一、标准流
标准流又称文档流,是浏览器渲染网页时默认采用的排版规则,即HTML标签的默认显示方式,如div独占一行、span同行排列等。
实际表现:
- 块级元素(如div):从上往下,垂直布局,独占一行
- 行内元素或行内块元素(如span、a):从左往右,水平布局,空间不够自动拆行
行内元素设置宽高无效,块级元素设置有效
二、定位流
属性position分类:
- 相对定位 relative
- 绝对定位 absolute
- 固定定位 fixed
- 静态定位 static
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>定位初识</title>
<link rel="stylesheet" type="text/css" href="../reset.css"/>
<style type="text/css">
.box{
width: 302px;height: 302px;border: 1px solid black;margin: 50px auto;
}
.pst1,.pst2,.pst3{
width: 100px;height: 100px;
}
.pst1{background: red;}
.pst2{background: green;}
.pst3{background: blue;}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-定位:规定元素的位置-->
<!-定位主要用于没有规律的元素的布局,他和浮动有着相同的地位-->
<!-定位的三种类型:相对定位,绝对定位,固定定位-->
<!-定位使用方法:-->
<!-1.规定是哪一个定位方式-->
<!-2.指定在方向上的偏移量:top bottom left right-->
<!-3.注意:top和bottom只有一个会生效,left和right只有一个会生效-->
<div class="box">
<div class="pst1"></div>
<div class="pst2"></div>
<div class="pst3"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
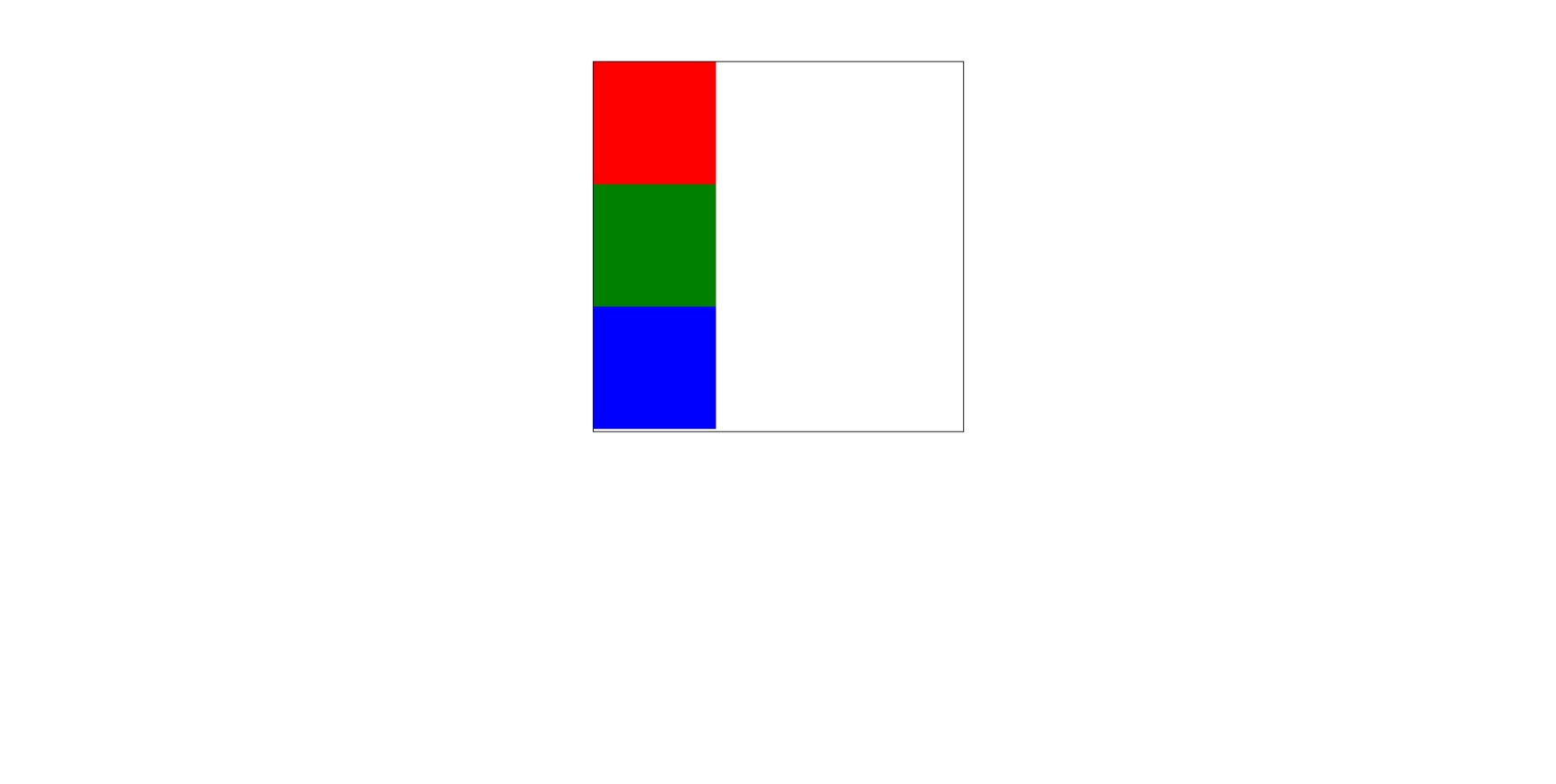
1)相对定位relatice
唯一一个不脱离文档流的属性值,始终在页面中占位置。
相对自身原位置的偏移(加位移向)需要配合使用。
特点:
- 不影响元素本身特性
- 不是元素脱离文档流(元素其实位置会被保留)
- 没有定向偏移量时,对元素无影响(相对于自身偏移量)
- 提高层级
.pst2{
background: green;
position: relative;
left:50px;
top:30px
}
如果只给该元素设置 position: relative; 相对定位,但不设置偏移量,那么该元素位置不会动,但该元素会漂浮起来
相对定位元素脱离了文档流,但该元素原来的位置还得保留
相对定位是相对于该元素原来的位置进行定位,如下图
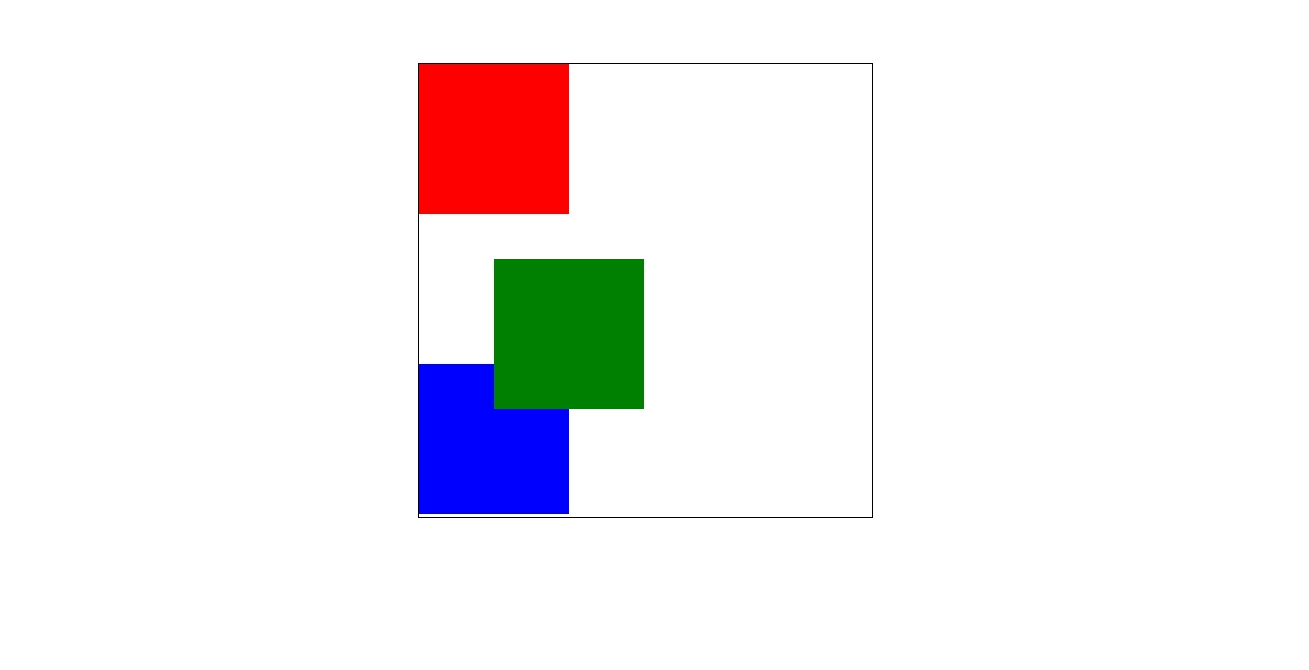
2)绝对定位 absolute
相对定位和绝对定位最大的区别就是一个元素绝对定位后,元素就是一个定位元素,完全脱离文档流,该元素会浮起来,但不会再霸占该元素的的位置
使元素完全脱离文档流
使内联元素支持宽高
块属性标签内容撑开宽度
相对于父元素偏移量,逐层上找,直到document
相对定位一般配合绝对定位使用
提升层级
若无父级没有定位,则会逐层上找。
.pst2{
background: green;
position: absolute;
left:50px;
top:30px
}
*绝对定位练习
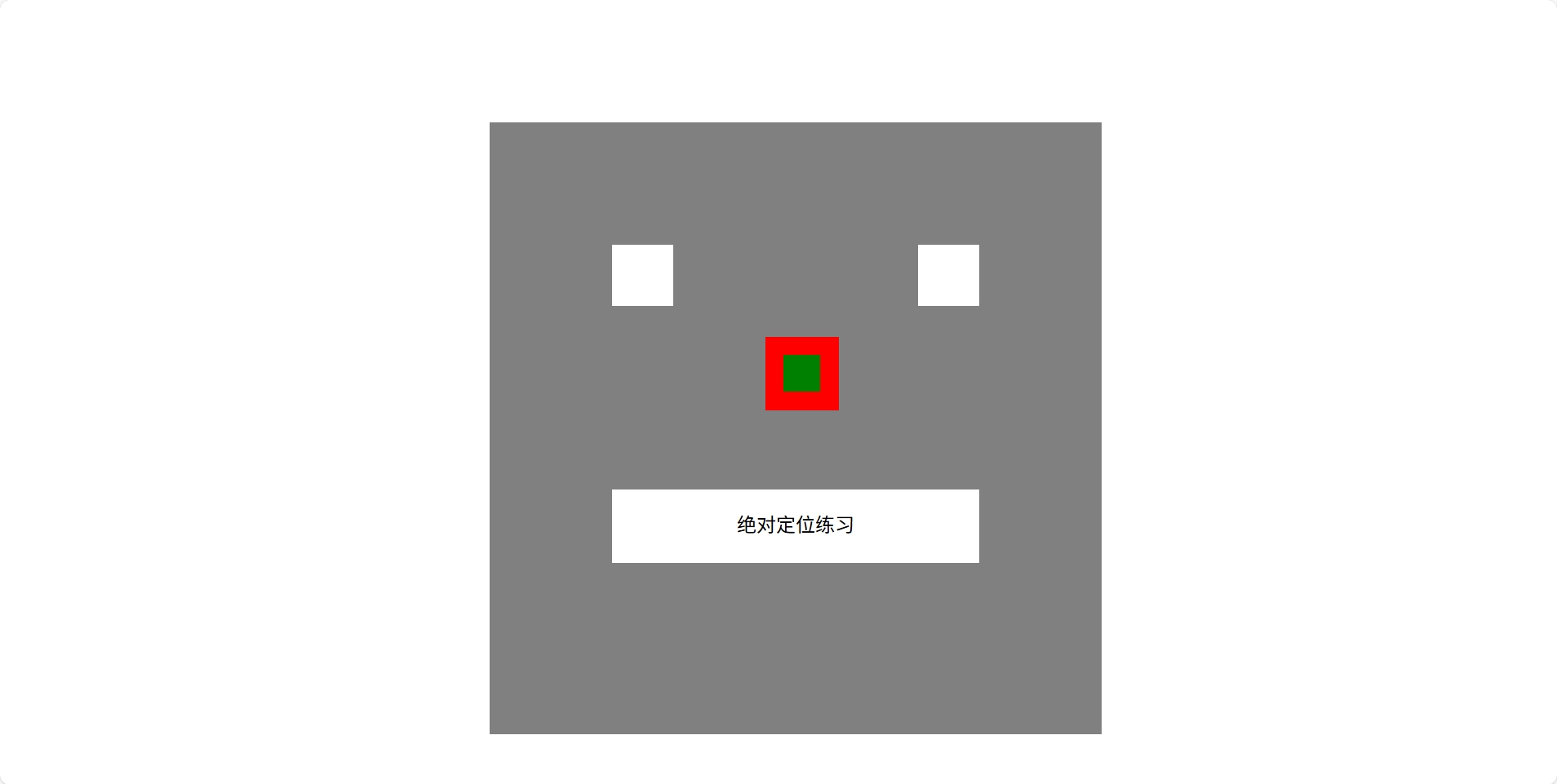
<!doctype html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style>
#face{
width: 500px;
height: 500px;
background-color: gray;
position: absolute;
left: 400px;
top: 100px;
}
#left_eye{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: white;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 100px;
}
#right_eye{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
background-color: white;
position: absolute;
left: 350px;
top: 100px;
}
#mouse{
width: 300px;
height: 60px;
background-color: white;
position: absolute;
left: 100px;
top: 300px;
}
#nose1{
width: 60px;
height: 60px;
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
left: 225px;
top: 175px;
}
#nose2{
width: 30px;
height: 30px;
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
left: 15px;
top: 15px;
}
p{
text-align: center;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div id="face">
<div id="left_eye"></div>
<div id="right_eye"></div>
<div id="mouse"><p>绝对定位练习</p></div>
<div id="nose1">
<div id="nose2"></div>
</div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
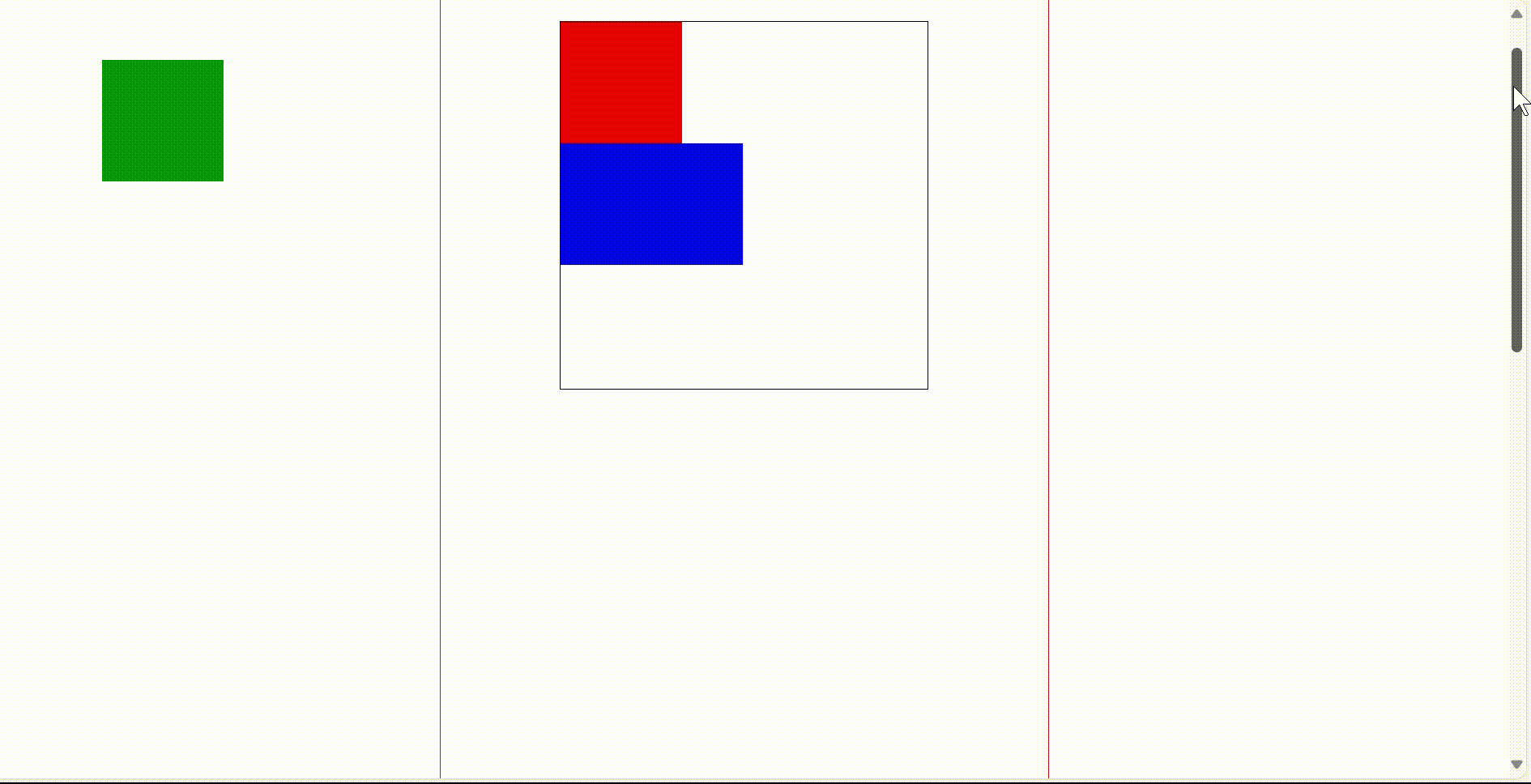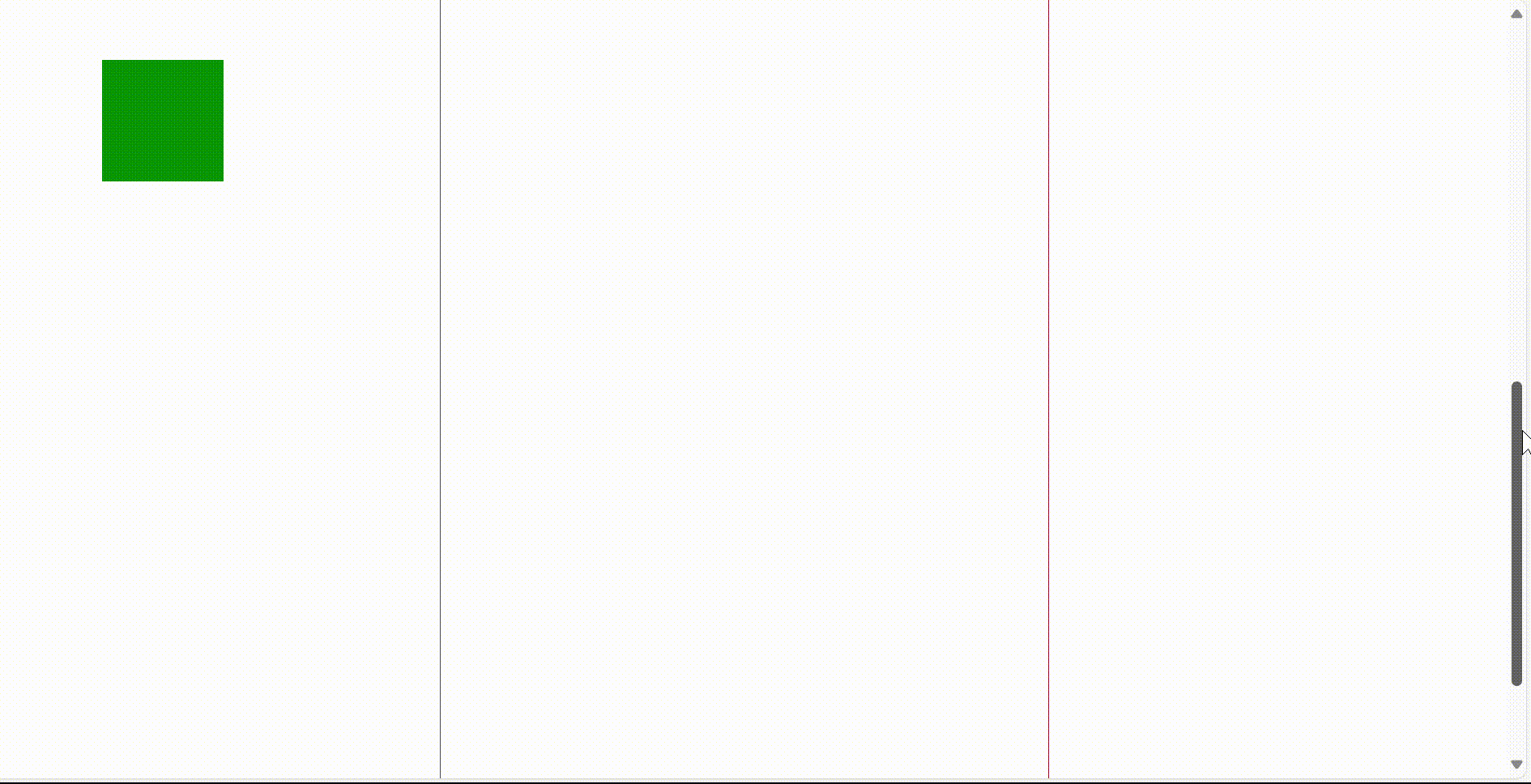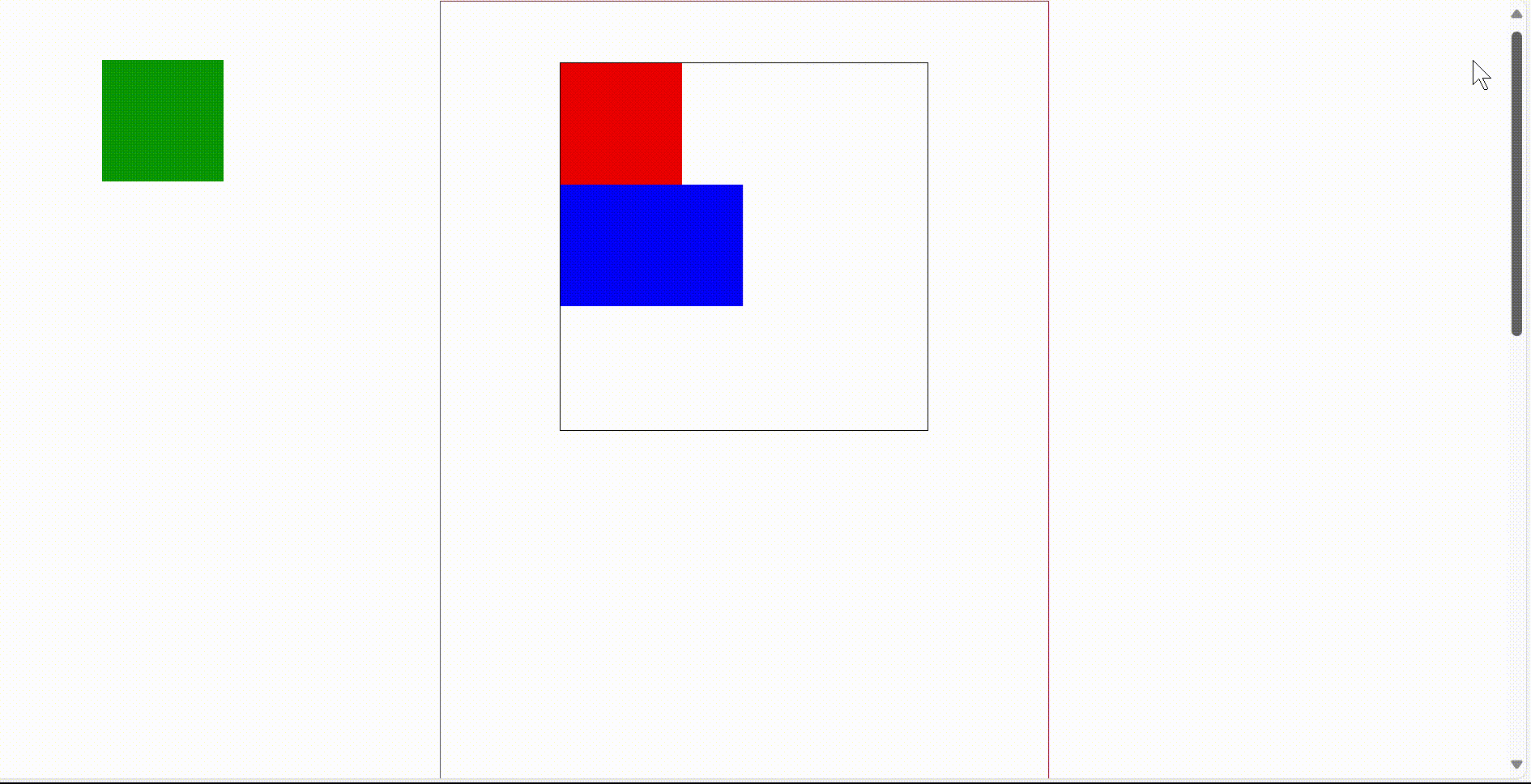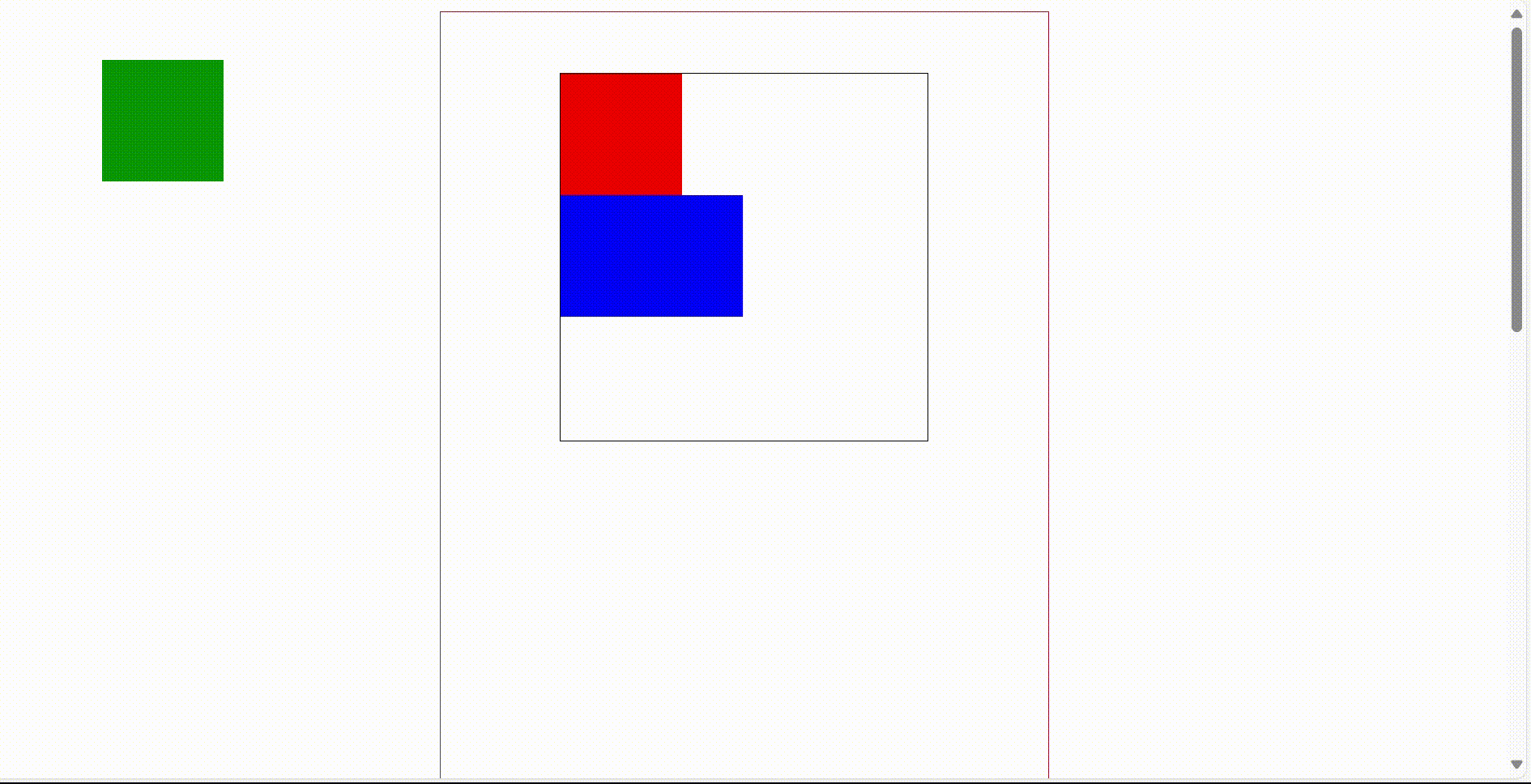
3)固定定位 fixed
固定定位是相对于浏览器窗口进行定位,他会固定在游览器窗口中特定的位置,不会移动,不论游览器窗口滚动条如何滚动,被固定位的元素他的位置是不会改变,他会一直待在浏览器窗口的特定位置。
固定定位的使用画圈的部分,在右侧滚动条不断滚动时,画圈位置的提示栏位置永远不会变





















 1214
1214

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








