Join Vs select 结果集作列
有时候我们需要关联很多表统计:
select f1, f2, count(*) from a join b join c join d join e ……
如果结果集很小,只统计出几条数据来,那么可以换成这样写
Select f1, f2, (select count(*) from a join b ) from c……
比如下面的例子:
2 t2.subject_name subjectName,
3 t3.dict_name assignType,
4 t1.assign_date assignDate,
5 t4.totalcount totalCount,
6 (select dict_name from bas_diction where dict_id = t5.assign_marks) as assignMarks,
7 (case t5.if_submit when 1 then '是' else '否' end) as ifSubmit,
8 t6.errorcount errorCount,
9 t6.nocheckCount,
10 case t1.online_assignment when 1 then '是' else '否' end as ifOnline,
11 (select dict_name from bas_diction where dict_id = t5.write_appraise) as writeAppraise
12 from hom_assignmentinfo t1,bas_subject t2,bas_diction t3,
13 (select t1.assignment_id,count(*) as totalcount from hom_assignmentinfo t1,hom_assignment t2
14 where t1.assignment_id = t2.hom_assignment_id
15 group by t1.assignment_id) t4,hom_assignment_appraise t5 left join
16 (select t1.assignment_id,t3.appraise_id,
17 sum(case t3.check_result when 3003001 then 0 else 1 end) as errorcount,
18 sum(case when t3.check_result=3003001 or t3.recheck_result=3003001 then 0 else 1 end)as nocheckCount
19 from hom_assignmentinfo t1,hom_check_assignment t3
20 where t1.assignment_id = t3.assignment_id
21 and t1.person_id='13042'
22 group by t1.assignment_id,t3.appraise_id) t6 on (t5.appraise_id= t6.appraise_id)
23 where t1.subject_id = t2.subject_id
24 and t1.assign_type = t3.dict_id
25 and t1.assignment_id = t4.assignment_id
26 and t1.assignment_id = t5.assignment_id
27 and not exists (select 1 from hom_assignmentinfo t11,hom_assignment_appraise t12
28 where t11.assignment_id=t12.assignment_id and
29 t11.online_assignment = 0 and
30 t12.person_id='13042' and
31 t11.subject_id = t1.subject_id and t11.assign_date > t1.assign_date)
32 and t1.assign_date is not null
33 and t5.person_id='13042'
34 order by t1.assign_date desc;
35
改写成下面的,速度由0.625秒优化到: 0.032
2 t2.subject_name subjectName,
3 t3.dict_name assignType,
4 t1.assign_date assignDate,
5 (select count(*) as totalcount from hom_assignmentinfo where assignment_id= t1.assignment_id) totalcnt,
6 (
7 select sum(case t3.check_result when 3003001 then 0 else 1 end )
8 from hom_check_assignment t3
9 where t1.assignment_id = t3.assignment_id
10 ) errorcount,
11 (
12 select sum(case when t3.check_result=3003001 or t3.recheck_result=3003001 then 0 else 1 end)as nocheckCount
13 from hom_check_assignment t3
14 where t1.assignment_id = t3.assignment_id
15 ) nocheckCount,
16 (select dict_name from bas_diction where dict_id = t5.assign_marks) as assignMarks,
17 (case t5.if_submit when 1 then '是' else '否' end) as ifSubmit,
18 case t1.online_assignment when 1 then '是' else '否' end as ifOnline,
19 (select dict_name from bas_diction where dict_id = t5.write_appraise) as writeAppraise
20 from hom_assignmentinfo t1,bas_subject t2,bas_diction t3, hom_assignment_appraise t5
21 where t1.subject_id = t2.subject_id
22 and t1.assign_type = t3.dict_id
23 and t1.assignment_id = t5.assignment_id
24 and not exists (select 1 from hom_assignmentinfo t11,hom_assignment_appraise t12
25 where t11.assignment_id=t12.assignment_id and
26 t11.online_assignment = 0 and
27 t12.person_id='13042' and
28 t11.subject_id = t1.subject_id and t11.assign_date > t1.assign_date)
29 and t1.assign_date is not null
30 and t5.person_id='13042'
31 order by t1.assign_date desc;
如果什么都做不了,试试全索引扫描
如果一个语句实在不能优化了,那么还有一个方法可以试试:索引覆盖。
如果一个语句可以从索引上获取全部数据,就不需要通过索引再去读表,省了很多I/O。比如这样一个表
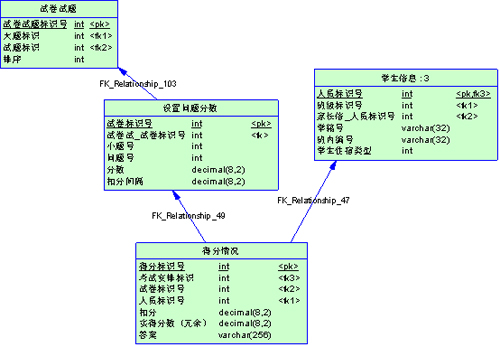
如果我要统计每个学生每道题的得分情况,我们除了要给每个表的主键外键建立索引,还要对【得分情况】的实际得分字段索引,这样,整个查询就可以从索引得到数据了。
Join、In、not in、exist、not exist并不是绝对的
网上很多教程讨论了join、in和exist 的性能差异,其实这不是绝对的,对于效率不理想的语句,还是应该换换写法试试看。
Like
Like毕竟效率太低,必要的话可以试试全文检索。对于中文全文检索,可以结合程序分词来实现。
什么情况下查询用不到索引
参见手册 7.4.3列索引, 7.4.4所列索引, 7.4.5 mysql如何使用索引
去掉不必要的排序,如果必要,尽量用主键排序代替
显而易见却容易被忽视的问题。
数据库参数配置
最重要的参数就是内存,我们主要用的innodb引擎,所以下面两个参数调的很大
# Additional memory pool that is used by InnoDB to store metadata
# information. If InnoDB requires more memory for this purpose it will
# start to allocate it from the OS. As this is fast enough on most
# recent operating systems, you normally do not need to change this
# value. SHOW INNODB STATUS will display the current amount used.
innodb_additional_mem_pool_size = 64M
# InnoDB, unlike MyISAM, uses a buffer pool to cache both indexes and
# row data. The bigger you set this the less disk I/O is needed to
# access data in tables. On a dedicated database server you may set this
# parameter up to 80% of the machine physical memory size. Do not set it
# too large, though, because competition of the physical memory may
# cause paging in the operating system. Note that on 32bit systems you
# might be limited to 2-3.5G of user level memory per process, so do not
# set it too high.
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 5G
对于myisam,需要调整key_buffer_size
当然调整参数还是要看状态,用show status语句可以看到当前状态,以决定改调整哪些参数
Cretated_tmp_disk_tables 增加tmp_table_size
Handler_read_key 高表示索引正确 Handler_read_rnd高表示索引不正确
Key_reads/Key_read_requests 应小于0.01 计算缓存损失率,增加Key_buffer_size
Opentables/Open_tables 增加table_cache
select_full_join 没有实用索引的链接的数量。如果不为0,应该检查索引。
select_range_check 如果不为0,该检查表索引。
sort_merge_passes 排序算法已经执行的合并的数量。如果该值较大,应增加sort_buffer_size
table_locks_waited 不能立即获得的表的锁的次数,如果该值较高,应优化查询
Threads_created 创建用来处理连接的线程数。如果Threads_created较大,要增加 thread_cache_size值。
缓存访问率的计算方法Threads_created/Connections。
合理的硬件资源和操作系统
如果你的机器内存超过4G,那么毋庸置疑应当采用64位操作系统和64位mysql
读写分离
如果数据库压力很大,一台机器支撑不了,那么可以用mysql复制实现多台机器同步,将数据库的压力分散。
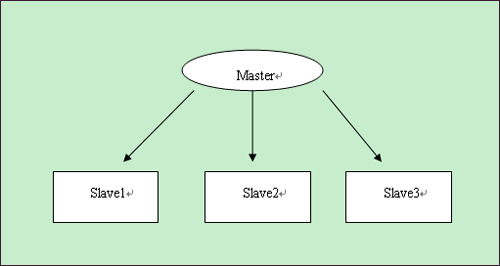
Master
Slave1
Slave2
Slave3
主库master用来写入,slave1—slave3都用来做select,每个数据库分担的压力小了很多。
要实现这种方式,需要程序特别设计,写都操作master,读都操作slave,给程序开发带来了额外负担。当然目前已经有中间件来实现这个代理,对程序来读写哪些数据库是透明的。官方有个mysql-proxy,但是还是alpha版本的。新浪有个amobe for mysql,也可达到这个目的,结构如下
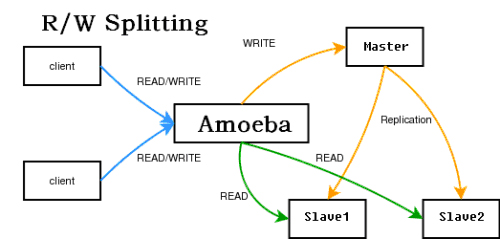
使用方法可以看amobe的手册。






















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








