androidx.collection.LruCache
// Callbacks to allow LinkedHashMap post-actions
//这三个函数是留给linkedHashMap实现的
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> p) { } //LinkedHashMap 把节点到尾部(重写newNode放入尾部)
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { } //双链表默认放入尾部 LinkedHashmap不用这个
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> p) { } //LinkedHashMap 从链表中删除
afterNodeAccess 把节点放到尾部
void afterNodeAccess(Node<K,V> e) { // move node to last
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> last;
if (accessOrder && (last = tail) != e) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
//省略指针操作 把节点放到尾结点
tail = p;
++modCount;
}
}
afterNodeRemoval从链表中删除
void afterNodeRemoval(Node<K,V> e) { // unlink
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> p =
(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>)e, b = p.before, a = p.after;
p.before = p.after = null;
if (b == null)
head = a;
else
b.after = a;
if (a == null)
tail = b;
else
a.before = b;
}
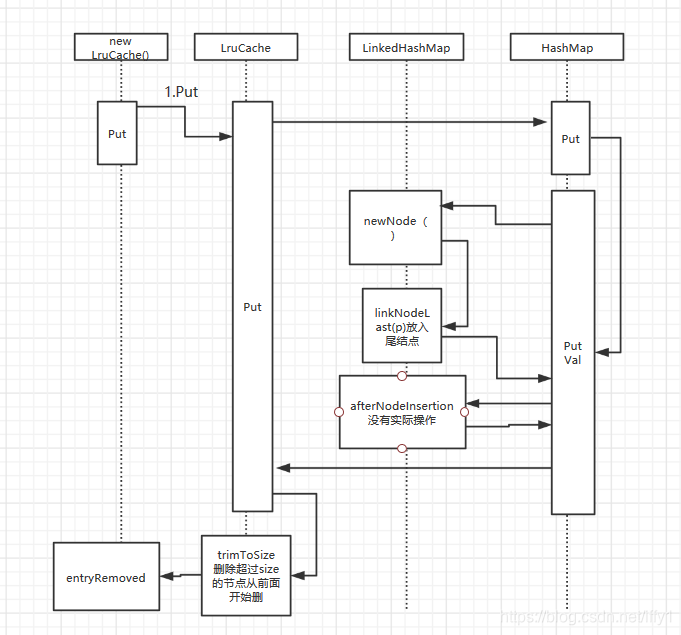
public V put(K key, V value) {
//evict默认为true
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent,
boolean evict) {
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
}
//evict默认为true
void afterNodeInsertion(boolean evict) { // possibly remove eldest年龄最大的
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> first;
if (evict && (first = head) != null && removeEldestEntry(first)) {
K key = first.key;
removeNode(hash(key), key, null, false, true);
}
}
//进入if 需要三个条件都为true
//第三个条件默认返回false,需要用户自己重写
protected boolean removeEldestEntry(Map.Entry<K,V> eldest) {
return false;
}
LruCache的一个回调函数本身没有实现,可重新。在新增或移除变量时会被调用。第一个参数为true时是移除变量,false时是新增变量。
protected void entryRemoved(boolean evicted, K key, V oldValue, V newValue) {}
//构造函数
public LruCache(int maxSize) {
if (maxSize <= 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("maxSize <= 0");
}
this.maxSize = maxSize;
//LinkedHashMap(int initialCapacity,
// float loadFactor,
// boolean accessOrder)
//false: 基于插入顺序
//true: 基于访问顺序
this.map = new LinkedHashMap<K, V>(0, 0.75f, true);
}
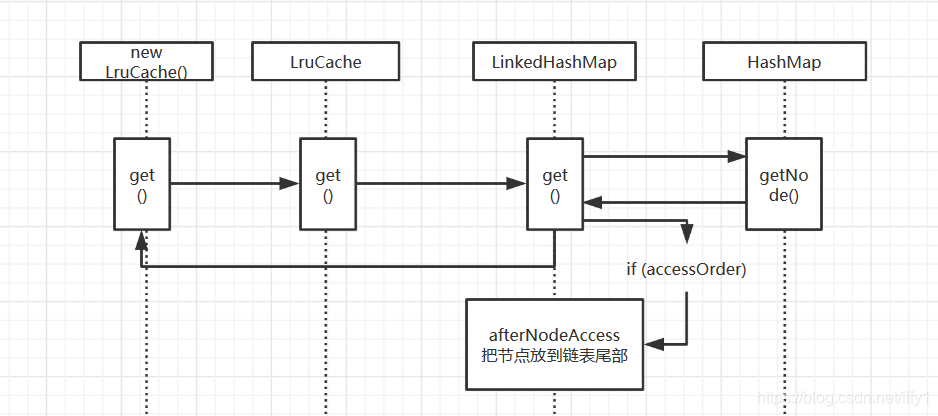
//get方法---------------------------------------
@Nullable
public final V get(@NonNull K key) {
if (key == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null");
}
V mapValue;
synchronized (this) {
//调用LinkedHashMap的get方法
mapValue = map.get(key);
if (mapValue != null) {
hitCount++;
return mapValue;
}
missCount++;
}
}
//LinkedHashMap
public V get(Object key) {
Node<K,V> e;
if ((e = getNode(hash(key), key)) == null)
return null;
if (accessOrder)
//基于访问顺序,把被访问的节点放到最前面
afterNodeAccess(e);
return e.value;
}
//put方法---------------------------------------
//LinkedHashMap重写了newNode()方法,通过此方法保证了插入的顺序性。
Node<K,V> newNode(int hash, K key, V value, Node<K,V> e) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> p =
new LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V>(hash, key, value, e);
linkNodeLast(p);
return p;
}
private void linkNodeLast(LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> p) {
LinkedHashMapEntry<K,V> last = tail;
tail = p;
if (last == null)
head = p;//设为头结点
else {
p.before = last;
last.after = p;
}
}
@Nullable
public final V put(@NonNull K key, @NonNull V value) {
if (key == null || value == null) {
throw new NullPointerException("key == null || value == null");
}
V previous;
synchronized (this) {
putCount++;
//先增加size
size += safeSizeOf(key, value);
//沿用了HashMap的Put方法 但是LinkedHashMap重写了newNode()方法,通过此方法保证了插 入的顺序性。
previous = map.put(key, value);
//有前值说明是覆盖操作,减去size
if (previous != null) {
size -= safeSizeOf(key, previous);
}
}
if (previous != null) {
//前值不为空覆盖操作,回调给用户做删除操作
entryRemoved(false, key, previous, value);
}
//检查是否超标,移除超过size的老元素
trimToSize(maxSize);
return previous;
}
//检查是否超标,移除超过size的老元素
public void trimToSize(int maxSize) {
//循环调用直到size符合要求
while (true) {
K key;
V value;
synchronized (this) {
if (size < 0 || (map.isEmpty() && size != 0)) {
throw new IllegalStateException(getClass().getName()
+ ".sizeOf() is reporting inconsistent results!");
}
if (size <= maxSize || map.isEmpty()) {
break;
}
Map.Entry<K, V> toEvict = map.entrySet().iterator().next();
key = toEvict.getKey();
value = toEvict.getValue();
map.remove(key);
size -= safeSizeOf(key, value);
evictionCount++;
}
//回调entryRemoved 通知使用者自己实现的entryRemoved方法
entryRemoved(true, key, value, null);
}
}





 本文详细解析了AndroidX Collection库中的LruCache实现原理,包括其构造函数、get和put方法的工作流程,以及如何通过LinkedHashMap实现缓存淘汰策略。
本文详细解析了AndroidX Collection库中的LruCache实现原理,包括其构造函数、get和put方法的工作流程,以及如何通过LinkedHashMap实现缓存淘汰策略。
















 1222
1222

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








