①对二叉树进行先序遍历,查找值为 x 的结点;
②找到值为 x 的结点时,栈中存放的是 x 的所有祖先结点。
思路:首先创建树,在树中找到值为x的节点,将祖先依次存放在栈中。
创建数据:
#define maxlen 50
typedef struct tree{
struct tree *lchild,*rchild,*parent;
char data;
}CStree,*CTree;
typedef struct{
CStree *Zx[maxlen];
int top;
}Z_list;
CStree *Q[maxlen];
算法:
创建树:CStree *Ctree();
查找对应节点:void X_b(CStree *T,char a)
将祖先放入栈中并出栈:void CZ_z(CStree *T)
完整代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define maxlen 50
typedef struct tree{
struct tree *lchild,*rchild,*parent;
char data;
}CStree,*CTree;
typedef struct{
CStree *Zx[maxlen];
int top;
}Z_list;
CStree *Q[maxlen];
CStree *Ctree(){
int front=1;
int rear=0;
char ch;
CStree *T,*S;//T:根节点;S:创建
T=NULL;
ch=getchar();
while(ch!='#'){//#终止符
S=NULL;
if(ch!='@'){//@虚指针
S=(CTree)malloc(sizeof(CStree));
S->data=ch;
S->lchild=NULL;
S->rchild=NULL;
}
rear++;Q[rear]=S;
if(rear==1){
T=S;
}else{
if(S!=NULL && Q[front]!=NULL){
if(rear%2==0){
Q[front]->lchild=Q[rear];
}else{
Q[front]->rchild=Q[rear];
}
Q[rear]->parent=Q[front];
}
if(rear%2==1) front++;
}
ch=getchar();
}
getchar();
return T;
}
void X_b(CStree *T,char a){
if(!T)
return ;
else{
if(T->data==a){
Q[0]=T;
return ;
}
X_b(T->lchild,a);
X_b(T->rchild,a);
}
}
void CZ_z(CStree *T){
Z_list *z=(Z_list*)malloc(sizeof(Z_list));z->top=-1;
CStree *L=T;
char ch;
printf("需要查找的节点:");
ch=getchar();
X_b(T,ch);
T=Q[0];
while(T){
if(!T->parent) break;
z->top++;
z->Zx[z->top]=T->parent;
T=T->parent;
}
while(z->top>=0){
printf("%c ",z->Zx[z->top]->data);
z->top--;
}
}
int main(){
CStree *T;
T=Ctree();
CZ_z(T);
return 0;
}
运行结果:
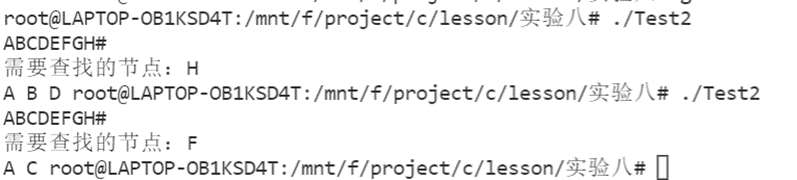
说明:第一行为创建树。
第二行输入查找的节点。
























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








