一、互斥锁
1. 函数原型
pthread_mutex_init(pthread_mutex_t *restrict mutex, const pthread_mutexattr_t *restrict attr);
pthread_mutex_destroy(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
分析:
- pthread_mutex_t 类型,其本质是一个结构体,为简化理解,应用时可忽略其实现细节,简单当成整数看待。
- pthread_mutex_t mutex:变量mutex只有两种取值0、1;
函数一参数1:传出参数,调用时应传&mutex
- restrict关键字:只用于限制指针,告诉编译器,所有修改该指针指向内存中内容的操作,只能通过本指针完成。不能通过除本指针以外的其他变量或指针修改。
函数一参数2:互斥属性。是一个传入参数,通常传NULL,选用默认属性(线程间共享).
- 静态初始化:如果互斥锁mutex是静态分配的(定义在全局,或加了static关键字修饰),可以直接使用宏进行初始化。pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
- 动态初始化:局部变量应采用动态初始化, pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
2. 函数原型:
pthread_mutex_lock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock(pthread_mutex_t *mutex);
分析:
- 函数1:没有被上锁,当前线程会将这把锁锁上;被锁上了,当前线程阻塞,锁被打开之后,线程解除阻塞(加锁。可理解为将mutex--(或-1))。
- 函数2:同时将阻塞在该锁上的所有线程全部唤醒解锁(可理解为将mtex++(或+1)).
二、代码清单
1. 测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *tfn(void *arg)
{
srand(time(NULL));
while(1)
{
printf("hello ");
sleep(rand() % 3); //模拟长时间操作共享资源,导致cpu易主,产生与时间有关的错误
printf("word\n");
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL);
while(1)
{
printf("HELLO ");
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("WORLD\n");
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return 0;
}
输出结果
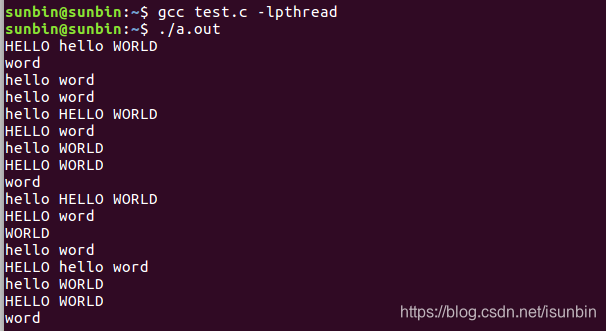
2. 测试代码
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
#include <pthread.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void *tfn(void *arg)
{
srand(time(NULL));
while(1)
{
printf("hello ");
sleep(rand() % 3); //模拟长时间操作共享资源,导致cpu易主,产生与时间有关的错误
printf("word\n");
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL);
while(1)
{
printf("HELLO ");
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("WORLD\n");
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return 0;
}
输出结果
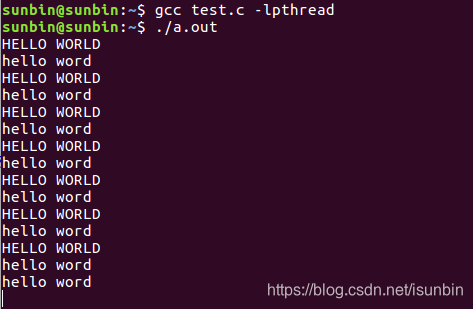
#include<pthread.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
void* tfn(void* arg)
{
srand(time(NULL));
while (1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("hello ");
sleep(rand() % 3); //模拟长时间共享资源,导致cpu易主。产生于时间有关的错误
printf("word\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
return NULL;
}
int main()
{
pthread_t tid;
srand(time(NULL));
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex, NULL);
pthread_create(&tid, NULL, tfn, NULL); //mutex == 1
while (1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("HELLO ");
sleep(rand() % 3);
printf("WORLD\n");
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
sleep(rand() % 3);
}
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
return 0;
}
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<stdio.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex = PTHREAD_MUTEX_INITIALIZER;
pthread_mutex_t *mp;
void add(void)
{
int i = 10;
i = i + 1;
i = i + 2;
i = i + 3;
printf("sum is %d\n", i);
}
void thread1(void)
{
{
pthread_mutex_lock(mp);
add();
pthread_mutex_unlock(mp);
sleep(1);
}
}
void thread2(void)
{
{
pthread_mutex_lock(mp);
add();
pthread_mutex_unlock(mp);
sleep(2);
}
}
int main(void)
{
pthread_t id1, id2;
int ret;
mp = (pthread_mutex_t*)malloc(sizeof(pthread_mutex_t));
pthread_mutex_init(mp, NULL);
ret = pthread_create(&id1, NULL, (void*)thread1, NULL);
if(ret < 0)
{
perror("pthread_create id1");
exit(1);
}
ret = pthread_create(&id2, NULL, (void*)thread2, NULL);
if(ret <0)
{
perror("pthread_create id2");
exit(1);
}
pthread_join(id1, NULL);
pthread_join(id2, NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(mp);
free(mp);
return 0;
}





 博客主要介绍了互斥锁相关内容。分析了pthread_mutex_t类型,包括其变量取值、函数参数含义,还介绍了静态和动态初始化方法。阐述了两个函数原型,一个用于加锁,一个用于解锁。最后给出了测试代码及输出结果。
博客主要介绍了互斥锁相关内容。分析了pthread_mutex_t类型,包括其变量取值、函数参数含义,还介绍了静态和动态初始化方法。阐述了两个函数原型,一个用于加锁,一个用于解锁。最后给出了测试代码及输出结果。
















 1062
1062

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








