PyTorch是在2017年1月由Facebook推出的。它是经典机器学习库Torch框架的一个端口,主要编程python。
提供两个高级功能:
1、具有强大的GPU加速的张量计算。
2、包含自动求导系统的深度神经网络。
安装
在线安装
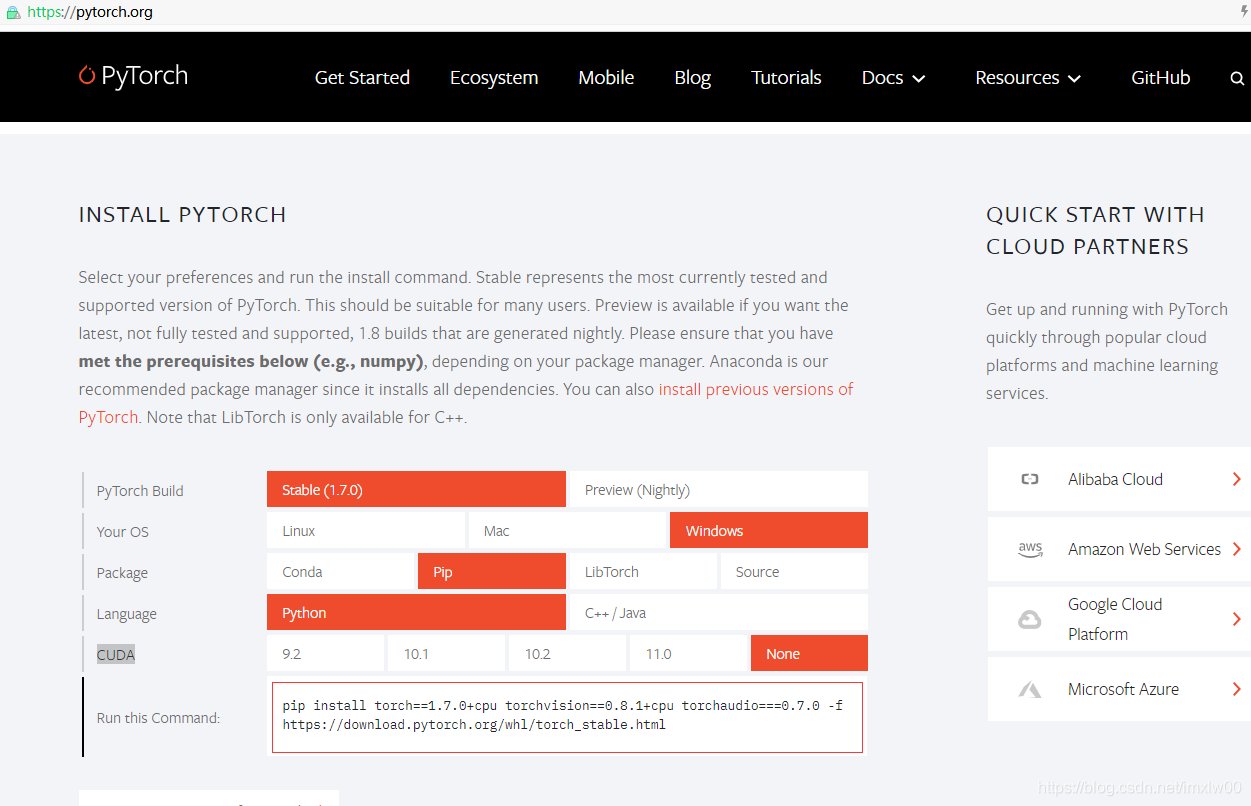
离线安装
官网 https://download.pytorch.org/whl/torch_stable.html 选择合适的版本torch/torchvision 都需要安装

pip install torch-1.2.0-cp37-cp37m-win amd64.whl
pip install torchvision-0.4.0-cp37-cp37m-win_amd64.whl
张量(Tensors)
张量类似于numpy的ndarrays,此外,张量还可以在GPU上使用以加速计算。
empty
import torch
# 构造一个未初始化的5x3矩阵:
x = torch.empty(5, 3)
print(x)
tensor([[ 2.9957e+15, 4.5835e-41, 2.9363e+15],
[ 4.5835e-41, 3.1136e+14, 4.5835e-41],
[ 2.8575e+15, 4.5835e-41, 2.9190e+15],
[ 4.5835e-41, 3.0335e+15, 4.5835e-41],
[-1.1152e+32, 4.5834e-41, -1.1153e+32]])
rand
# 构造一个随机初始化的矩阵:
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x)
tensor([[0.9625, 0.3586, 0.0863],
[0.9301, 0.4169, 0.3780],
[0.1867, 0.4127, 0.8691],
[0.8618, 0.0886, 0.5225],
[0.5478, 0.7549, 0.2517]])
zeros
# 构造一个填充为零且类型为long的矩阵
x = torch.zeros(5, 3, dtype=torch.long)
print(x)
tensor([[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0]])
tensor
# 使用数据构造张量
x = torch.tensor([5.5, 3])
print(x)
tensor([5.5000, 3.0000])
randn_like
x = x.new_ones(5, 3, dtype=torch.double) # new_* methods take in sizes
print(x)
x = torch.randn_like(x, dtype=torch.float) # override dtype!
print(x) # result has the same size
size和shape
可以通过下面两种方式得到tensor 的大小
print(x.shape)
print(x.size())
torch.Size([5, 3])
torch.Size 实际上是一个元组,因此它支持所有元组操作。
type
# 得到tensor的数据类型
print(x.type())
# torch.FloatTensor
dim
得到tensor的维度
#
x=torch.randn(5,2)
x.dim()
# 2
操作
加法
# 语法1
x = torch.rand(5, 3)
y = torch.rand(5, 3)
print(x + y)
# 语法2
print(torch.add(x, y))
# 提供输出张量作为参数
result = torch.Tensor(5, 3)
torch.add(x, y, out=result)
print(result)
# 原地操作
y.add_(x)
print(y)
任何使张量原地发生变化的操作,都用固定 “_”。例如:x.copy_(y),x.t_(),将改变x。
view
# 调整张量的大小/形状
x = torch.randn(4, 4)
y = x.view(16)
z = x.view(-1, 8) # the size -1 is inferred from other dimensions
print(x.size(), y.size(), z.size())
item
# 获取一个元素张量的数字
x = torch.randn(1)
print(x)
print(x.item())
Torch和NumPy转换
a = torch.ones(5)
print(a)
b = a.numpy()
print(b)
import numpy as np
a = np.ones(5)
b = torch.from_numpy(a)
np.add(a, 1, out=a)
print(a)
print(b)
























 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








