说明
为了向大神看齐,遂响应号召,每天刷一下POJ上面的水题,每天学习一点ACM,做一点ACM题目。
我相信积少成多,更相信,开头是艰难的,但是一旦走进去,就会别有一番感受,速度也会加快吧。
so ,today is the first day .
题目
第一题
POJ 1003 (传送门:http://poj.org/problem?id=1003)
题目描述:
Description
How far can you make a stack of cards overhang a table? If you have one card, you can create a maximum overhang of half a card length. (We're assuming that the cards must be perpendicular to the table.) With two cards you can make the top card overhang the bottom one by half a card length, and the bottom one overhang the table by a third of a card length, for a total maximum overhang of 1/2+1/3=5/6 card lengths. In general you can makencards overhang by 1/2+1/3+1/4+...+1/(n+1) card lengths, where the top card overhangs the second by 1/2, the second overhangs tha third by 1/3, the third overhangs the fourth by 1/4, etc., and the bottom card overhangs the table by 1/(n+1). This is illustrated in the figure below.
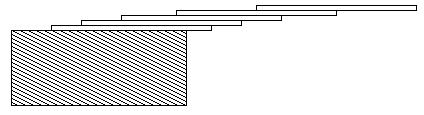
Input
Output
第二题
找所有的(n, k), 满足:1+2+..+(n-1)=(n+1)+(n+2)…+k 。输出按k排序的前6个。
解答过程
第一题:简答的数学题
/***** 简单ACM水题 ********/
/******** written by C_Shit_Hu ************/
////////////////POJ 1003///////////////
/****************************************************************************/
/*
求平均数。
*/
/****************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int i;
float len,s;
while(cin >> len && len != 0.00)
{
s = 0.0;
for(i = 2; ; i++)
{
s+=1.0/i;
if(s >= len)
break;
}
cout << i-1 <<" card(s)" << endl;
}
return 0;
}运行结果:

第二题:数论相关的题目
----要么k是完全平方数
----要么k/2是完全平方数
分别设k=m2和2m2, 枚举m
/***** 简单ACM水题 ********/
/******** written by C_Shit_Hu ************/
///////////////////////////////
/****************************************************************************/
/*
找所有的(n, k), 满足:
1+2+..+(n-1)=(n+1)+(n+2)…+k
输出按k排序的前10个
*/
/****************************************************************************/
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
using namespace std;
bool sing(int j)
{
long int k, n;
double m;
k = j * j;
n = k*(k+1) / 2;
m = sqrt(n);
if ( floor(m + 0.5) == m)
{
// printf("n = %d, k = %d\n", m, k);
cout << m << " " << k << endl;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
bool doub(int j)
{
long int k, n;
double m;
k = 2 * j * j;
n = k*(k+1) / 2;
m = sqrt(n);
if ( floor(m + 0.5) == m)
{
cout << m << " " << k << endl;
return true;
}
else
return false;
}
int main( )
{
// freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
// freopen("out.txt","w",stdout);
int i, j;
for (i=1,j=1; i< 7 ; j++)
{
if(sing(j))
i ++ ;
if(doub(j))
i ++ ;
}
return 0;
}
/******************************************************/
/******************** 心得体会 **********************/
/*
*/
/******************************************************/运行结果:





 本文解析了两道ACM编程挑战题目,第一题通过累积求和算法解决卡片悬空长度问题;第二题利用数论原理找出特定的(n,k)组合,满足一定条件的等式,并给出完整的代码实现。
本文解析了两道ACM编程挑战题目,第一题通过累积求和算法解决卡片悬空长度问题;第二题利用数论原理找出特定的(n,k)组合,满足一定条件的等式,并给出完整的代码实现。
















 4817
4817

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








