由于某些原因需要给某对象提供一个代理以控制该对象的访问,这时,访问对象不适合或者说不能直接引用目标对象,代理对象作为访问对象与目标对象之间的中介.
java中根据代理类生成的时机不同分为静态代理和动态代理
静态代理是指代理类在编译时期就生成
动态代理是指代理类在java运行时期动态生成的代理类
代理Proxy有三种角色:
抽象主题: 通过接口或者抽象类声明真是主体和代理对象实现业务的方法.
真实主题: 实现了轴向主题中的具体业务,也就是需要被代理的对象.
代理类proxy: 代理真实主题 它实现了与真实主题相同的接口,并引用了真实主题.可以对真实主题的方法进行扩展
1.静态代理
抽象主题: 代理类和真实主题都需要实现该接口 重写接口中的全部方法
/**
* 静态代理: 代理类在编译时期生成
* 动态代理: 代理类在java程序运行时期,动态生成
* 抽象主题: 抽象的业务方法 给真实主题实现 以及代理类实现
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public interface TestInterface {
/**
* 抽象主题的抽象方法
*/
void doSomeThing();
}
真实主题: 需要被代理的对象,实现抽象主题 重写抽象主题中的党发
/**
* 真实主题: 实现抽象主题 重写抽象主题的方法
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestInterfaceImpl implements TestInterface {
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
System.out.println("假设我这里是火车站卖票!");
}
}
代理类proxy: 同样的实现抽象主题,并且引用了真实主题
/**
* 代理 : 与真实主题实现相同的接口 其作用是替代真实主题完成卖票任务
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestProxy implements TestInterface {
private TestInterfaceImpl impl;
public TestProxy(TestInterfaceImpl impl) {
this.impl = impl;
}
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
// 收取手续费
System.out.println("代售点收取部分手续费!");
// 真实主题售票
impl.doSomeThing();
}
}
测试:
/**
* 静态代理测试类
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 相当于火车站售票窗口
TestInterfaceImpl testInterface = new TestInterfaceImpl();
testInterface.doSomeThing();
System.out.println("=================================");
// 代理点售票
TestProxy proxy = new TestProxy(new TestInterfaceImpl());
proxy.doSomeThing();
}
测试结果:
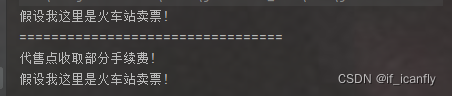
可以看到代售点对售票做了扩展,增加了收取手续费这个操作.
2.动态代理
-2.1 jdk动态代理
抽象主题:真实主题需要实现该接口 重写接口中的全部方法
/**
* 静态代理: 代理类在编译时期生成
* 动态代理: 代理类在java程序运行时期,动态生成
* 抽象主题: 抽象的业务方法 给真实主题实现 以及代理类实现
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public interface TestInterface {
/**
* 抽象主题的抽象方法
*/
void doSomeThing();
}
真实主题: 需要被代理的对象,实现抽象主题 重写抽象主题中的党发
/**
* 真实主题: 实现抽象主题 重写抽象主题的方法
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestInterfaceImpl implements TestInterface {
@Override
public void doSomeThing() {
System.out.println("假设我这里是火车站卖票!");
}
}
代理类:
使用ProxyFactory工厂的模式生成代理对象
/**
* jdk动态代理实现方式I: 使用ProxyFactory工厂的模式生成代理对象
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestProxyI {
private TestInterfaceImpl impl;
public TestProxyI(TestInterfaceImpl impl) {
this.impl = impl;
}
public TestInterface getProxyObject() {
/**
* 使用Porxy获取代理对象
* 通过调用Proxy的newProxyInstance()方法来生成代理对象
* newProxyInstance()方法参数说明
* ClassLoader loader, 类加载器 通过真实对象可以获得impl.getClass().getClassLoader()
* Class<?>[] interfaces, 真实对象实现的接口 impl.getClass().getInterfaces()
* InvocationHandler h 代理对象调用的处理逻辑 这里使用的lamand表达式
*
* InvocationHandler参数说明
* proxy: 代理对象
* method:对应于在代理对象上调用的接口方法的Method实例
* args: 传递的参数
*/
TestInterface o = (TestInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(impl.getClass().getClassLoader(), impl.getClass().getInterfaces(), (proxy, method, args) -> {
System.out.println("代售点收取手续费!");
// 执行真实对象的方法
Object invoke = method.invoke(impl, args);
return invoke;
});
return o;
}
实现InvocationHandler接口
/**
* jdk动态代理实现方式II: 实现InvocationHandler接口
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestProxyII implements InvocationHandler {
private Object impl;
public TestProxyII(Object impl) {
this.impl = impl;
}
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("代售点收取手续费");
Object invoke = method.invoke(impl, args);
return invoke;
}
}
测试:
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用ProxyFactory工厂的模式生成代理对象
TestProxyI proxyI = new TestProxyI(new TestInterfaceImpl());
TestInterface proxy = proxyI.getProxyObject();
proxy.doSomeThing();
System.out.println("=================================");
// 实现InvocationHandler接口的方式
TestInterfaceImpl testInterface = new TestInterfaceImpl();
TestProxyII proxyII = new TestProxyII(testInterface);
TestInterface proxyi = (TestInterface) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
testInterface.getClass().getClassLoader(),
testInterface.getClass().getInterfaces(),
proxyII);
proxyi.doSomeThing();
}
}
debug查看:
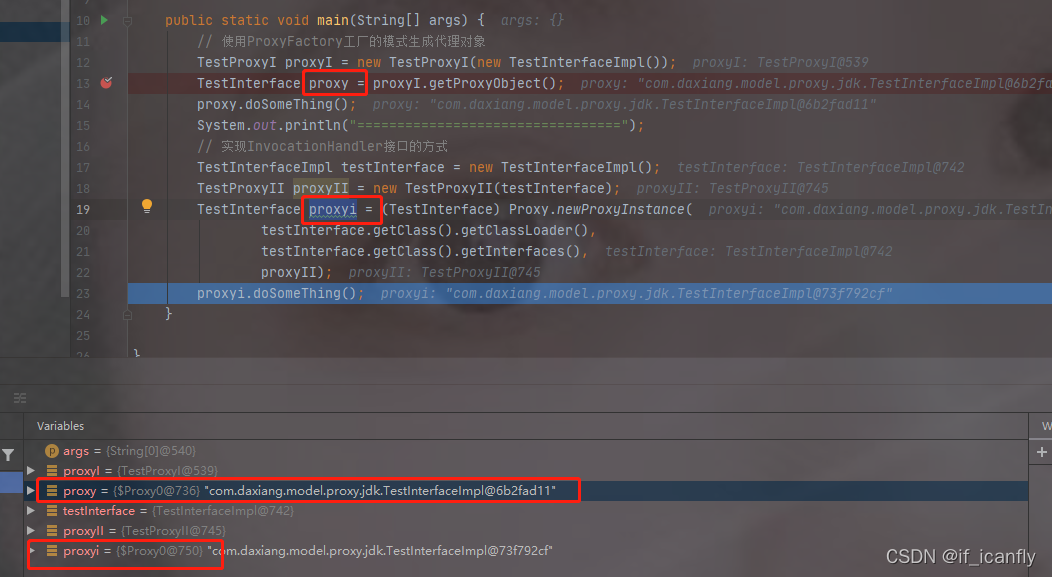
上图看出2种方式生成的对象都是代理类($开头)
结果:
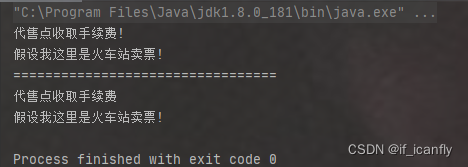
-2.2cglib动态代理
cglib动态代理只需要真实主题与代理类
导入cglib依赖包
<dependency>
<groupId>cglib</groupId>
<artifactId>cglib</artifactId>
<version>2.2.2</version>
</dependency>
真实主题: 需要被代理的对象
/**
* 真实主题:
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestInterfaceImpl {
public void doSomeThing() {
System.out.println("假设我这里是火车站卖票!");
}
}
代理对象:代理真实主题
/**
* cglib动态代理 : 实现MethodInterceptor接口 重写intercept方法
*
* @author Administrator
*/
public class TestProxy implements MethodInterceptor {
private TestInterfaceImpl impl;
public TestProxy(TestInterfaceImpl impl) {
this.impl = impl;
}
public Object getProxyObject() {
// 创建Enhancer对象
Enhancer enhancer = new Enhancer();
// 设置回调函数 也就是下面的intercept方法
enhancer.setCallback(this);
// 设置父类的字节码对象
enhancer.setSuperclass(impl.getClass());
// 创建代理对象
Object o = enhancer.create();
return o;
}
/**
* @param o 道理对象
* @param method 真实对象中的方法的Method对实例
* @param objects 实际参数
* @param methodProxy 代理对象中的方法的method实例
* @return
* @throws Throwable
*/
@Override
public Object intercept(Object o, Method method, Object[] objects, MethodProxy methodProxy) throws Throwable {
System.out.println("代售点收取手续费!");
Object invoke = methodProxy.invokeSuper(o, objects);
return invoke;
}
}
测试:
/**
* @author Administrator
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestInterfaceImpl impl = new TestInterfaceImpl();
TestProxy proxy = new TestProxy(impl);
TestInterfaceImpl proxyObject = (TestInterfaceImpl) proxy.getProxyObject();
proxyObject.doSomeThing();
}
}
结果:
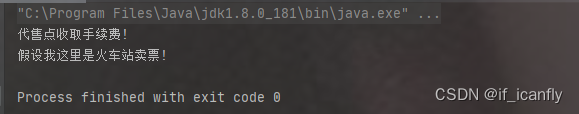
-2.3.cglib动态代理与jdk动态代理的区别:
cglib动态代理不需要被代理对象(真实主题)实现接口.它使用的是cglib包enhancer来创建的代理对象
jdk动态代理需要被代理的对象(真实主题)实现接口.他使jdk提供的Proxy类的newProxyInstance生成代理对象
3.使用代理的优点:
1.代理对象可以扩展目标对象的功能.
2.代理模式可以将客户端与目标对象分离 在一定程度上实现解耦
3.代理对象隔离了目标对象与客户端,在一定程度上保护了目标对象.
4.使用代理的缺点:
增加了系统的复杂性.




















 1606
1606

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








