一、实现一个简单的 ViewGroup
该自定义 ViewGroup 类似 LinearLayout 垂直布局的形式
-
布局
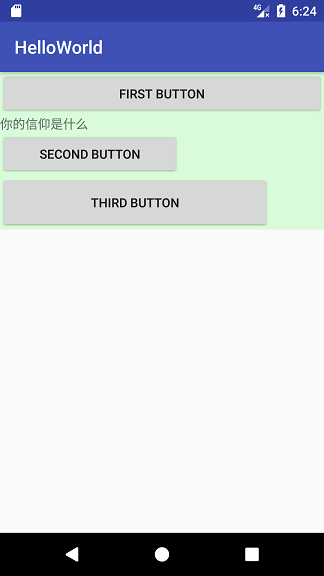
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent"> <cc.catface.helloworld.view.SimpleVG android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#20f0"> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="first button" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="你的信仰是什么" /> <Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:text="second button" /> <Button android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="60dp" android:text="third button" /> </cc.catface.helloworld.view.SimpleVG> </LinearLayout> -
onMeasure方法中遍历测得所有子控件的宽高
@Override protected void onMeasure(int widthMeasureSpec, int heightMeasureSpec) { super.onMeasure(widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); int widthSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(widthMeasureSpec); int widthSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(widthMeasureSpec); int heightSpecMode = MeasureSpec.getMode(heightMeasureSpec); int heightSpecSize = MeasureSpec.getSize(heightMeasureSpec); // 保存实际布局的宽高 int width = 0; int height = 0; // 轮询遍历所有子控件的宽高 for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // 得到子控件的宽高 int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 整个布局的高为所有子控件高值的总和 height += childHeight; // 整个布局的宽为所有子空间中最宽的那个控件的宽值 width = Math.max(width, childWidth); } setMeasuredDimension((widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) ? width : widthSpecSize, (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) ? height : heightSpecSize); }-
简述一下上面代码中的最后一行setMeasuredDimension(…),实际为以下代码的简写
if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST && heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(width, height); } else if (widthSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(width, heightSpecSize); } else if (heightSpecMode == MeasureSpec.AT_MOST) { setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, height); } else { setMeasuredDimension(widthSpecSize, heightSpecSize); }也就是说,宽或高谁是 wrap_content(AT_MOST),那么就将自己测量处理的到的结果交给系统。反之,如果是 match_parent(EXACTLY)或者具体 dp/px值(EXACTLY),那么就将父容器的建议值交给系统,就是 MeasureSpec.getSize方法得到的宽或高值交给系统
-
-
onLayout方法中确定所有子控件的位置
@Override protected void onLayout(boolean changed, int l, int t, int r, int b) { int top = 0; for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 该行即确定各个子控件的left,top,right,button位置坐标点,具体分析如下图 child.layout(0, top, childWidth, top + childHeight); top += childHeight; } }上面代码 **
child.layout(0, top, childWidth, top + childHeight);**的分析图
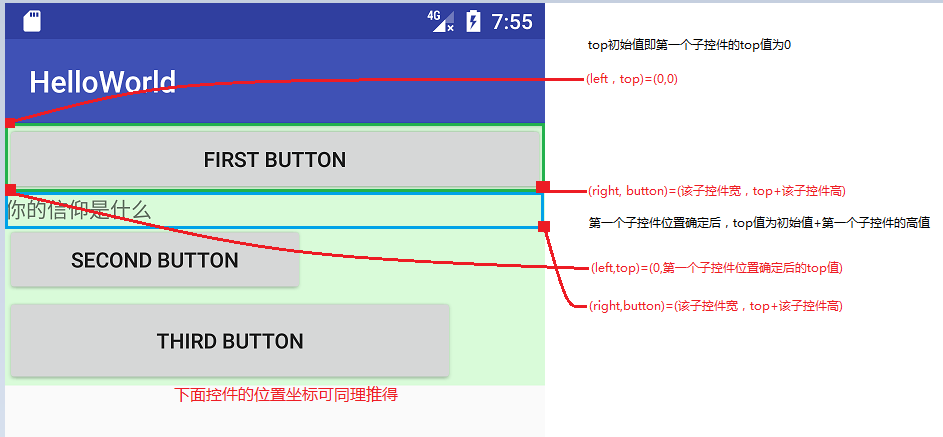
而、为自定义布局中的子控件添加 margin
-
布局
<!-- 为增加展示效果,为各子控件添加了背景色,并添加同样效果的LinearLayout布局作为对比 --> <?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="match_parent" android:orientation="vertical"> <cc.catface.helloworld.view.SimpleVG android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#20f0"> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="30px" android:background="#100f" android:text="first button" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="60px" android:background="#200f" android:text="你的信仰是什么" /> <Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="15px" android:layout_marginLeft="20px" android:layout_marginRight="30px" android:layout_marginTop="90px" android:background="#300f" android:text="second button" /> <Button android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="60dp" android:layout_marginTop="120px" android:background="#400f" android:text="third button" /> </cc.catface.helloworld.view.SimpleVG> <View android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="10px" android:background="#000" /> <LinearLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:background="#20f0" android:orientation="vertical"> <Button android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="30px" android:background="#100f" android:text="first button" /> <TextView android:layout_width="match_parent" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginTop="60px" android:background="#200f" android:text="你的信仰是什么" /> <Button android:layout_width="200dp" android:layout_height="wrap_content" android:layout_marginBottom="15px" android:layout_marginLeft="20px" android:layout_marginRight="30px" android:layout_marginTop="90px" android:background="#300f" android:text="second button" /> <Button android:layout_width="300dp" android:layout_height="60dp" android:layout_marginTop="120px" android:background="#400f" android:text="third button" /> </LinearLayout> </LinearLayout>结果如下,margin作用并没有显示出来
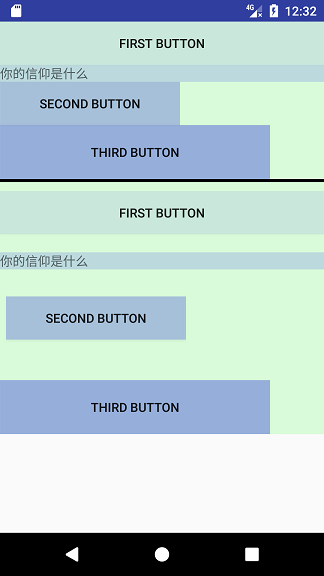
原因很容易得出,因为布局中添加了margin,肯定要在父容器的测量和规划布局中得到 margin值并做对应处理啊。也就是在 onMeasure方法和 onLayout方法中获取 margin值并做对应处理,具体处理情况如下
-
针对 margin 重新 measure 和 layout
具体就是通过 MarginLayoutParams 获取到 margin值,然后做相应处理
-
onMeasure:重点是两条*号中间的处理
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); measureChild(child, widthMeasureSpec, heightMeasureSpec); // ******************************************************************************************// MarginLayoutParams childMarginarginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); // 分别为当前子控件的宽/高 int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 分别为当前布局的中宽/高(添加对应各子控件的margin值) width = Math.max(width, childWidth + childMarginarginLayoutParams.leftMargin + childMarginarginLayoutParams.rightMargin); height += childHeight + childMarginarginLayoutParams.topMargin + childMarginarginLayoutParams.bottomMargin; // ******************************************************************************************************\\ } -
onLayout:重点是两条*号中间的处理
for (int i = 0; i < getChildCount(); i++) { View child = getChildAt(i); // *******************************************************************************************/ MarginLayoutParams childMarginarginLayoutParams = (MarginLayoutParams) child.getLayoutParams(); // 子控件的宽/高 int childWidth = child.getMeasuredWidth(); int childHeight = child.getMeasuredHeight(); // 子控件的各margin值 int leftMargin = childMarginarginLayoutParams.leftMargin; int topMargin = childMarginarginLayoutParams.topMargin; int rightMargin = childMarginarginLayoutParams.rightMargin; int bottomMargin = childMarginarginLayoutParams.bottomMargin; // 先记录各个子控件的topMargin值 top += topMargin; // 左上位置坐标(leftMargin, top)很好理解 // 子控件宽/高分别就是左上坐标加上自己的测量宽高值 child.layout(leftMargin, top, leftMargin + childWidth, top + childHeight); // 当前子控件位置确定后,记录下一个子控件的top点为当前子控件高度+当前子控件的bottomMargin值 // 当记录下一个子控件的top点时,配合上面的 top += topMargin 即可得到结果 top += (childHeight + bottomMargin); // *******************************\\ }
-
-
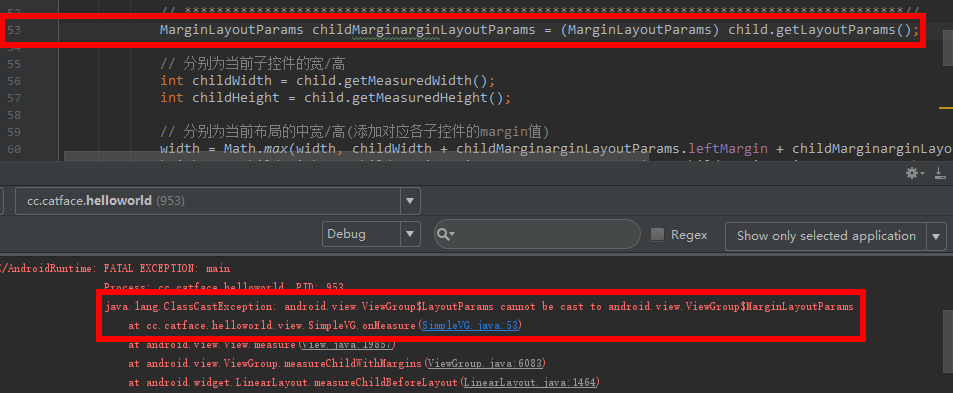
效果
结果报错:类转换异常
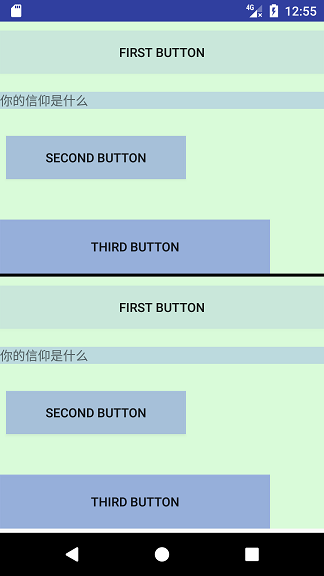
针对 margin 在 onMeasure方法和 onLayout方法中做处理,需要复写如下三个方法
// 为当前自定义ViewGroup获取MarginLayoutParams以对margin做相关处理 @Override protected LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(LayoutParams p) { return new MarginLayoutParams(p); } @Override public LayoutParams generateLayoutParams(AttributeSet attrs) { return new MarginLayoutParams(getContext(), attrs); } @Override protected LayoutParams generateDefaultLayoutParams() { return new MarginLayoutParams(LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT, LayoutParams.MATCH_PARENT); }上述过程处理完成后的最终效果如下







 本文介绍如何创建一个自定义ViewGroup,实现类似于LinearLayout的垂直布局,并处理子视图的margin属性。
本文介绍如何创建一个自定义ViewGroup,实现类似于LinearLayout的垂直布局,并处理子视图的margin属性。

















 1390
1390

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








