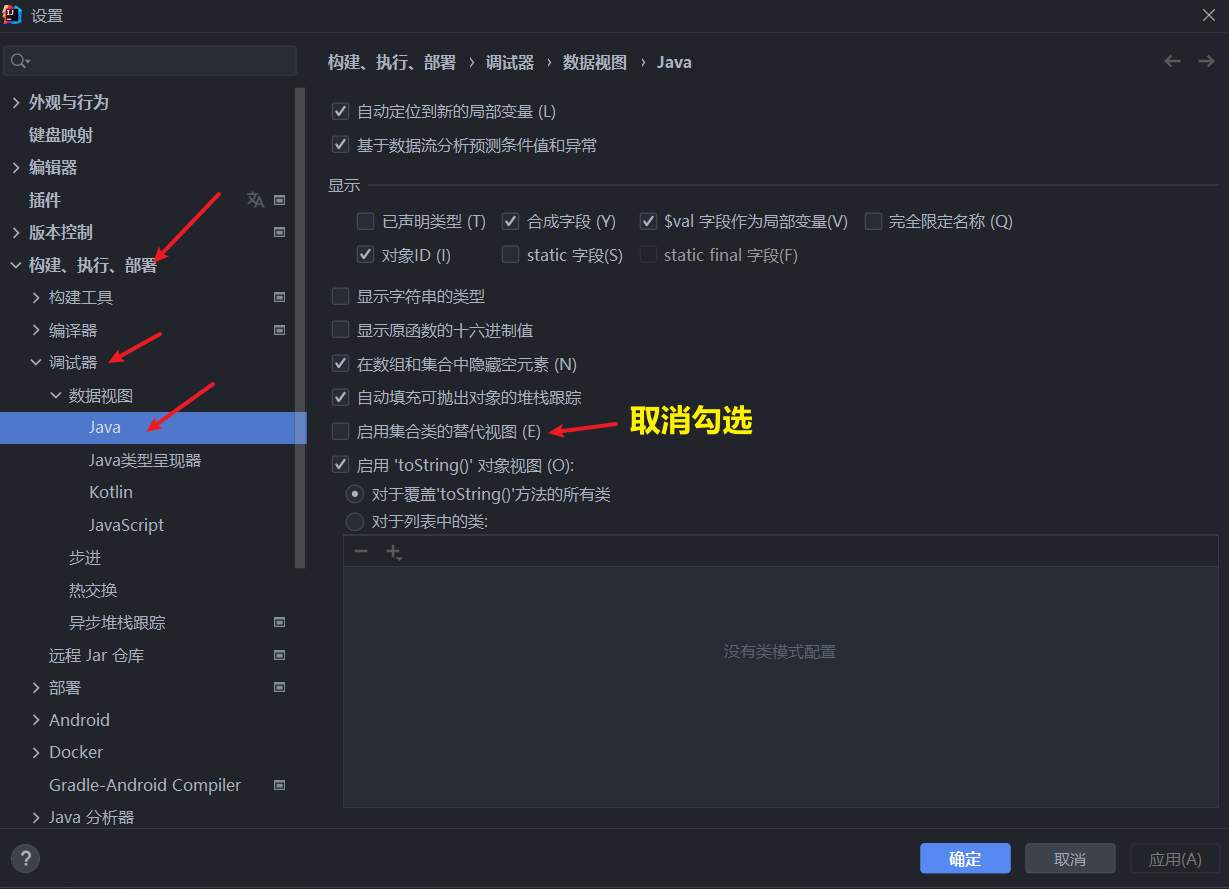
调试代码示例
public static void main(String[] args) {
ArrayList list = new ArrayList();
// 默认初始化10个大小的容量
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
// 查看扩容的原理
for (int i = 10; i < 13; i++) {
list.add(i);
}
}
1. 调用无参构造器,创建了一个数组(transient Object[] elementData)
public ArrayList() {
this.elementData = DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA;
}
补充:在add之前会进行valueOf()方法的执行进行装箱,这部分略过不看
2. 执行add()方法
public boolean add(E e) {
ensureCapacityInternal(size + 1); // Increments modCount!!
elementData[size++] = e;
return true;
}
3. 进入ensureCapacityInternal()方法
private void ensureCapacityInternal(int minCapacity) {
if (elementData == DEFAULTCAPACITY_EMPTY_ELEMENTDATA) {
minCapacity = Math.max(DEFAULT_CAPACITY, minCapacity);
}
ensureExplicitCapacity(minCapacity);
}
4. 进入ensureExplicitCapacity()方法
private void ensureExplicitCapacity(int minCapacity) {
modCount++;
// overflow-conscious code
if (minCapacity - elementData.length > 0)
grow(minCapacity);
}
5. 进入grow()方法
-
向右位移(
>>)一个大小:就是除以二的意识,即如果数组需求的空间比默认值大,就在原基础上扩容为 1.5 倍 -
使用
Arrays.copyOf()方法先完成原内容的复制,扩容部分的位置值是null,之后返回add()方法,添加新内容到elementData[]数组中,完成内容的添加
private void grow(int minCapacity) {
// overflow-conscious code
int oldCapacity = elementData.length;
int newCapacity = oldCapacity + (oldCapacity >> 1);
if (newCapacity - minCapacity < 0)
newCapacity = minCapacity;
if (newCapacity - MAX_ARRAY_SIZE > 0)
newCapacity = hugeCapacity(minCapacity);
// minCapacity is usually close to size, so this is a win:
elementData = Arrays.copyOf(elementData, newCapacity);
}
2. Vector
Vector等价于ArrayList,区别在于底层扩容机制的不同
基本介绍
1. 结构:public class Vector<E> extends AbstractList<E> implements List<E>, RandomAccess, Cloneable, java.io.Serializable
2. Vecotr 底层也是一个对象数组:protected Object[] elementData
3. Vector是线程同步的,即线程安全(该类方法中都带有关键字synchronized)
举例
public synchronized int indexOf(Object o, int index) {
if (o == null) {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (elementData[i]==null)
return i;
} else {
for (int i = index ; i < elementCount ; i++)
if (o.equals(elementData[i]))
return i;
}
return -1;
}
4. 关于底层扩容机制
唯一和ArrayList不同的点在:如需要再次扩容,则扩容 elementData 为 2 倍。
5. ArrayList 和 Vector 的区别
| 底层结构 | 版本 | 线程安全(同步) | 效率 | 扩容机制 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | jdk1.2 | 不安全, 效率高 | 如果有参数构造 1.5 倍, 如果是无参 1. 第一次 x 10 2. 从第二次开始 x 1.5 倍 |
| Vector | 可变数组 Object[] | jdk1.0 | 安全, 效率不高 | 1. 如果是无参, 默认为 10, 满后, 就按 2 倍扩容 2. 如果指定大小, 则每次直接按 2 倍扩容 |
3. LinkedList
1. 基本介绍
(1)底层实现了双向链表和双端队列特点
(2)可以添加任意元素(元素可以重复),包括null
(3)线程不安全,没有实现同步
2. 底层结构示意图

3. 属性说明
4. 模拟双向链表的操作
public class pra {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/*
模拟插入节点:jack,java,tom
1. 首先生成节点
2. 把节点连接起来
*/
node jack = new node("jack");
node java = new node("java");
node tom = new node("tom");
// 连接 jack 和 java
jack.next = java;
java.pre = jack;
// 连接 java 和 tom
java.next = tom;
tom.pre = java;
tom.next = null;
// 设置头尾指针
node head = jack;
node tail = tom;
System.out.print("从头到尾遍历:");
// 遍历链表(从头到尾巴)
while (true){
if(head == null){
break;
}else{
System.out.print(head.item + " ---> ");
head = head.next;
}
}
System.out.println();
System.out.print("从尾到头遍历:");
// 遍历链表(从尾到头)
while (true){
if(tail == null){
break;
}else{
System.out.print(tail.item + " ---> ");
tail = tail.pre;
}
}
}
}
class node {
Object item; // 节点元素值
node pre; // 前驱结点指针
node next; // 后继节点指针
public node(Object item) {
this.item = item;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "node{" +
"item=" + item +
'}';
}
}
// 输出结果
从头到尾遍历:jack ---> java ---> tom --->
从尾到头遍历:tom ---> java ---> jack --->
5. LinkedList 方法
| 方法 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| 增 | |
add(E e) | 向链表末尾添加元素。 |
add(int index, E element) | 在指定索引处插入元素。 |
addFirst(E e) | 在链表的开头添加元素。 |
addLast(E e) | 在链表的末尾添加元素。 |
| 删 | |
remove(int index) | 删除指定索引位置的元素。 |
remove(Object o) | 删除首次出现的指定元素。 |
removeFirst() | 删除链表的第一个元素。 |
removeLast() | 删除链表的最后一个元素。 |
| 改 | |
set(int index, E element) | 替换指定索引位置的元素,并返回被替换的元素。 |
| 查 | |
get(int index) | 获取指定索引位置的元素。 |
getFirst() | 获取链表的第一个元素。 |
getLast() | 获取链表的最后一个元素。 |
| 其他方法 | |
clear() | 清空链表中的所有元素。 |
contains(Object o) | 判断链表中是否包含指定元素。 |
size() | 获取链表中的元素数量。 |
isEmpty() | 判断链表是否为空。 |
6. ArrayList 和 LinkedList 的比较
| 底层结构 | 增删的效率 | 查找的效率 |
|---|---|---|
| ArrayList | 可变数组 | 较低 |
| LinkedList | 双向链表 | 较高,通过链表添加 |






















 828
828

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










