explain作用:
这是一个在SQL优化中必不可少的部分,他用户分析查询的SQL语句的执行,看一条查询的SQL语句是怎么去执行的,有没有用到索引,需不需要回表查询,需不需要额外排序的情况,然后我们针对SQL语句执行来进行一些特定语句。
来看代码把:
demo1表:
expalindemo, CREATE TABLE `expalindemo` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
demo2表:
expalindemo2, CREATE TABLE `expalindemo2` (
`id` int(11) DEFAULT NULL,
`name` varchar(20) DEFAULT NULL,
`age` int(11) DEFAULT NULL
) ENGINE=InnoDB DEFAULT CHARSET=utf8mb4 COLLATE=utf8mb4_0900_ai_ci
先看一下explain语句执行效果:
explain select * from expalindemo;
id, select_type, table, partitions, type, possible_keys, key, key_len, ref, rows, filtered, Extra
1, SIMPLE, expalindemo, , ALL, , , , , 1, 100.00,
逐一解释字段意义:
id:指执行的优先级,id越大优先级越大;值相同的时候,从上往下,依次执行。
看一个例子,做一个联表查询,第一个表中插入2条数据,第二个表中查询3条数据,查询表1和表2中name相同的数据:
insert into expalindemo values(1,'aa',12),(2,'ss',14);
insert into expalindemo2 values(1,'cc',12),(2,'ss',14),(3,'ww',14);
explain select * from expalindemo,expalindemo2 where expalindemo.name=expalindemo2.name;
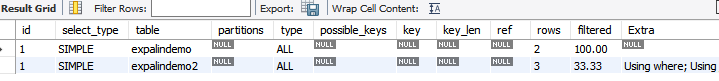
可以看到结果id相同,从上往下依次执行,先去查询的表一。
往表一再添加2条数据,重新执行:
insert into expalindemo values(3,'cc',12),(4,'zz',14);
explain select * from expalindemo,expalindemo2 where expalindemo.name=expalindemo2.name;
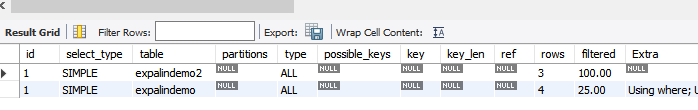
可以看到先去表二中查的,这是因为他会选择哪个表中数据比较少,优先去数据少的表去查。
id值不同的情况一般出现在子表查询的过程中。
select_type:
simple:简单的select,不使用union或子查询;
primary:最外层的select(子查询中);
union:在selec之后用了union;
depedent union :union语句中的第二个select,依赖于外部子查询;
union result:union的结果
subquery:子查询中的第一个select
dependent subquery:子查询中的第一个select,取决于外面的查询。(dependent类型一般使用了in的子查询)
derived:导出表的select(from子句的子查询)
因为这一步部分不是很重要索引就不贴代码实验了。
table:
这个没什么可说的,就是你去哪个表里查询;
partitions:
如果表中存在分区,则显示命中分区的清空,如果没有分区显示null;
type:
这个是很重要的一个标志,指查询的方式,
从好到坏依次是:system,const,eq_ref,ref,range,index,all
system:表中只有一条数据(引擎只能使MYISAM和MEMORY)。
#修改引擎为MyISAM
ALTER TABLE `world`.`expalindemo`
ENGINE = InnoDB ;
#关闭安全模式,删除数据使表中只有一条数据
SET SQL_SAFE_UPDATES = 0;
delete from expalindemo where id>1;
#查看执行结果
explain select * from expalindemo;
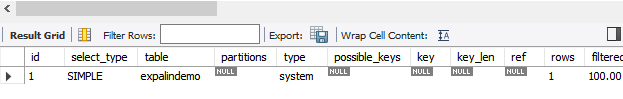
const:使用唯一索引或者主键,用where限制条件后返回一条数据(有且只有一条)
#设置主键(id)
ALTER TABLE `world`.`expalindemo2`
ADD PRIMARY KEY (`id`);
;
#查看执行结果
explain SELECT * FROM world.expalindemo2 where id=1;
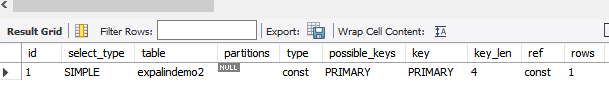
eq_ref:唯一性索引,对每个索引的查询只能返回匹配的唯一一条数据,
#设置两个表中的name分别为各个表中的主键
#两个表中的name中的值要同时存在两个表中,不能多也不能少
explain select expalindemo2.name from expalindemo2,expalindemo where expalindemo2.name=expalindemo.name;
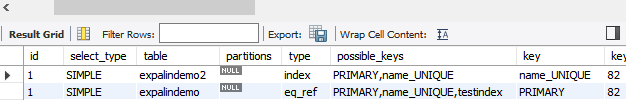
ref:非唯一性索引,对每个索引返回匹配的所有
#给表一name建立索引
create index idindex on expalindemo(id);
#给表一添加一条id重复的数据
insert into expalindemo values(1,'dd',22);
#查看结果:
explain select * from expalindemo where id =1;
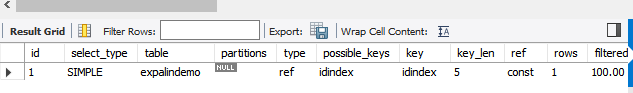
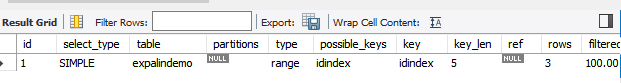
range:索引指定范围的行,where后边是范围;
explain select * from expalindemo where id >1;
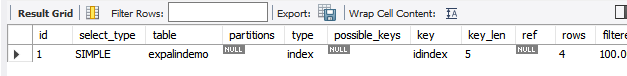
index:查询索引的全部数据
explain select id from expalindemo;
all:查询所有数据
explain select * from expalindemo;

possible_keys:
可能用到的索引;
key:
实际用到的索引
key_len
索引长度:
一般utf一个字符占3个字节,如果设置了可以为空用1位标识,对于varchar可变长度用2个字节标识
ref:
指明当前表所参考的字段。
rows:
查询时估计查询的数据条数;
fiftered:
查询时这条sql语句占一堆sql的时间百分比
extra:
这也是一个重点的字段:
using filesort:需要额外的排序,性能损耗
using temporary:使用到了临时表,性能损耗
using index: 索引覆盖,性能提升
using where :需要回表查询
impossible where:where子句永远为false;







 本文围绕SQL优化中explain的作用展开,介绍其用于分析查询SQL语句的执行情况,如是否用索引、是否回表查询等。还详细解释了explain各字段意义,包括id、select_type、type等,以及不同情况的表现和对性能的影响。
本文围绕SQL优化中explain的作用展开,介绍其用于分析查询SQL语句的执行情况,如是否用索引、是否回表查询等。还详细解释了explain各字段意义,包括id、select_type、type等,以及不同情况的表现和对性能的影响。
















 1286
1286

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








